| [1] Hu H, Yang B, Li Y, et al. Blocking of the P2X7 receptor inhibits the activation of the MMP-13 and NF-kappaB pathways in the cartilage tissue of rats with osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Med. 2016.[2] Lima MA, Dos Santos L, Turri JA, et al. Prognostic Value of ADAMTS Proteases and Their Substrates in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Pathobiology. 2016;83(6):316-326.[3] Gavella M, Lipovac V. Protective effects of exogenous gangliosides on ROS-induced changes in human spermatozoa. Asian J Androl. 2013;15(3):375-381.[4] Sunde RA, Thompson KM, Fritsche KL, et al. Minimum Selenium Requirements Increase When Repleting Second-Generation Selenium-Deficient Rats but Are Not Further Altered by Vitamin E Deficiency. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016.[5] Goldar S, Baradaran B, Shekari Khaniani M, et al. Extracts of Scrophularia frigida Boiss display potent antitumor effects in human breast cancer cells by inducing apoptosis and inhibition of expression of the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2016;62(9): 83-89.[6] Schmolz L, Birringer M, Lorkowski S, et al. Complexity of vitamin E metabolism. World J Biol Chem. 2016;7(1):14-43.[7] Sharma AN, da Costa e Silva BF, Soares JC, et al. Role of trophic factors GDNF, IGF-1 and VEGF in major depressive disorder: A comprehensive review of human studies. J Affect Disord. 2016;197:9-20.[8] Bauge C, Girard N, Lhuissier E, et al. Regulation and Role of TGFbeta Signaling Pathway in Aging and Osteoarthritis Joints. Aging Dis. 2014;5(6):394-405.[9] Iwona BS. Growth factors in pathogenesis of retinal neurodegeneration in diabetes mellitus Affiliation. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2016.[10] Baltanas A, Miguel-Carrasco J, San Jose G, et al. A synthetic peptide from transforming growth factor-beta(1) type III receptor inhibits NADPH oxidase and prevents oxidative stress in the kidney of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013;19(14):1607-1618.[11] Liegl R, Lofqvist C, Hellstrom A, et al. IGF-1 in retinopathy of prematurity, a CNS neurovascular disease. Early Hum Dev. 2016.[12] Fernandez-Sola J, Planavila Porta A. New Treatment Strategies for Alcohol-Induced Heart Damage. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(10). pii: E1651.[13] Ripamonti U, Duarte R, Parak R, et al. Redundancy and Molecular Evolution: The Rapid Induction of Bone Formation by the Mammalian Transforming Growth Factor-beta3 Isoform. Front Physiol. 2016;7:396.[14] Cruz JS, Machado FS, Ropert C, et al. Molecular mechanisms of cardiac electromechanical remodeling during Chagas disease: Role of TNF and TGF-beta. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2016.[15] Grinberg YY, Dibbern ME, Levasseur VA, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 abrogates microglial oxidative stress and TNF-alpha responses to spreading depression. J Neurochem. 2013;126(5):662-672.[16] van der Kraan PM. Age-related alterations in TGF beta signaling as a causal factor of cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis. Biomed Mater Eng. 2014;24(1 Suppl):75-80.[17] Sipila KH, Ranga V, Rappu P, et al. Extracellular citrullination inhibits the function of matrix associated TGF-beta. Matrix Biol. 2016;55:77-89.[18] Li Y, Wang Y, Chubinskaya S, et al. Effects of insulin-like growth factor-1 and dexamethasone on cytokine-challenged cartilage: relevance to post-traumatic osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(2):266-274.[19] Kumar P, Kumar A, Srivastava MK, et al. Association of Transforming Growth Factor Beta-1-509C/T Gene Polymorphism with Ischemic Stroke: A Meta Analysis. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2016;7(2):91-96.[20] Nithiananthan S, Crawford A, Cooper Knock J, et al. Physiological Fluid Flow Moderates Fibroblast Responses to TGF-beta1. J Cell Biochem. 2016.[21] Hagopian MM, Brekken RA. Stromal TGFbetaR2 signaling: a gateway to progression for pancreatic cancer. Mol Cell Oncol. 2015;2(3):e975606.[22] Kocer G, Naziroglu M, Celik O, et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor attenuates bisphosphonate-induced oxidative injury but decreases zinc and copper levels in oral epithelium of rat. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2013;153(1-3):251-256.[23] Li X, Su G, Wang J, et al. Exogenous bFGF promotes articular cartilage repair via up-regulation of multiple growth factors. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(10):1567-1575.[24] Niderla-Bielinska J, Ciszek B, Jankowska-Steifer E, et al. Mouse Proepicardium Exhibits a Sprouting Response to Exogenous Proangiogenic Growth Factors in vitro. J Vasc Res. 2016;53(1-2):83-93.[25] Groeger G, Doonan F, Cotter T, et al. Reactive oxygen species regulate prosurvival ERK1/2 signaling and bFGF expression in gliosis within the retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53(10):6645-54.[26] Hirano T, Mori Y. Anti-atherogenic and anti-inflammatory properties of glucagon-like peptide-1, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypepide, and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in experimental animals. J Diabetes Investig. 2016;7 Suppl 1:80-86.[27] Mohammed KP, Aarey A, Tamkeen S, et al. Forskolin: genotoxicity assessment in Allium cepa. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2015;777:29-32.[28] Brohlin M, Kingham PJ, Novikova LN, et al. Aging effect on neurotrophic activity of human mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45052.[29] Majeed M, Nagabhushanam K, Natarajan S, et al. Efficacy and safety of 1% forskolin eye drops in open angle glaucoma - An open label study. Saudi J Ophthalmol. 2015; 29(3):197-200.[30] Cavallaro G, Bijker E, Strackx E, et al. Age-related changes and effects of mild hypothermia on carotid artery reactivity in newborn rats. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2015; 14(1):91-101.[31] Hu LM, Kemp SF, Elders MJ, et al. Metabolic effects of forskolin in chick chondrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989;1013(3):294-299.[32] Gusan S, Anand-Srivastava MB. cAMP attenuates the enhanced expression of Gi proteins and hyperproliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells from SHR: role of ROS and ROS-mediated signaling. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013; 304(12):C1198-1209.[33] Kamata H, Tanaka C, Yagisawa H, et al. Nerve growth factor and forskolin prevent H2O2-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells by glutathione independent mechanism. Neurosci Lett. 1996;212(3):179-182.[34] Finno CJ, Bordbari MH, Valberg SJ, et al. Transcriptome profiling of equine vitamin E deficient neuroaxonal dystrophy identifies upregulation of liver X receptor target genes. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016.[35] Boubakri H, Gargouri M, Mliki A, et al. Vitamins for enhancing plant resistance. Planta. 2016;244(3):529-543.[36] Oh YI, Kim JH, and Kang CW. Protective effect of short-term treatment with parathyroid hormone 1-34 on oxidative stress is involved in insulin-like growth factor-I and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 in rat bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells. Regul Pept. 2014; 189:1-10. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
椎板软骨:椎体终板是椎体在生长发育过程中,椎体上下面的骨骺板骨化停止后形成骨板,呈轻度凹陷,即为骨性终板。椎体终板的中央仍为一薄层透明软骨覆盖,并终生存在,即为软骨终板,上下软骨终板与髓核和纤维环连接共同构成椎间盘。主要作用是防止椎间盘髓核组织嵌入椎体,同时具有平衡分散应力的作用。
抗氧化:是指抗氧化自由基的简称。人体因为与外界的持续接触,包括呼吸(氧化反应)、外界污染、放射线照射等因素不断的在人体体内产生自由基。研究证明,人体的抗氧化系统是一个可与免疫系统相比拟的、具有完善和复杂功能的系统,机体抗氧化的能力越强,就越健康,生命也越长。
文题释义:
椎板软骨:椎体终板是椎体在生长发育过程中,椎体上下面的骨骺板骨化停止后形成骨板,呈轻度凹陷,即为骨性终板。椎体终板的中央仍为一薄层透明软骨覆盖,并终生存在,即为软骨终板,上下软骨终板与髓核和纤维环连接共同构成椎间盘。主要作用是防止椎间盘髓核组织嵌入椎体,同时具有平衡分散应力的作用。
抗氧化:是指抗氧化自由基的简称。人体因为与外界的持续接触,包括呼吸(氧化反应)、外界污染、放射线照射等因素不断的在人体体内产生自由基。研究证明,人体的抗氧化系统是一个可与免疫系统相比拟的、具有完善和复杂功能的系统,机体抗氧化的能力越强,就越健康,生命也越长。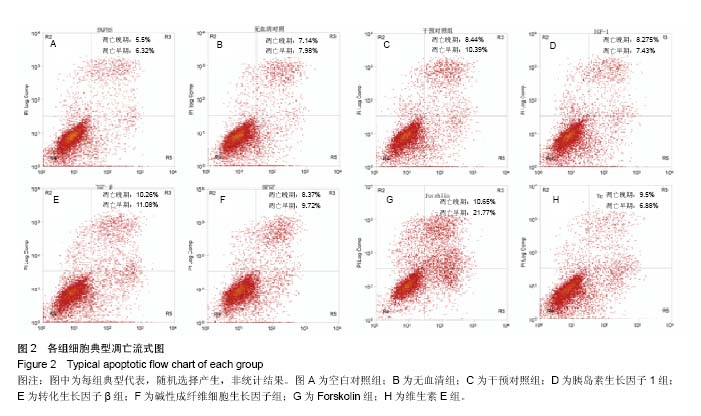
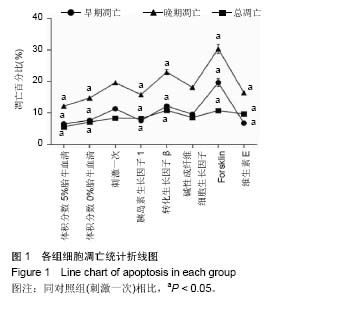
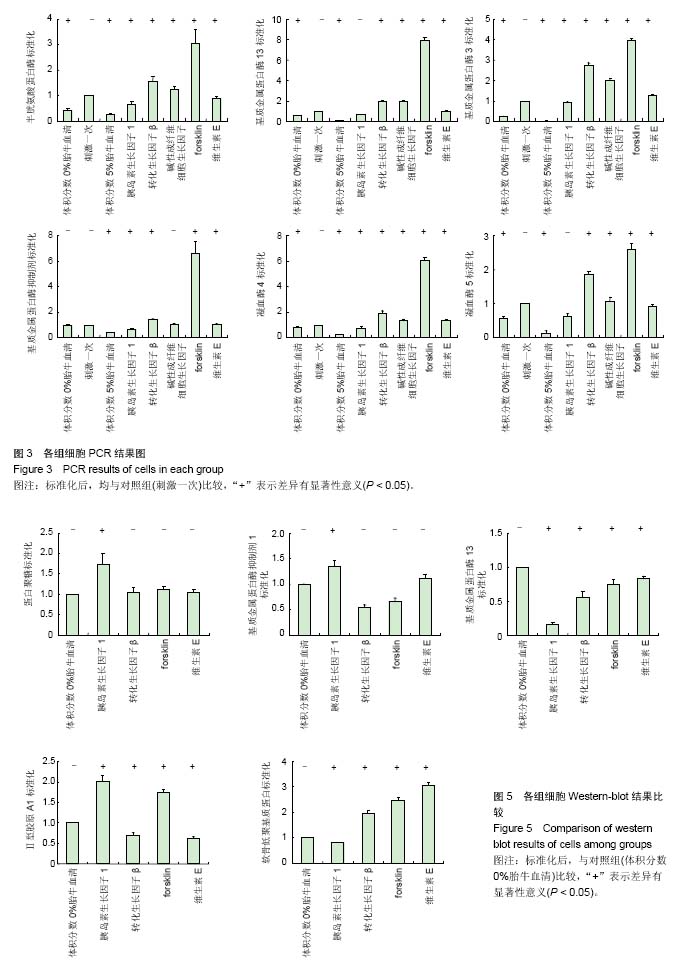
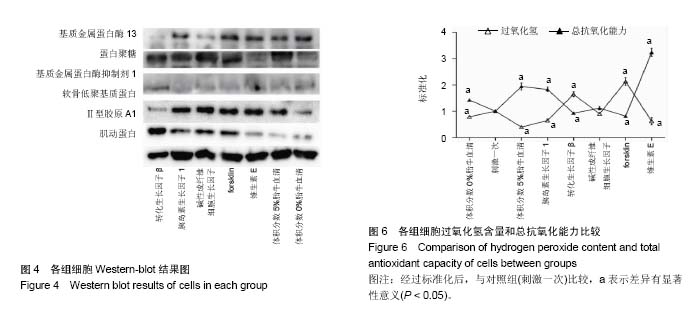
.jpg) 文题释义:
椎板软骨:椎体终板是椎体在生长发育过程中,椎体上下面的骨骺板骨化停止后形成骨板,呈轻度凹陷,即为骨性终板。椎体终板的中央仍为一薄层透明软骨覆盖,并终生存在,即为软骨终板,上下软骨终板与髓核和纤维环连接共同构成椎间盘。主要作用是防止椎间盘髓核组织嵌入椎体,同时具有平衡分散应力的作用。
抗氧化:是指抗氧化自由基的简称。人体因为与外界的持续接触,包括呼吸(氧化反应)、外界污染、放射线照射等因素不断的在人体体内产生自由基。研究证明,人体的抗氧化系统是一个可与免疫系统相比拟的、具有完善和复杂功能的系统,机体抗氧化的能力越强,就越健康,生命也越长。
文题释义:
椎板软骨:椎体终板是椎体在生长发育过程中,椎体上下面的骨骺板骨化停止后形成骨板,呈轻度凹陷,即为骨性终板。椎体终板的中央仍为一薄层透明软骨覆盖,并终生存在,即为软骨终板,上下软骨终板与髓核和纤维环连接共同构成椎间盘。主要作用是防止椎间盘髓核组织嵌入椎体,同时具有平衡分散应力的作用。
抗氧化:是指抗氧化自由基的简称。人体因为与外界的持续接触,包括呼吸(氧化反应)、外界污染、放射线照射等因素不断的在人体体内产生自由基。研究证明,人体的抗氧化系统是一个可与免疫系统相比拟的、具有完善和复杂功能的系统,机体抗氧化的能力越强,就越健康,生命也越长。