| [1] Williams TJ , Pepitone ME , Christensen SE, et al. Finger-length ratios and sexualorientation. Nature. 2000;404(6777): 455-456 .
[2] Goodman FR, Scambler PJ .Human HOX gene mutations. Clin Genet, 2001;59(1):1-11 .
[3] Herault Y, Fradeau N, Zakany JU.A regulatory mutation inducing both loss-of-functions ofposteri or Hoxd genes. Development.1997;124(18):3493-3500.
[4] Manning J T,Scutt D,Wilson J,et al.The ratio of 2nd to 4th digit length: A predictor of sperm numbers and concentrations of testosterone,luteinising hormone and oestroge. HumanReproduction.1998;13(11):3000-3004.
[5] Hönekopp J, T Manning J, Müller C,et al. Digit ratio (2D:4D) and physical fitness in males and females: Evidence for effects of prenatal androgens on sexually selected traits. Horm Behav. 2006;49(4): 545-549.
[6] Sarah MC,John TM,Leanne R,et al.Directional asymmetry (right–left differences) in digit ratio (2D:4D) predict indirect aggression in women. Personality and Individual Differences. 2007, 43(4): 865-872.
[7] Manning JT, Taylor RP. Second to fourth digit ratio and male ability in sport: implications for sexual selection in humans. Evol Hum Behav. 2001;22(1):61-69.
[8] Vanessa AS, John TM. Second to fourth digit ratio in elite musicians: Evidence for musical ability as an honest signal of male fitness. Evolution and Human Behavior.2000;21(1):1-9.
[9] Zabuliene L, Tutkuviene J.Body composition and polycysticovary syndrome. Medicina (Kaunas). 2010; 46( 2):142-157.
[10] Honekopp J,Watson S. Meta-analysis of digit ratio2D: 4D shows greater sex difference in the right hand.Am J Hum Biol.2010;22(5):619-630.
[11] Noipayak P. TheRatio of 2nd and 4th Digit Lengthin Autistic Children. J Med Assoc Thai.2009;92(8): 1040-1045.
[12] Benderlioglu Z, Nelson RJ. Digit length ratios predict reactive aggression in women, but not in men.Horm Behav.2004;46(5):558-564 .
[13] Lutchmaya S, Baron-Cohen S, Raggatt P, et al.2nd to 4th digit ratios, fetal testosterone and estradiol.Early Hum Dev.2004;77(1-2):23-28.
[14] Williams JH, Green halgh KD , Manning JT .Second to fourth finger ratio and possible precursors of developmental psychopathology inpreschool children. Early Hum Dev.2003;72(1):57-65 .
[15] McIntyre MH , Cohn BA , Elli son PT .Sex dimorphism in the digit al formulae of children.Am J Phys An Thropol. 2006;129(1):143-150.
[16] Jǜrimae T, Voracek M, Jǜrimae J, et al. Relation ships between finger length ratios, ghrelin, lept in, IGF axis , and sex steroids in young male and female swimmers.Eur J Appl Physiol.2008;104(3):523-529 .
[17] Manning JT , Wood S, Vang E, et al.Second to fourth digit ratio (2D :4D)and testosterone in men.Asian J Androl.2004;6(3):211-215.
[18] Honekopp J, Bartholdt L, Beier L,et al. Second t o fourth digit lengthratio(2D :4D)and adult sex hormone levels :new data and a met analytic review.Psychoneuroendocrinology.2007;32(4):313-32.
[19] 袁建琴,阮昌雄,刘承宜等.食指与无名指指长比率(2D︰4D)与运动能力研究评述[J].广州:体育学刊,2009,16(4): 104-107.
[20] 党晓云,梁芝栋,张强等.游泳运动员指长比的运动等级差异和排序[J].河南师范大学学报:自然科学版,2010,38(4): 140-143.
[21] 梁芝栋,党晓云,张建等.游泳运动员指长比与运动能力的相关分析[J].北京体育大学学报,2011,34(2):135-137.
[22] 秦学林.击剑运动员食指与无名指指长比(2D︰4D)与运动能力关系研究[J].体育与科学,2011,32(6):69-71.
[23] 何玉秀,李梅,贾立鑫,等.体能类项目运动员指长比与其运动能力的相关研究[J].中国解剖学会2013年年会论文文摘汇编,2013.
[24] 李芳辉.小学生第二根与第四根手指长度的比率与运动能力和文化成绩的相关性分析[D].广州:华南师范大学, 2007.
[25] 石峰.体育院校大学生指长比(2D:4D)与文化成绩、体育成绩、体质的相关性研究[D].广州:华南师范大学,2008.
[26] 任占兵,杜兴兰,韩格格等.食指和无名指指长比率(2D:4D)与跑步经济性的相关性研究[J].广州体育学院学报,2016, 36(1):97-101.
[27] Paul SN,Kato BS, Hunkin JL,et al. The big finger:the second to fourth digit ratio is a predictor of sporting ability in women.Br J Sports Med.2006;40(12): 981-983.
[28] Pokrywka L,Rachon D,Suchecka-Rachoń K,et al. The second to fourth digit ratio in elite and non-elite female athletes.American Journalof Human Biology.2005; 17(6):796-800.
[29] Tester N, Campbel A.Sporting achievement: what is the contribution of digit ratio? J Pers. 2007;75(4): 663-677.
[30] Voracek M,Reimer B,Dressler S.Digit ratio( 2D∶ 4D)predicts sporting success among female fencers indepedent from physical,experience,and personality factors. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2010 Dec;20(6): 853-860.
[31] Bescos R,Esteve M,Portal J,et al.Prenatal programming of sporting success: Associations of digit ratio(2D:4D), a putative marker for prenatal androgen action, with world rankings in female fencers. J Sports Sci. 2009 ;27(6):625-632.
[32] Manning JT ,Morris N,Caswell N.Endurance running and digit ratio (2D:4D): implications for fetal testosterone effects on running speed and vascular health. Am J Hum Biol. 2007;19(3):416-421.
[33] Manning JT,Hill MR.Digit ratio ( 2D∶4D) and Spring Speed inboy. Am J Hum Biol. 2009 ;21(2):210-213.
[34] Bennett M, Manning JT, Cook CJ, et al. Digit ratio ( 2D:4D) and performance in elite rugby players.J Sports Sci.2010;28(13):1415-1421.
[35] Honekopp J, Watson S. Meta-analysis of digit ratio 2D: 4D shows greater sex difference in the right hand[J]. Am J Hum Biol. 2010;22(5):619-630.
[36] Honekopp J, Schuster M. A meta-analysis on 2D: 4D and athletic prowess: Substantial relationships but neither hand out-predicts the other. Personality and Individual Differences.2010;48(1):4-10.
[37] Hill R, Simpson B, Manning J, et al. Right-left digit ratio( 2D: 4D)and maximal oxygen uptake. J Sports Sci.2012;30(2):129-134.
[38] Auyeung TW,Lee J S,Kwok T,et al. Testosterone but not estradiol level is positively related to muscle strength and physical performance independent of muscle mass: a cross-sectional study in 1489 older men. Eur J Endocrinol. 2011;164(5) : 811-817.
[39] Fink B,Thanzaml V,Seydel H,et al. Digit ratio and hand-grip strength in German and Mizos men: cross-cultural evidence for an organizing effect of prenatal testosterone on strength. Am J Hum Biol. 2006;18(6):776-782.
[40] Ranson R,Stratton G,Taylor S R.Digit ratio (2D:4D) and physical fitness (Eurofit test battery) in school children. Early Hum Dev. 2015;91(5):327-331.
[41] Kanchan T,Kumar GP,Menezes RG.Index and ring finger ratio-A new sex determinant in south Indian population. Forensic Sci Int. 2008;181(1-3):53.e1-4.
[42] Manning JT, Leinster S. The ratio of 2nd to 4th digit length and age at presentation of breast cancer: A link with prenatal oestrogen. Breast.2001; 10(4):335-357.
[43] 赵晓进.太行山猕猴掌骨和跖骨长度比率的性别差异[J].解剖学报,2009,40(6):1002-1004.
[44] McFadden D, Bracht MS .Sex differences in length ratios from theextremi ties of humans , gorillas , and chimpanzees .Horm Behav.2002;41(4):479-480 .
[45] McFadden D, Bracht MS .Sex difference in the relative lengths of metacarpals and metatarsals in gorillas and chimpanzees .Horm Behav.2005;47(1):99-111.
[46] McFadden D, Bracht MS .The relative lengths and weights of metacarpals and metatarsals in baboons (Papio hamadryas).Horm Behav.2003;43(2):347-355.
[47] McFadden D, Shubel E.Relative lengths of fingers and toes in human males and females.Horm Behav.2002; 42(4):492-500.
[48] 刘元龙.手掌指长比提取算法研究[D].昆明:云南大学, 2015. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
指长比:是指手指长度的比值,1D表示第1手指(大拇指)长度,2D表示第2手指(食指)长度,以此类推,3D、4D和5D;2D:4D表示第2手指长度与第4手指长度的比值,其他同理;趾长比是指脚趾长度比值,1P表示第1脚趾(大脚趾)长度,2P表示第2脚趾的长度,以此类推,3P、4P和5P;2P:3P表示第2脚趾和第3脚趾长度的比值,其他同理。
运动能力:是指人参加运动和训练所具备的能力,是人的身体形态、素质、机能、技能和心理能力等因素的综合表现。从生物化学的观点分析,运动能力高低主要取决于运动过程中能量的供给、转移和利用的能力。
文题释义:
指长比:是指手指长度的比值,1D表示第1手指(大拇指)长度,2D表示第2手指(食指)长度,以此类推,3D、4D和5D;2D:4D表示第2手指长度与第4手指长度的比值,其他同理;趾长比是指脚趾长度比值,1P表示第1脚趾(大脚趾)长度,2P表示第2脚趾的长度,以此类推,3P、4P和5P;2P:3P表示第2脚趾和第3脚趾长度的比值,其他同理。
运动能力:是指人参加运动和训练所具备的能力,是人的身体形态、素质、机能、技能和心理能力等因素的综合表现。从生物化学的观点分析,运动能力高低主要取决于运动过程中能量的供给、转移和利用的能力。.jpg) 文题释义:
指长比:是指手指长度的比值,1D表示第1手指(大拇指)长度,2D表示第2手指(食指)长度,以此类推,3D、4D和5D;2D:4D表示第2手指长度与第4手指长度的比值,其他同理;趾长比是指脚趾长度比值,1P表示第1脚趾(大脚趾)长度,2P表示第2脚趾的长度,以此类推,3P、4P和5P;2P:3P表示第2脚趾和第3脚趾长度的比值,其他同理。
运动能力:是指人参加运动和训练所具备的能力,是人的身体形态、素质、机能、技能和心理能力等因素的综合表现。从生物化学的观点分析,运动能力高低主要取决于运动过程中能量的供给、转移和利用的能力。
文题释义:
指长比:是指手指长度的比值,1D表示第1手指(大拇指)长度,2D表示第2手指(食指)长度,以此类推,3D、4D和5D;2D:4D表示第2手指长度与第4手指长度的比值,其他同理;趾长比是指脚趾长度比值,1P表示第1脚趾(大脚趾)长度,2P表示第2脚趾的长度,以此类推,3P、4P和5P;2P:3P表示第2脚趾和第3脚趾长度的比值,其他同理。
运动能力:是指人参加运动和训练所具备的能力,是人的身体形态、素质、机能、技能和心理能力等因素的综合表现。从生物化学的观点分析,运动能力高低主要取决于运动过程中能量的供给、转移和利用的能力。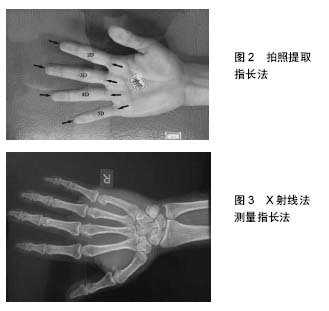
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
指长比:是指手指长度的比值,1D表示第1手指(大拇指)长度,2D表示第2手指(食指)长度,以此类推,3D、4D和5D;2D:4D表示第2手指长度与第4手指长度的比值,其他同理;趾长比是指脚趾长度比值,1P表示第1脚趾(大脚趾)长度,2P表示第2脚趾的长度,以此类推,3P、4P和5P;2P:3P表示第2脚趾和第3脚趾长度的比值,其他同理。
运动能力:是指人参加运动和训练所具备的能力,是人的身体形态、素质、机能、技能和心理能力等因素的综合表现。从生物化学的观点分析,运动能力高低主要取决于运动过程中能量的供给、转移和利用的能力。
文题释义:
指长比:是指手指长度的比值,1D表示第1手指(大拇指)长度,2D表示第2手指(食指)长度,以此类推,3D、4D和5D;2D:4D表示第2手指长度与第4手指长度的比值,其他同理;趾长比是指脚趾长度比值,1P表示第1脚趾(大脚趾)长度,2P表示第2脚趾的长度,以此类推,3P、4P和5P;2P:3P表示第2脚趾和第3脚趾长度的比值,其他同理。
运动能力:是指人参加运动和训练所具备的能力,是人的身体形态、素质、机能、技能和心理能力等因素的综合表现。从生物化学的观点分析,运动能力高低主要取决于运动过程中能量的供给、转移和利用的能力。