| [1]Miyata T,Asami N,Uragami TJ.Future perspectives and recent advances in stimuli-responsive materials.J Polym Sci. 2009; 47: 2144-2157.[2]Reza Saboktakin M,Maharramov A,Ali Ramazanov M. pH-sensitive starch hydrogels via free radical graft copolymerization, synthesis and properties.Carbohyd Polym. 2009;77:634-638.[3]Haraguchi K,Takada T.Characteristic sliding frictional behavior on the surface of nanocomposite hydrogels consisting of organic-inorganic network structure. Macromol Chem Phys.2015;206(15):1530-1540.[4]Liu YY,Tung TH,Lin KH.Structural evolution and copper-ion release behavior of Cu-pHEMA hybrids synthesized in situ.Advance Engin Mater.2009;11(11):219-226.[5]Shen XY,Torg H,Jiang T. Enzymatic synthesis of amorphous calcium phosphate-chitosan nanocomposites and their processing into hierarchical structure.Compo Sci Tech.2007; 67:2238-2245.[6]Arantes TM,Mambrini GP,Stroppa DG,et al. Stable colloidal suspensions of nanostructured Zirconium Oxid synthesized by hydrothermal process.J Nano Res.2010;12:3105-3110.[7]You CG,Han CM,Wang XG,et al.The progress of silver nanopparticles in the antibacterial mechanism,clinical application and cytotoxicity.Mol Biol Rep.2012;9(39): 9193-9201.[8]孔杰,李国强,叶菁芸,等.纳米银/壳聚糖复合水凝胶的原位制备、表征及抗菌性能研究[J].功能材料,2012,12(43):1662-1664.[9]Hsu YW,Yang KH,Chang KM,et al.Synthesis and crystallization behavior of 3 mol% Yttria stabilized tetragonal Zirconia polycrystals(3Y-YZP) nanosized powders prepared using a simple co-precipitation process. J Alloys Compd.2011; 509:6864-6870.[10]黄虹.玻璃纤维桩用于前牙残冠残根修复效果探讨[J].航空航天医学杂志,2013,24(12):1514-1518[11]姚超,卜令学,王科,等. 应用细胞片层技术构建组织工程骨修复犬下颌骨缺损的实验研究[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志,2012,30 (3): 229-233.[12]王尖,孙斌,李玉宝,等.聚氨酯基抗菌根管充填材料的制备与性能研究[J].功能材料,2014,14(45): 2001-2004.[13]柳磊,曾曙光,石勇,等.丝素蛋白-壳聚糖三维多孔支架材料生物相容性及促成骨性能研究[J].广东牙病防治,2013,21(2):75-80.[14]Li D,Wang W,Guo R,et al. Restoration of rat calvarial defects by poly(lactide-co-glycolide)/hydroxyapatite sca olds loaded with bone mesenchymal stem cells and DNA complexes. Chin Sci. 2012;57(5):435-444.[15]Zulkifli FH,Jahir Hussain FS,Abdull Rasad MS,et al. Improved cellular response of chemically crosslinked collagen incorporated hydroxyethyl cellulose/poly (vinyl)alcohol nanofibers scaffold. J Biomater Appl. 2015;29(7):1014-1027.[16]Du CH,Li NY,Gao N,et al. A preliminary study on the application of bone marrow stromal cell sheet on the formation of functional tissue-engineered bone in dogs. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;71(9): 1531. e1-1531. e10.[17]Tang Z,Akiyama Y,Okano T. Recent development of temperature responsive cell culture surface using poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). J Polymer Sci. 2014;52(14): 917-926.[18]张剑英,付云,俞少杰.人牙周韧带细胞膜片的体外实验研究.中华口腔医学研究杂志(电子版),2013,7(1):31-34.[19]钱伯章.国内外碳纤维应用领域、市场需求以及碳纤维产能的进展(2)[J].高科技纤维与应用,2010,35(1):44-47.[20]钱伯章.国内外碳纤维应用领域、市场需求以及碳纤维产能的进展(3)[J].高科技纤维与应用,2010,35(2):29-33.[21]田超,杨莉,马寒冰.纳米二氧化硅增韧改性环氧树脂的性能研究[J].西南科技大学学报,2012,27(4):11-14.[22]Gilbert EN, Hayes BS,Seferis JC. Interlayer toughened unidirectional carbon prepreg systems: effect of preformed particle morphology. Appl Sci Manufact. 2013;34(3): 242-252. [23]Hollaway LC. A review of the present future utilization of FRP composites in the civil infrastructure with reference to their important in service properties. Constr Build Mat,2010,24(11): 2419. [24]Park SJ,Jung YJ,Kim S.Effect of fluorine–oxygen mixed gas treated graphite fibers on electrochemical behaviors of platinum–ruthenium nanoparticles toward methanol oxidation. J Flu Chem. 2012;144: 124. [25]Kafi A,Huson M,Creighton C,et al. Effect of surface functionality of PAN-based carbon fibres on the mechanical performance of carbon/epoxy composites. Comp Sci Technol. 2014;94: 89. [26]杨洪斌,王靖,吴惠敏,等.硅溶胶改性处理对碳纤维/环氧树脂复合材料拉伸性能的影响[J]. 材料研究学报,2013,27(1): 108. [27]Zhu N W, Chen X, Zhang T, et al. Improved performance of membrane free single-chamber air-cathode microbial fuel cells with nitric acid and ethylenediamine surface modified activated carbon fiber felt anodes. Biores Technol. 2011; 102(1): 422-426. [28]刘书田,侯玉品. 基于铺层参数的铺层方式与纤维分布协同优化的层合板最大刚度设计[J]. 计算力学学报,2012,29(4): 475. [29]易增博,冯利邦,郝相忠,等.表面处理对碳纤维及其复合材料性能的影响[J]. 材料研究学报,2015,29(1): 67-74. [30]赵丽斌,冯利邦,易增博,等. 酶解木质素改性酚醛泡沫塑料的制备与性能[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程,2015,31(3): 138-141. |
.jpg)
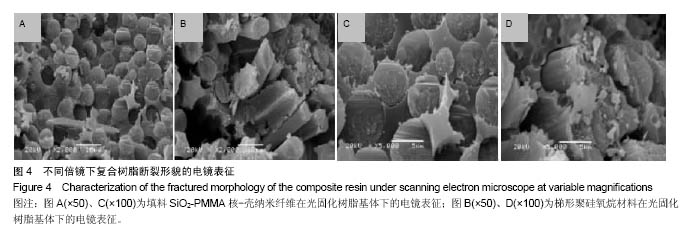


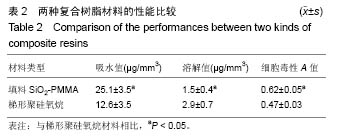
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)