| [1] Wang CM,Hyakusoku H,Asano G,et al.Genetic predispositions to keloid and hypertrophic scar.Japan PRS.2001;21(2):241-244.
[2] Chwu M,Sayah D,Freymiller E,et al.Down regulation of apoptosis-related genes in keloid tissues.J Den Res. 2000;79(S1):309-312.
[3] Marnerous AG,Norris JE,Watanabe S,et al.Genome scans provide evidence for keloid susceptibility Lovi on chromosomes 2q23 and 7q11.J Invest Dermatol.2004; 122(5):1126-1132.
[4] Ramgolam K, Lauriol J,Lalou C,et al.Melanoma Spheroids Grown Under Neural Crest Cell Conditions Are Highly Plastic Migratory/Invasive Tumor Cells Endowed with Immunomodulator Function.PLoS One. 2011;6(4): e18784.
[5] Ekmekcioglu S, Ellerhorst J, Mhashilkar AM, et al.Down-regulated melanoma differentiation associated gene (MDA27) expression in human melanomas. Cancer.2001;94(1):54-59.
[6] Ishikawa S, Nakagawa T, Miyahara R, et al.Expression of MDA27? IL-24 and its clinical significance in resected non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(2):1198-1202.
[7] Sauane M, Lebedeva IV, Su ZZ, et al.Melanoma different iation associated gene Il-24 promotes tumor cell specific apoptosis through both secretory and nonsecretory pathways. Cancer Res.2004;64(9): 988-993.
[8] Saeki T,Mhashikar A,Swanson X,et al.Inhibition of human lung cancer growth following adenovirus mediated MDA27 gene expression in vivo. Oncogene. 2002;21(29):4558-4566.
[9] Ramesh R,Mhashilkar AM,Tanaka F,et al.Melanoma differentiation associated gene-7 IL-24 is a novel ligand that regulates angiogenesis via the IL-22 receptor. Cancer Res.2003;63(16):5105-5113.
[10] Chen X, Liu D, Wang J, et al.Suppression effect of recombinant adenovirus vector containing hIL-24 on Hep-2 laryngeal carcinoma cells. Oncol Lett. 2014; 7(3):771-777.
[11] Xubin Wei,Li liu,Gang Wang,et al.Targeting eradication of chronic myeloid leukemia using chimeric oncolytic adenovirus to drive IL-24 expression.Int J Clin Exp Pathol.2015; 8(4):3775-3784.
[12] Weiss R, Sachet M, Zinngrebe J,et al.IL-24 sensitizes tumor cells to TLR3-mediated apoptosis. Cell Death Differ.2013; 20(6):823-833.
[13] Wang M, Liang P.Interleukin-24 and its receptors. mmunology.2005; 114(2): 166-170.
[14] Cazzalini O, Sommatis S, Tillhon M,et al.CBP and p300 acetylate PCNA to link its degradation with nucleotide excision repair synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res.2014; 42(13): 8433-8448.
[15] Inoue A, Kikuchi S, Hishiki A,et al.A Small Molecule Inhibitor of Monoubiquitinated Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen (PCNA) Inhibits Repair of Interstrand DNA Cross-link, Enhances DNA Double Strand Break, and Sensitizes Cancer Cells to Cisplatin.J Biol Chem. 2014; 289(10): 7109-7120.
[16] Kucukguven A1, Khalil RA.Matrix Metalloproteinases as Potential Targets in the Venous Dilation Associated with Varicose Veins. Curr Drug Targets.2013; 14(3): 287-324.
[17] ?ukaszewicz-Zaj?c M, Mroczko B, S?owik A.Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their tissue inhibitors (TIMPs) in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).J Neural Transm.2014; 121(11): 1387-1397.
[18] Herszényi L, Hritz I, Lakatos G,et al.The Behavior of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors in Colorectal Cancer. Int J Mol Sci.2012; 13(10): 13240-13263.
[19] Spyros A. Syggelos, Alexios J, et al. Extracellular Matrix Degradation and Tissue Remodeling in Periprosthetic Loosening and Osteolysis: Focus on Matrix Metalloproteinases, Their Endogenous Tissue Inhibitors, and the Proteasome. Biomed Res Int.2013; 20(13): 230-235.
[20] Wieczorek E, Jablonska E, Wasowicz W,et al.Matrix metalloproteinases and genetic mouse models in cancer research: a mini-review. Tumour Biol.2015; 36(1): 163-175.
[21] Zhou Q, Gil-Krzewska A, Peruzzi G,et al.Matrix metalloproteinases inhibition promotes the polyfunctionality of human natural killer cells in therapeutic antibody-based anti-tumour immunotherapy. Clin Exp Immunol.2013; 173(1): 131-139.
[22] Dasu MR,Barrow RE,Spies M,et al.Matrix metalloproteinase expression in cytokine stimulated human dermal fibroblasts. Burns.2013;29(6):527-531.
[23] Chakraborti S,Mandal M,Das S, et al.Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase: an overview. Mol Cell Biochem. 2003;253(1-2):269-285.
[24] Peshavariya HM, Chan EC, Liu GS,et al.Transforming growth factor-β1 requires NADPH oxidase 4 for angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Mol Med.2014; 18(6): 1172-1183.
[25] Ghosh D, Lili L, McGrail DJ, et al.Integral Role of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor in Mediating Transforming Growth Factor-β1-Dependent Mesenchymal Stem Cell Stiffening. Stem Cells Dev. 2014; 23(3): 245-261.
[26] Chen NF, Huang SY, Lu CH, et al.Flexibilide Obtained from Cultured Soft Coral Has Anti-Neuroinflammatory and Analgesic Effects through the Upregulation of Spinal Transforming Growth Factor-β1 in Neuropathic Rats.Mar Drugs.2014; 12(7): 3792-3817.
[27] Feng XX, Luo J, Liu M, et al.Sirtuin 6 promotes transforming growth factor-β1/H2O2/HOCl-mediated enhancement of hepatocellular carcinoma cell tumorigenicity by suppressing cellular senescence. Cancer Sci.2015; 106(5): 559-566.
[28] Fu MY, He YJ, Lv X, et al.Transforming growth factor-β1 reduces apoptosis via autophagy activation in hepatic stellate cells. Mol Med Rep.2014;10(3): 1282-1288.
[29] Flanders KC, Heger CD, Conway C, et al.Brightfield Proximity Ligation Assay Reveals Both Canonical and Mixed Transforming Growth Factor-β/Bone Morphogenetic Protein Smad Signaling Complexes in Tissue Sections.J Histochem Cytochem.2014; 62(12): 846-863.
[30] Rodrigues-Diez R, Rodrigues-Diez RR, Lavoz C, et al.Gremlin Activates the Smad Pathway Linked to Epithelial Mesenchymal Transdifferentiation in Cultured Tubular Epithelial Cells. Biomed Res Int.2014; 20(14): 802-811.
[31] Yoshida K, Murata M, Yamaguchi T,et al.Reversible Human TGF-β Signal Shifting between Tumor Suppression and Fibro-Carcinogenesis: Implications of Smad Phospho-Isoforms for Hepatic Epithelial- Mesenchymal Transitions.J Clin Med. 2016; 5(1): 7. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
瘢痕疙瘩:是继发于皮肤损伤如创伤、烧伤或手术后,以胶原过度沉积于真皮和皮下组织为特征的皮肤胶原性疾病。与增生性瘢痕不同,瘢痕疙瘩超过皮损边缘呈浸润性生长, 侵犯临近组织,无自限性, 易造成功能障碍,有好发部位,多见于有色人种,不发生退行性变化,单纯手术切除后易复发,必须辅以电子线照射等综合治疗,有良性真皮肿瘤之称。
hIL-24基因:是研究较明确的抑癌基因,属于是单拷贝基因,定位于的1q32-41,由7个外显子和6个内含子组成,含有49个氨基酸的信号肽。可激活免疫应答效应,又可发挥特异性地抑制癌细胞生长作用,抑制癌周新生血管增生。由于其受体在不同组织、细胞中的表达存在差异,从而hIL-24发挥不同功能。
文题释义:
瘢痕疙瘩:是继发于皮肤损伤如创伤、烧伤或手术后,以胶原过度沉积于真皮和皮下组织为特征的皮肤胶原性疾病。与增生性瘢痕不同,瘢痕疙瘩超过皮损边缘呈浸润性生长, 侵犯临近组织,无自限性, 易造成功能障碍,有好发部位,多见于有色人种,不发生退行性变化,单纯手术切除后易复发,必须辅以电子线照射等综合治疗,有良性真皮肿瘤之称。
hIL-24基因:是研究较明确的抑癌基因,属于是单拷贝基因,定位于的1q32-41,由7个外显子和6个内含子组成,含有49个氨基酸的信号肽。可激活免疫应答效应,又可发挥特异性地抑制癌细胞生长作用,抑制癌周新生血管增生。由于其受体在不同组织、细胞中的表达存在差异,从而hIL-24发挥不同功能。.jpg) 文题释义:
瘢痕疙瘩:是继发于皮肤损伤如创伤、烧伤或手术后,以胶原过度沉积于真皮和皮下组织为特征的皮肤胶原性疾病。与增生性瘢痕不同,瘢痕疙瘩超过皮损边缘呈浸润性生长, 侵犯临近组织,无自限性, 易造成功能障碍,有好发部位,多见于有色人种,不发生退行性变化,单纯手术切除后易复发,必须辅以电子线照射等综合治疗,有良性真皮肿瘤之称。
hIL-24基因:是研究较明确的抑癌基因,属于是单拷贝基因,定位于的1q32-41,由7个外显子和6个内含子组成,含有49个氨基酸的信号肽。可激活免疫应答效应,又可发挥特异性地抑制癌细胞生长作用,抑制癌周新生血管增生。由于其受体在不同组织、细胞中的表达存在差异,从而hIL-24发挥不同功能。
文题释义:
瘢痕疙瘩:是继发于皮肤损伤如创伤、烧伤或手术后,以胶原过度沉积于真皮和皮下组织为特征的皮肤胶原性疾病。与增生性瘢痕不同,瘢痕疙瘩超过皮损边缘呈浸润性生长, 侵犯临近组织,无自限性, 易造成功能障碍,有好发部位,多见于有色人种,不发生退行性变化,单纯手术切除后易复发,必须辅以电子线照射等综合治疗,有良性真皮肿瘤之称。
hIL-24基因:是研究较明确的抑癌基因,属于是单拷贝基因,定位于的1q32-41,由7个外显子和6个内含子组成,含有49个氨基酸的信号肽。可激活免疫应答效应,又可发挥特异性地抑制癌细胞生长作用,抑制癌周新生血管增生。由于其受体在不同组织、细胞中的表达存在差异,从而hIL-24发挥不同功能。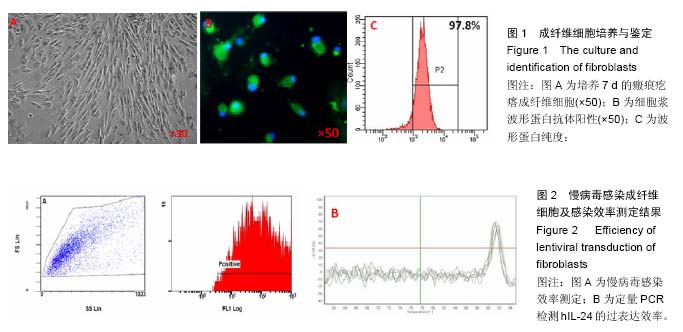
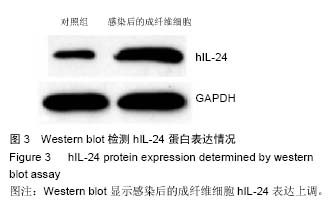
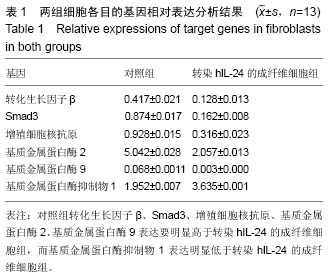
.jpg) 文题释义:
瘢痕疙瘩:是继发于皮肤损伤如创伤、烧伤或手术后,以胶原过度沉积于真皮和皮下组织为特征的皮肤胶原性疾病。与增生性瘢痕不同,瘢痕疙瘩超过皮损边缘呈浸润性生长, 侵犯临近组织,无自限性, 易造成功能障碍,有好发部位,多见于有色人种,不发生退行性变化,单纯手术切除后易复发,必须辅以电子线照射等综合治疗,有良性真皮肿瘤之称。
hIL-24基因:是研究较明确的抑癌基因,属于是单拷贝基因,定位于的1q32-41,由7个外显子和6个内含子组成,含有49个氨基酸的信号肽。可激活免疫应答效应,又可发挥特异性地抑制癌细胞生长作用,抑制癌周新生血管增生。由于其受体在不同组织、细胞中的表达存在差异,从而hIL-24发挥不同功能。
文题释义:
瘢痕疙瘩:是继发于皮肤损伤如创伤、烧伤或手术后,以胶原过度沉积于真皮和皮下组织为特征的皮肤胶原性疾病。与增生性瘢痕不同,瘢痕疙瘩超过皮损边缘呈浸润性生长, 侵犯临近组织,无自限性, 易造成功能障碍,有好发部位,多见于有色人种,不发生退行性变化,单纯手术切除后易复发,必须辅以电子线照射等综合治疗,有良性真皮肿瘤之称。
hIL-24基因:是研究较明确的抑癌基因,属于是单拷贝基因,定位于的1q32-41,由7个外显子和6个内含子组成,含有49个氨基酸的信号肽。可激活免疫应答效应,又可发挥特异性地抑制癌细胞生长作用,抑制癌周新生血管增生。由于其受体在不同组织、细胞中的表达存在差异,从而hIL-24发挥不同功能。