| [1] Hackl M, Lappen S, Burkhart KJ, et al. Elbow Positioning and Joint Insufflation Substantially Influence Median and Radial Nerve Locations. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2015;11(473):3627-3634.
[2] Tang H C,Xiang M,Chen H,et al. Arthroscopic surgery for the treatment of stiff elbow. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2014;11(27):943-947.
[3] Kayalar M,Ozerkan F,Bal E,et al. Elbow arthrolysis in severely stiff elbows. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2008;10(128):1055-1063.
[4] Wegmann K, Lappen S, Pfau DB,et al. Course of the radial nerve in relation to the center of rotation of the elbow--the need for a rational safe zone for lateral pin placement. J Hand Surg Am. 2014;39(6):1136-1140.
[5] Hackl M,Lappen S,Burkhart K J,et al. The course of the median and radial nerve across the elbow: an anatomic study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2015; 7(135):979-983.
[6] Rhee YG,Cho NS,Lim CT,et al. Debridement arthroplasty for post-traumatic stiff elbow: intraoperative factors affecting the clinical results of surgical treatment. Clinics in orthopedic surgery.2009; 1(1):27-33.
[7] Kim SJ, Moon HK, Chun YM,et al.Arthroscopic treatment for limitation of motion of the elbow: the learning curve. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;6(19):1013-1018.
[8] Pederzini LA, Nicoletta F, Tosi M,et al. Elbow arthroscopy in stiff elbow. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2014;2(22):467-473.
[9] Gohlke F. The stiff elbow joint. Orthopade.2011;4(40): 281-283.
[10] Ersen A,Demirhan M,Atalar AC,et al. Stiff elbow: distraction interposition arthroplasty with an Achilles tendon allograft: long-term radiological and functional results. Acta orthopaedica et traumatologica turcica. 2014;5(48):558-562.
[11] 王虎,蔡道章.肘关节镜入路选择的应用解剖研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2007,4(25):369-372.
[12] 陈光兴,唐康来,杨柳,等.关节镜下肘关节松解术[J].中华骨科杂志,2006,8(26):512-524.
[13] 蔡江瑜,王伟,范存义.肘关节开放松解联合内固定取出术治疗创伤后关节僵硬[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2015; 29(7): 826-830.
[14] Sahajpal D, Choi T, Wright T W. Arthroscopic release of the stiff elbow. J Hand Surg Am. 2009;34(3): 540-544.
[15] Koh KH,Lim TK,Lee HI,et al. Surgical release of elbow stiffness after internal ?xation of intercondylar fracture of the distal humerus.JShoulder Elbow Surg. 2013; 22(2):268-274.
[16] Pederzini L A,Nicoletta F,Tosi M, et al. Elbow arthroscopy in stiff elbow. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2014;2(22):467-473.
[17] 唐浩琛,向明,陈杭,等. 关节镜下治疗肘关节僵硬[J].中国骨伤, 2014;11(27):943-947.
[18] 黄竞敏,赵力,唐建军,等. 关节镜下松解及清理术在肘关节屈伸功能障碍方面的应用[J].中华骨科杂志,2005; 25(9): 533-536.
[19] 闫飞, 王忠远,张湘生,等.关节镜治疗肘骨关节病[J].中国内镜杂志,2010; 16(1):93-95.
[20] Achtnich A, Forkel P, Metzlaff S, et al. Arthroscopic arthrolysis of the elbow joint. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2013;25:205–214.
[21] Lindenhovius AL,Jupiter JB. The posttraumatic stiff elbow: a review of the literature. J Hand Surg Am. 2007;10(32):1605-1623.
[22] Chen S,Yu SY,Yan H,et al.The time point in surgical excision of heterotopic ossification of post-traumatic stiff elbow: recommendation for early excision followed by early exercise. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2015; 8(24): 1165-1171.
[23] 蔡江瑜,王伟,范存义.肘关节开放松解术后并发症的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2015,29(1):113-117.
[24] Keener J D, Galatz L M . Arthroscopic management of the stiff elbow. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011; 19(5): 265-274.
[25] Stothers K, Day B, Regan WR. Arthroscopy of the elbow: anatomy, portal sites, and a description of the proximal lateral portal. Arthroscopy.1995;8(11):449–457.
[26] Tucker SA,Savoie FH Rd,O'Brien MJ. Arthroscopic management of the post-traumatic stiff elbow. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2011;2(20):83-89.
[27] Omid R, Hamid N, Keener JD,et al.Relation of the radial nerve to the anterior capsule of the elbow: anatomy with correlation to arthroscopy. Arthroscopy. 2012;13(28):1800-1804.
[28] Nandi S,Maschke S,Evans P J,et al. The stiff elbow. Hand (N Y).2009;4(4):368-379.
[29] Gallucci G L,Boretto JG,Davalos MA,et al. The use of dynamic orthoses in the treatment of the stiff elbow. 2014;8(24):1395-1400.
[30] Unlu MC,Kesmezacar H,Akgun I,et al.Anatomic relationship between elbow arthroscopy portals and neurovascular structures in different elbow and forearm positions. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2006; 22(15):457-462.
[31] Haapaniemi T,Berggren M,Adolfsson L.Complete transection of the median and radial nerves during arthroscopic release of post-traumatic elbow contracture. Arthroscopy.1999;5(15):784-787.
[32] Singh H,Nam KY,Moon YL. Arthroscopic management of stiff elbow. Orthopedics.2011;6(34):167-169.
[33] Lichtenberg S.Elbow contracture. Use of an arthroscopic procedure or an an open procedure? . Obere Extremitat.2014;13(9):163-171.
[34] Morimoto D,Isu T,Kim K,et al. Proximal Entrapment Neuropathy of the Median Nerve above the Elbow-Case Report. J Nippon Med Sch.2015;6(82): 287-289. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
关节镜:关节镜是一种观察关节内部结构的直径5 mm左右的棒状光学器械,是用于诊治关节疾患的内窥镜。关节镜在一根细管的端部装有一个透镜,将细管插入关节内部,关节内部的结构便会在监视器上显示出来。关节镜不仅用于疾病的诊断,而且已经广泛用于关节疾病的治疗。关节镜手术是一种微创手术,开始主要应用于膝关节,后相继应用于髋关节,肩关节,踝关节,肘关节及手指等小关节等。
正中神经:正中神经在肘关节上端,在肱动脉内侧进入肘窝,在肘窝处位于肱二头肌腱膜与肱肌之间,在肘窝的内侧缘多穿旋前圆肌浅、深两头进入前臂。因正中神经在肘关节前方与关节囊的位置关系密切,在行肘关节镜手术时易损伤此神经引起严重并发症。
文题释义:
关节镜:关节镜是一种观察关节内部结构的直径5 mm左右的棒状光学器械,是用于诊治关节疾患的内窥镜。关节镜在一根细管的端部装有一个透镜,将细管插入关节内部,关节内部的结构便会在监视器上显示出来。关节镜不仅用于疾病的诊断,而且已经广泛用于关节疾病的治疗。关节镜手术是一种微创手术,开始主要应用于膝关节,后相继应用于髋关节,肩关节,踝关节,肘关节及手指等小关节等。
正中神经:正中神经在肘关节上端,在肱动脉内侧进入肘窝,在肘窝处位于肱二头肌腱膜与肱肌之间,在肘窝的内侧缘多穿旋前圆肌浅、深两头进入前臂。因正中神经在肘关节前方与关节囊的位置关系密切,在行肘关节镜手术时易损伤此神经引起严重并发症。.jpg) 文题释义:
关节镜:关节镜是一种观察关节内部结构的直径5 mm左右的棒状光学器械,是用于诊治关节疾患的内窥镜。关节镜在一根细管的端部装有一个透镜,将细管插入关节内部,关节内部的结构便会在监视器上显示出来。关节镜不仅用于疾病的诊断,而且已经广泛用于关节疾病的治疗。关节镜手术是一种微创手术,开始主要应用于膝关节,后相继应用于髋关节,肩关节,踝关节,肘关节及手指等小关节等。
正中神经:正中神经在肘关节上端,在肱动脉内侧进入肘窝,在肘窝处位于肱二头肌腱膜与肱肌之间,在肘窝的内侧缘多穿旋前圆肌浅、深两头进入前臂。因正中神经在肘关节前方与关节囊的位置关系密切,在行肘关节镜手术时易损伤此神经引起严重并发症。
文题释义:
关节镜:关节镜是一种观察关节内部结构的直径5 mm左右的棒状光学器械,是用于诊治关节疾患的内窥镜。关节镜在一根细管的端部装有一个透镜,将细管插入关节内部,关节内部的结构便会在监视器上显示出来。关节镜不仅用于疾病的诊断,而且已经广泛用于关节疾病的治疗。关节镜手术是一种微创手术,开始主要应用于膝关节,后相继应用于髋关节,肩关节,踝关节,肘关节及手指等小关节等。
正中神经:正中神经在肘关节上端,在肱动脉内侧进入肘窝,在肘窝处位于肱二头肌腱膜与肱肌之间,在肘窝的内侧缘多穿旋前圆肌浅、深两头进入前臂。因正中神经在肘关节前方与关节囊的位置关系密切,在行肘关节镜手术时易损伤此神经引起严重并发症。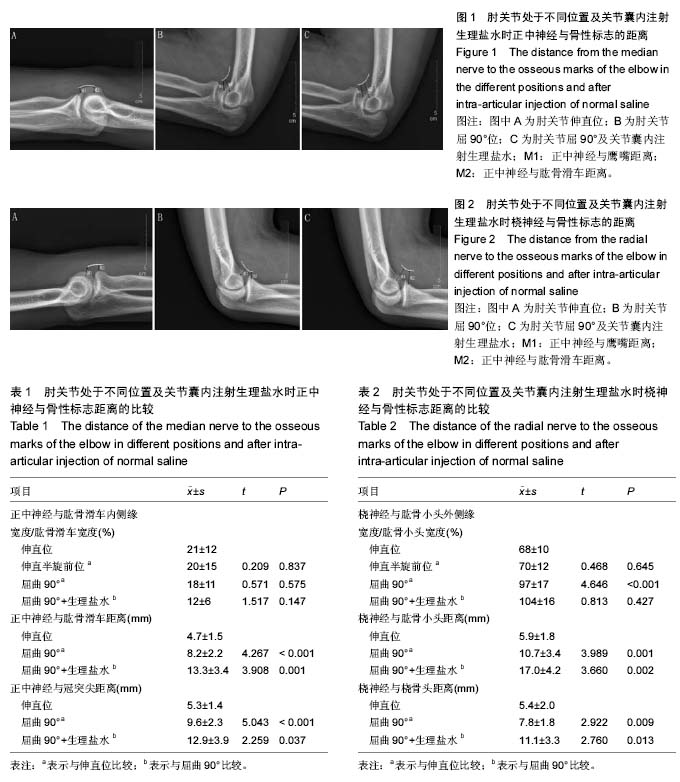
.jpg) 文题释义:
关节镜:关节镜是一种观察关节内部结构的直径5 mm左右的棒状光学器械,是用于诊治关节疾患的内窥镜。关节镜在一根细管的端部装有一个透镜,将细管插入关节内部,关节内部的结构便会在监视器上显示出来。关节镜不仅用于疾病的诊断,而且已经广泛用于关节疾病的治疗。关节镜手术是一种微创手术,开始主要应用于膝关节,后相继应用于髋关节,肩关节,踝关节,肘关节及手指等小关节等。
正中神经:正中神经在肘关节上端,在肱动脉内侧进入肘窝,在肘窝处位于肱二头肌腱膜与肱肌之间,在肘窝的内侧缘多穿旋前圆肌浅、深两头进入前臂。因正中神经在肘关节前方与关节囊的位置关系密切,在行肘关节镜手术时易损伤此神经引起严重并发症。
文题释义:
关节镜:关节镜是一种观察关节内部结构的直径5 mm左右的棒状光学器械,是用于诊治关节疾患的内窥镜。关节镜在一根细管的端部装有一个透镜,将细管插入关节内部,关节内部的结构便会在监视器上显示出来。关节镜不仅用于疾病的诊断,而且已经广泛用于关节疾病的治疗。关节镜手术是一种微创手术,开始主要应用于膝关节,后相继应用于髋关节,肩关节,踝关节,肘关节及手指等小关节等。
正中神经:正中神经在肘关节上端,在肱动脉内侧进入肘窝,在肘窝处位于肱二头肌腱膜与肱肌之间,在肘窝的内侧缘多穿旋前圆肌浅、深两头进入前臂。因正中神经在肘关节前方与关节囊的位置关系密切,在行肘关节镜手术时易损伤此神经引起严重并发症。