| [1] 袁磊,龚济钦,张海霞,等.KA1亚受体在内质网应激致海马神经元死亡中的作用[J].南方医科大学学报,2015,35(2):191-195.
[2] Luoma PV. Elimination of endoplasmic reticulum stress and cardiovascular, type 2 diabetic, and other metabolic diseases. Ann Med. 2013;45(2):194-202.
[3] Mihailidou C, Chatzistamou I, Papavassiliou AG, et al. Improvement of chemotherapeutic drug efficacy by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2015; 22(2):229-238.
[4] Wang H, Wang X, Ke ZJ, et al. Tunicamycin-induced unfolded protein response in the developing mouse brain. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015;283(3):157-167.
[5] Imai T, Kosuge Y, Endo-Umeda K, et al. Protective effect of S-allyl-L-cysteine against endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced neuronal death is mediated by inhibition of calpain. Amino Acids. 2014;46(2):385-393.
[6] Carlisle RE, Brimble E, Werner KE, et al. 4-Phenylbutyrate inhibits tunicamycin-induced acute kidney injury via CHOP/GADD153 repression. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e84663.
[7] Jiang H, Zou J, Zhang H, et al. Unfolded protein response inducers tunicamycin and dithiothreitol promote myeloma cell differentiation mediated by XBP-1. Clin Exp Med. 2015;15(1): 85-96.
[8] Cabral Miranda F, Adão-Novaes J, Hauswirth WW, et al. CHIP, a carboxy terminus HSP-70 interacting protein, prevents cell death induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress in the central nervous system. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015;8:438.
[9] 付政祺.GSK-3β介导了内质网应激诱导的tau蛋白过度磷酸化及大鼠空间记忆障碍[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2010.
[10] Ono Y, Tanaka H, Tsuruma K, et al. A sigma-1 receptor antagonist (NE-100) prevents tunicamycin-induced cell death via GRP78 induction in hippocampal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;434(4):904-909.
[11] Ono Y, Shimazawa M, Ishisaka M, et al. Imipramine protects mouse hippocampus against tunicamycin-induced cell death. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012;696(1-3):83-88.
[12] 袁磊,张海霞,钱诗蕾,等.红藻氨酸诱导内质网应激模型的途径[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(36):5861-5867.
[13] 郭东华,刘湘华,曾杰,等.KA1表达再分布对神经元兴奋毒性的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(2):287-290.
[14] Paxinos G, Franklin KB. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates(Second Edition).New York: Academic Press, 2001:90-110.
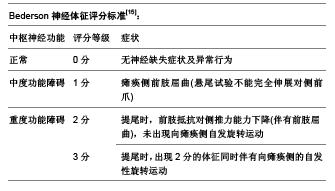
[15] Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Tsuji M, et al. Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination. Stroke. 1986;17(3):472-476.
[16] Chen ZL, Yu H, Yu WM, et al. Proteolytic fragments of laminin promote excitotoxic neurodegeneration by up-regulation of the KA1 subunit of the kainate receptor. J Cell Biol. 2008; 183(7):1299-1313.
[17] 袁磊,龚济钦,张海霞,等.红藻氨酸受体与神经退行性变疾病相关性的研究进展[J].中国临床新医学,2014,7(4):367-371.
[18] 袁磊,徐斌,张海霞,等.以内质网应激浅谈糖尿病及其并发脑病的研究进展[J].解剖学研究,2014,36(5):380-384.
[19] Xia JG, Xu FF, Qu Y, et al. Atorvastatin post-conditioning attenuates myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury via inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-related apoptosis. Shock. 2014;42(4):365-371.
[20] Solanki S, Dube PR, Tano JY, et al. Reduced endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis and impaired unfolded protein response in TRPC3-deficient M1 macrophages. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014;307(6):C521-531.
[21] Schönthal AH. Pharmacological targeting of endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling in cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013;85(5):653-666.
[22] Zhang R, Piao MJ, Kim KC, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling is involved in silver nanoparticles-induced apoptosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012;44(1):224-232.
[23] 高伟娜.孤核受体NR4A家族的表达与内质网应激的关系及其在胰岛β细胞中调控胰岛素基因表达的机制研究[D].济南:山东大学,2014.
[24] 马美娟,李妍,张英梅,等.不同程度内质网应激对巨噬细胞自噬的影响[J].现代生物医学进展,2014,14(2):209-213.
[25] Fu Z, Zou F, Deng H, et al. Estrogen protects SGC7901 cells from endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis by the Akt pathway. Oncol Lett. 2014;7(2):560-564.
[26] Jiang L, Kon N, Li T, et al. Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated activity during tumour suppression. Nature. 2015;520(7545): 57-62.
[27] Wang Y, Feng ZY, Wang J, et al.Somatosensory stimulation suppresses the excitability of pyramidal cells in the hippocampal CA1 region in rats. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9 (11): 1138-1144 |
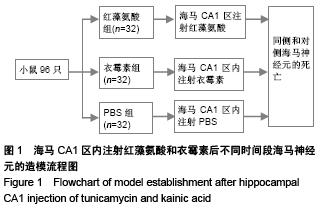
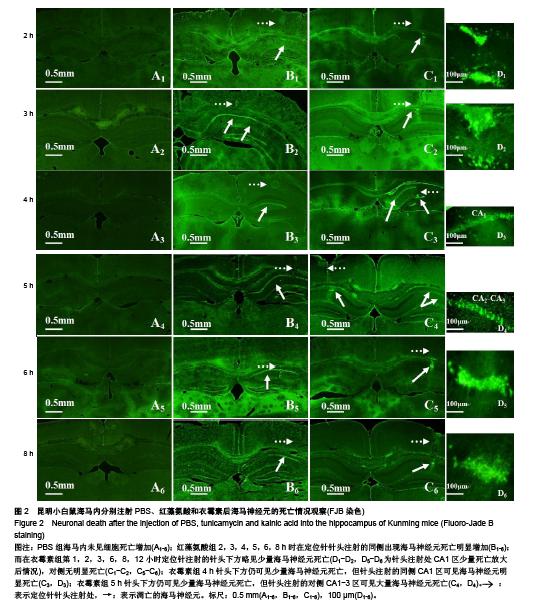
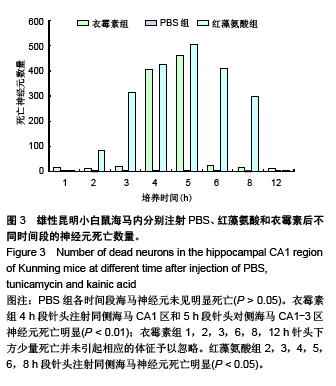
.jpg)