| [1] 李斌斌,董福生,董玉英,等.放疗对纯钛种植体周围骨组织影响的骨计量学研究.[J]现代口腔医学杂志,2004,18(4): 302-305.[2] Le Gu’ehennec L, Soueidan A, Layrolle P, et al. Surface treatments of titanium dental implants for rapid osseolntegration. Dent Mat. 2007;23(7):44-54.[3] 陈安玉.口腔种植学[M].成都:四川科学技术出版社, 1991: 93.[4] Meijer GJ, Cune MS, Vandooren M. A comparative study of flexible(poly active versus rigid hydroxyapatite) per mucosal dental implants:clinical aspects. J Oral Rehabil. 1997;24(2):85. [5] Meijer GJ, Dalmeijer RA, Deputter C. A comparative study of flexible(poly active versus rigid hydroxyapatite) per mucosal dental implants: histological aspects. J Oral Rehabil. 1997;24(2):93.[6] 罗智斌,丁学强.低弹性模量纯钛种植体的生物力学测试--体外模型实验[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2002,7(3): 118-201.[7] Craig RG,Le Geros RZ. Early events associated with periodontal connective tissue attachment formation in titanium and hydroxyapatite. J Biomed Mater Res. 1999; 47(4):575-584.[8] Baler RE,Meyer AE. Implant surface preparation. J Biomed Mater Res. 1999;47(4):585-594.[9] Han CH. Quantitative and qualitative investigations of surface enlarged titanium and titanium alloy implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1998;9(1): 1-10.[10] Klokkevold PR, Johnson P, Dadgostari S, et al. Early endosseous integration enhanced by dual acid etching of titanium: a torque removal study in the rabbit. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2001;12(2): 350-359.[11] 陈海军,张安生,林均舟,等. 锌对钛种植体骨融合的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(51):9518-9522.[12] French D, Nadji N, Shariati B,et al. Survival and Success Rates of Dental Implants Placed Using Osteotome Sinus Floor Elevation Without Added Bone Grafting: A Retrospective Study with a Follow-up of up to 10 Years. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2016;36:s89-s97.[13] Saghiri MA, Asatourian A, Garcia-Godoy F, et al. The role of angiogenesis in implant dentistry part I: Review of titanium alloys, surface characteristics and treatments. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2016. [Epub ahead of print][14] Burgueño-Barris G, Cortés-Acha B, Figueiredo R, et al. Aesthetic perception of single implants placed in the anterior zone. A cross-sectional study. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2016. [Epub ahead of print][15] Kumar R,Gill PS,Rattan PJ. Variations in plasma trace-elements concentration during fracture healing in dogs. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol. 1991; 35:58-60.[16] Zavgorodniy AV, Borrero-López O, Hoffman M, et al. Mechanical stability of two-step chemically deposited hydroxyapatite coating on Ti substrate: Effect of various surface preatments. J Biomed Mater Res. 2001; 14: 108-113.[17] Nieri M. Research in focus. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2016; 9(1):97-98.[18] Spies BC, Kohal RJ, Balmer M, et al. Evaluation of zirconia-based posterior single crowns supported by zirconia implants: preliminary results of a prospective multicenter study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016. doi: 10.1111/clr.12842.[19] Tirone F, Salzano S, D'orsi L, et al. Is a high level of total cholesterol a risk factor for dental implants or bone grafting failure? A retrospective cohort study on 227 patients. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2016; 9(1):77-84.[20] Larsen PE,Stronczek MJ,Back FM,et al. Osteointegration of implants in radiated bone with and without adjunctive hyperbaric oxygen. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1993;51:280-287.[21] Jacobsson M, Jonsson A. Dose-response for bone regeneration after single doses of 60Co irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1985; 11:1963.[22] Iwanabe Y, Masaki C, Tamura A, et al. The effect of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on wound healing using scratch assay in epithelial cells. J Prosthodont Res. 2016.[23] Hun SA, Larsen PE. The effect of radiation at the titanium bone interface. J Dent Res. 1990; 69: 291.[24] Summer DR, Turner TM. Effects of radiation on fixation of non-cemented porous-coated implants in a canine model. J Bone Joint Surg. 1990; 72-A: 1527.[25] Khateery S, Waite PD, Lemons JE. The influence of radiation therapy on subperiosteal hydroxyapatite implants in rabbits. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1991;49:730.[26] Razayi R, Niroomand-Rad A, Session RB, et al. Use of dental plants for rehabilitation of mandibulectomy patients prior to radiation therapy. J Oral Implantol. 1995;21(2):138.[27] Wong M,Eulenberger J,Schenk R,et al. Effect of surface topology on the oseointegration of implant materials in trabecular bone. J Biomed Mater Res. 1995;29:1567-1575.[28] 陈海军,张安生,朱孝春,等. 60Co放射及微量元素锌对钛种植体骨融合的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(30): 4800-4804.[29] 陈海军,刘宝林.种植体骨结合过程中骨锌含量的实验研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,1998,14(4):273-274.[30] 陈海军,刘宝林.补锌对种植体骨整合率影响的实验研究[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志,2002,18(4):332-334.[31] 陈海军,林均舟,南福清,等.补锌对种植体固位强度的影响[J].中国临床康复,2004, 8(35):7958-7959.[32] Esfahanizadeh N, Motalebi S, Daneshparvar N, et al. Morphology, proliferation, and gene expression of gingival fibroblasts on Laser-Lok, titanium, and zirconia surfaces. Lasers Med Sci. 2016. [Epub ahead of print][33] Moraschini V, Velloso G, Luz D, et al. Fixed Rehabilitation of Edentulous Mandibles Using 2 to 4 Implants: A Systematic Review. Implant Dent. 2016. [Epub ahead of print][34] Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Patients with Orthopedic Implants Undergoing Dental Procedures: A Review of Clinical Effectiveness, Safety, and Guidelines [Internet]. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health,2016.[35] Nobre Mde A, Maló P, Gonçalves Y, et al. Outcome of dental implants in diabetic patients with and without cardiovascular disease: A 5-year post-loading retrospective study. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2016; 9(1): 87-95.[36] Fage SW, Muris J, Jakobsen SS, et al. Titanium: a review on exposure, release, penetration, allergy, epidemiology, and clinical reactivity. Contact Dermatitis. 2016. doi: 10.1111/cod.12565. [Epub ahead of print][37] Cannizzaro G, Felice P, Loi I, et al. Immediate loading of bimaxillary total fixed prostheses supported by five flapless-placed implantswith machined surfaces: A 6-month follow-up prospective single cohort study. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2016;9(1):67-74.[38] Ribeiro AR, Gemini-Piperni S, Travassos R, et al. Trojan-Like Internalization of Anatase Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles by Human Osteoblast Cells. Sci Rep. 2016;6:23615.[39] Felice P. Posterior jaws rehabilitated with partial prostheses supported by 4.0 x 4.0 mm or by longer implants: One-year post-loading results from a multicenter randomised controlled trial. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2016; 9(1):35-45.[40] Hong SB, Kusnoto B, Kim EJ, et al. Prognostic factors associated with the success rates of posterior orthodontic miniscrew implants: A subgroup meta-analysis. Korean J Orthod. 2016;46(2):111-126. [41] Merli M. Bone augmentation at implant dehiscences and fenestrations. A systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2016;9(1):11-32.[42] van Oirschot BA, Eman RM, Habibovic P, et al. Osteophilic Properties of Bone Implant Surface Modifications in a Cassette Model on a Decorticated Goat Spinal Transverse Process. Acta Biomater. 2016. pii: S1742-7061(16)30133-7.[43] Ciuca S, Badea M, Pozna E, et al. Evaluation of Ag containing hydroxyapatite coatings to the Candida albicans infection. J Microbiol Methods. 2016;125: 12-18. |
.jpg)
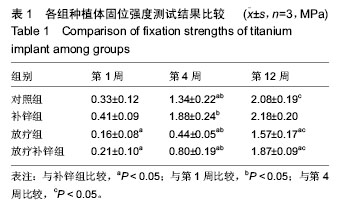
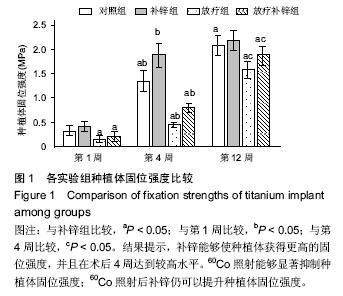
.jpg)