中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (22): 3536-3540.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.22.016
• 组织工程口腔材料 tissue-engineered oral materials • 上一篇 下一篇
钛芯与骨形成蛋白复合材料修复即刻种植牙槽骨缺陷的评价
杨玉鹏1,赵海静2,谷建琦1,程凤峡1,郑 瑶1,李 娟1,郝 玮1,王西西1,吴永生1
- 河北省人民医院,1口腔科,2老干部处,河北省石家庄市 050051
Titanium core/bone morphogenetic protein composite materials used to repair alveolar bone defects after immediate implant placement
Yang Yu-peng1, Zhao Hai-jing2, Gu Jian-qi1, Cheng Feng-xia1, Zheng Yao1, Li Juan1, Hao Wei1, Wang Xi-xi1, Wu Yong-sheng1
- 1Department of Stomatology, 2Department of Veteran Cadre, Hebei Provincial People’s Hospital, Shijiazhuang 050051, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
钛芯羟基磷灰石材料:综合了羟基磷灰石与钛金属材料的良好的特性,不仅有一定的机械强度,而且有优越的生物相容性和骨引导牵引作用,缩短骨与生物人工材料结合时间。
骨形成蛋白:作为人体内最重要的骨诱导生长因子,能够诱导骨细胞的一切生理活动,通过一系列的活动诱导未分化细胞进行增殖行动,慢慢分化为软骨母细胞,并进一步成为成熟软骨细胞,最终通过软骨内骨化的过程形成新骨组织。但骨形成蛋白不宜单独植入生物体内,容易发生降解作用,因此通过钛芯羟基磷灰石作为一个载体,进入牙齿窝间隙中,起到促进骨细胞生长作用,又能诱导骨细胞与种植体间相接触联系。
背景:致力于种植牙槽骨缺损修复的实验和临床研究是现代科技发展方向,寻找适合的骨替代材料成为人们研究的热门课题。
目的:研究钛芯羟基磷灰石与骨形成蛋白复合材料修复即刻种植后牙槽骨缺陷的效果。
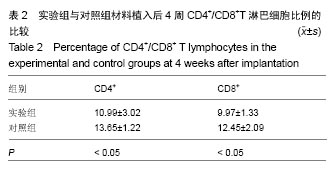
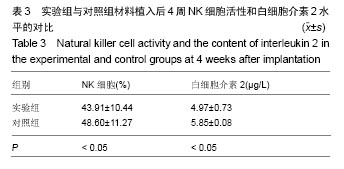
方法:将24只新西兰兔随机分为3组,正常组不进行任何处理,实验组、对照组制作股骨大转子区骨缺损模型,实验组于骨缺损处植入种植体及钛芯羟基磷灰石与骨形成蛋白复合材料;对照组植入种植体及钛芯羟基磷灰石材料。植入后4周,检测血CD4+、CD8+淋巴细胞比例及NK细胞活性、白细胞介素2水平;植入后16周,采用X射线检测骨密度,组织学观察种植体周围成骨情况。
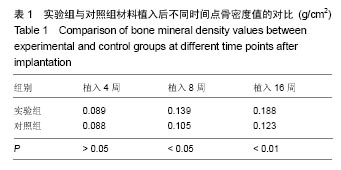
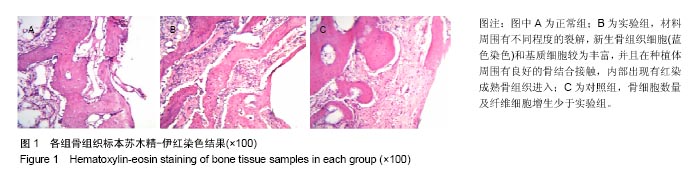
结果与结论:①实验组骨密度高于对照组(P < 0.05);②实验组复合材料周围有不同程度的裂解,新生骨组织细胞和基质细胞较为丰富,并且在种植体周围有良好的骨结合接触,内部出现有红染成熟骨组织进入;对照组骨细胞数量、纤维细胞增生少于实验组;③实验组CD4+与CD8+淋巴细胞比例、NK细胞活性、白细胞介素2水平低于对照组(P < 0.05);④结果表明,钛芯羟基磷灰石与骨形成蛋白复合材料能够有效修复即刻种植后牙槽骨缺陷区域,引导骨细胞生长。
中图分类号:
.jpg)