中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (7): 1031-1036.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.07.017
• 组织构建与生物活性因子 tissue construction and bioactive factors • 上一篇 下一篇
退行性腰椎侧凸的炎症反应
孟宁波
- 解放军济南军区第148医院骨科二区,山东省济南市 255300
Inflammation induced by degenerative lumbar scoliosis
Meng Ning-bo
- Second Ward, Department of Orthopedics, the 148th Hospital of Nanjing Military Region, Jinan 255300, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
肿瘤坏死因子:是一种由激活的巨噬细胞产生的能抑制成骨细胞和刺激破骨细胞的细胞因子,能够直接杀伤肿瘤细胞而对正常细胞无明显毒性,是迄今为止所发现的直接杀伤肿瘤作用最强的生物活性因子之一。
白细胞介素1β:主要是由单核巨噬细胞和淋巴细胞分泌产生的一种细胞因子,是临床上发现的第一个白细胞介素因子,具有很强的生物活性。可以介导炎症反应,促进炎症因子的形成,并且也可以通过促进淋巴因子的形成调节免疫反应。
背景:研究显示,伴随着腰椎侧凸的出现机体血清中的各种细胞因子含量会出现异常变化,这与患者发病过程有着密切联系。
目的:监测退行性腰椎侧凸患者发病期间血清中肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β浓度的变化。
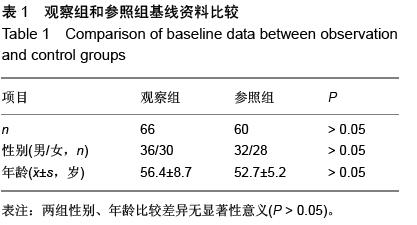
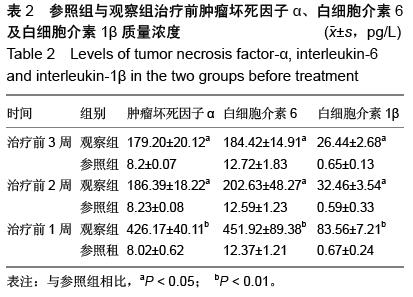
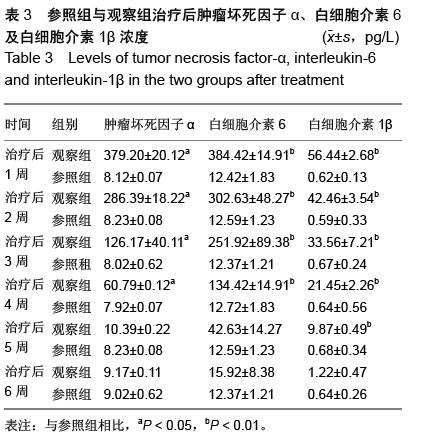
方法:退行性腰椎侧凸患者66例为观察组,腰椎侧凸程度依据Schwab评价系统分为Ⅰ型16例,Ⅱ型32例,Ⅲ型18例。并抽取同期体检健康者60例作为参照组。分别在患者治疗前1,2,3周和相应治疗后第1,2,3,4,5,6周抽取患者的血液进行肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6及白细胞介素1β质量浓度的测定,并对三者的变化规律进行观察。
结果与结论:观察组患者的肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6和白细胞介素1β水平在治疗前3周均呈现升高趋势,治疗后6周呈降低的趋势。肿瘤坏死因子α水平则在入院后的第1,2,3,4周显著高于参照组(P < 0.05);白细胞介素6在入院后的第1,2,3,4,5周均要显著高于参照组(P < 0.05);白细胞介素1β则在入院后第1,2,3,4,5周均显著高于参照组(P < 0.05)。结果表明,白细胞介素6及肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β水平均在治疗前1周到达峰值,随后逐渐下降。肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6及白细胞介素1β的水平变化对患者病情的发展具有重要的评估作用,提示根据细胞因子的变化可以判定炎症反应的进行程度,选择适当的治疗方法。
ORCID: 0000-0002-2540-5085(孟宁波)