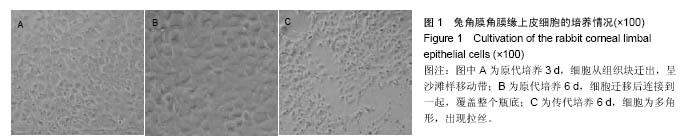
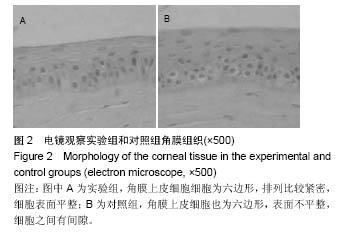
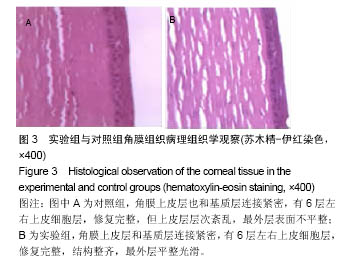
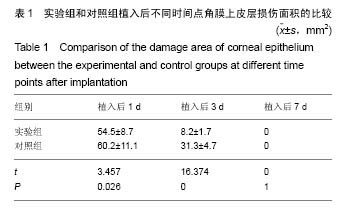
| [1]Torricelli AA,Santhanam A,Wu J,et al.The corneal fibrosis response toepithelial-stromal injury.Exp Eye Res. 2016;142: 110-118.[2]孙亚杰,李爱朋,潘志强.几种抗炎滴眼液对兔角膜上皮损伤和愈合影响的实验研究[J].眼科,2012,21(3):166-171.[3]穆剑,王梅,胡玉新,等.角膜上皮损伤引起复发性角膜上皮糜烂12例分析[J].广州医药,2012,43(4):29-30.[4]Xiang J,Le Q,Li Y,et al.In vivo confocal microscopy of early cornealepithelial recovery in patients with chemical injury.Eye (Lond).2015;29(12):1570-1578. [5]Hua X,Deng R,Li J,et al.Protective Effects of L-Carnitine Against OxidativeInjury by Hyperosmolarity in Human CornealEpithelial Cells.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015;56(9): 5503-5511. [6]Zhu KY,Merzendorfer H,Zhang W,et al.Biosynthesis, Turnover, and Functions of Chitin in Insects.Annu Rev Entomol.2016;61: 177-196. [7]Zhang W,Wang Y,Sui X,et al.Effects of chitin and sepia ink hybrid sponge on the healing of burning wound rats and its impact on macrophages in vitro.Acta Cir Bras. 2016;31(2): 119-125. [8]Sayari N,Sila A,Abdelmalek BE,et al.Chitin and chitosan from the Norway lobster by-products: Antimicrobial and anti-proliferative activities.Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;87:163-171. [9]Usman A,Zia KM,Zuber M,et al.Chitin and chitosan based polyurethanes: A review of recent advances and prospective biomedical applications.Int J Biol Macromol.2016;86: 630-645. [10]隋鲜鲜.甲壳素载体支架的生物相容性和对角膜上皮损伤的修复研究[D].中国海洋大学, 2013.[11]吴伟,李朝阳,王智崇,等.小牛血去蛋白提取物与重组人表皮生长因子促进兔角膜上皮损伤愈合和血管新生[J].眼科新进展,2014, 34(5):401-404. [12]Oh JY,Ko JH,Kim MK,et al.Effects of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells on cultures of corneal epithelial progenitor cells with ethanol injury.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014; 55(11): 7628-7635. [13]Sumioka T,Okada Y,Reinach PS,et al.Impairment of corneal epithelialwound healing in a TRPV1-deficient mouse.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014;55(5):3295-3302.[14]黄晨晨,廖荣丰,汪枫,等.糖尿病大鼠角膜上皮损伤修复过程中occludin的重塑特点[J].安徽医科大学学报, 2015,50(11): 1583-1587.[15]Song IS,Kang SS,Kim ES,et al.Heat shock protein 27 phosphorylation is involved in epithelial cell apoptosis as well as epithelialmigration during cornealepithelial wound healing. Exp Eye Res.2014;118:36-41. [16]Kim TH,Park YW,Ahn JS,et al.Effects of conditioned media from human amnioticepithelial cells on corneal alkali injuries in rabbits.J Vet Sci.2013;14(1):61-67.[17]Gehlsen U,Oetke A,Szaszák M,et al.Two-photon fluorescence lifetime imaging monitors metabolic changes during wound healing ofcorneal epithelial cells in vitro.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012;250(9): 1293-1302. [18]Zhang Y,Kobayashi T,Hayashi Y,et al.Important role of epiregulin in inflammatory responses during corneal epithelial wound healing.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53(4): 2414-2423. [19]Kadar T,Horwitz V,Sahar R,et al.Delayed loss of corneal epithelialstem cells in a chemical injury model associated with limbal stem celldeficiency in rabbits.Curr Eye Res.2011; 36(12):1098-1107. [20]Szabó DJ,Noer A,Nagymihály R,et al.Long-Term Cultures of Human CorneaLimbal Explants Form 3D Structures Ex Vivo - Implications for Tissue Engineering and Clinical Applications.PLoS One. 2015;10(11):e0143053. [21]Miotto M,Gouveia RM,Connon CJ.Peptide Amphiphiles in Corneal Tissue Engineering.J Funct Biomater.2015;6(3): 687-707. [22]Levis HJ,Kureshi AK,Massie I,et al.Tissue Engineering the Cornea: The Evolution of RAFT.J Funct Biomater.2015; 6(1):50-65. [23]Parke-Houben R,Fox CH,Zheng LL,et al. Interpenetrating polymer network hydrogel scaffolds for artificial cornea periphery.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2015;26(2):107. [24]Li W,Long Y,Liu Y,et al.Fabrication and characterization of chitosan-collagen crosslinked membranes for corneal tissue engineering.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2014;25(17): 1962-1972. [25]颜静.明胶/PLLA复合纤维膜的制备及在角膜组织工程中的性能研究[D].吉林大学,2012.[26]张孟雨.组织工程角膜支架材料研究进展[J].现代妇女(下旬), 2015, 31(1):230.[27]Long K,Liu Y,Li W,et al.Improving the mechanical properties of collagen-based membranes using silk fibroin for cornealtissue engineering.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015; 103(3):1159-1168. [28]Salehi S,Grünert AK,Bahners T,et al.New nanofibrous scaffold for cornealtissue engineering.Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2014;231(6):626-630. [29]Wang HY,Wei RH,Zhao SZ.Evaluation of corneal cell growth on tissue engineering materials as artificial cornea scaffolds. Int J Ophthalmol.2013;6(6):873-878. [30]Tonsomboon K,Strange DG,Oyen ML.Gelatin nanofiber-reinforced alginate gel scaffolds for corneal tissue engineering.Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2013;2013: 6671-6674.[31]Mi S,Connon CJ.The formation of a tissue-engineered cornea using plastically compressed collagen scaffolds and limbal stem cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1014:143-155. [32]Hanazono Y,Takeda K,Niwa S,et al.Crystal structures of chitin binding domains of chitinase from Thermococcus kodakarensis KOD1.FEBS Lett.2016;590(2):298-304.[33]Zhao L,Wu Y,Chen S,et al.Preparation and characterization of cross-linked carboxymethyl chitin porous membrane scaffold for biomedical applications.Carbohydr Polym.2015;126: 150-155. [34]Abehsera S,Glazer L,Tynyakov J,et al.Binary gene expression patterning of the molt cycle: the case of chitin metabolism.PLoS One.2015;10(4):e0122602.[35]Alvarenga ES,Mansur JF,Justi SA,et al.Chitin is a component of the Rhodnius prolixus midgut.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2016; 69:61-70. [36]Kadokawa J,Endo R,Tanaka K,et al.Fabrication of porous chitin with continuous substructure by regeneration from gel with CaBr2•2H2O/methanol.Int J Biol Macromol. 2015;78: 313-317. [37]Zdarta J,Klapiszewski ?,Wysokowski M,et al. Chitin-lignin material as a novel matrix for enzyme immobilization.Mar Drugs.2015;13(4):2424-2446.[38]张卫.甲壳素及其衍生物共混膜的制备、性质和对创面的愈合作用研究[D].中国海洋大学,2013.[39]李玉文,张梁栋.甲壳素及其衍生物在医药领域的应用[J].潍坊学院学报,2011,11(4):80-84. |
.jpg)
.jpg)