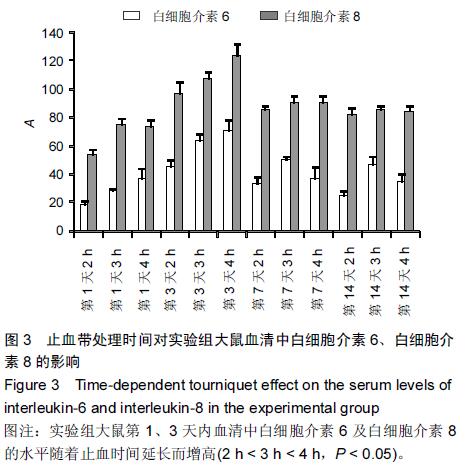
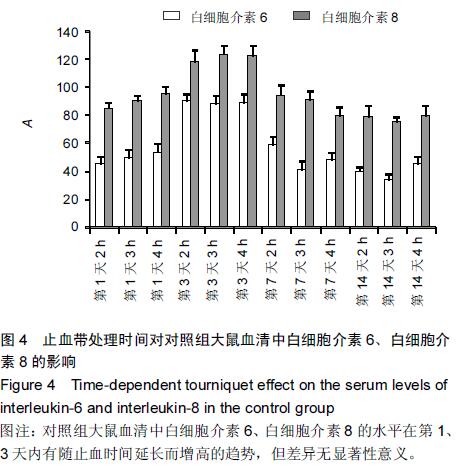
[2] Adembri C,Kastamoniti E,Bertolozzi I,et al.Pulmonary injury follows systemic inflammatory reaction in infrarenal aortic surgery.Crit Care Med.2004;32(5):1170-1177.
[3] Yasa H,Yakut N,Emrecan B,et al.Protective effects of levosimendan and iloprost on lung injury induced by limb ischemia reperfusion:a rabbit model.J Surg Res. 2008; 147(1):138-1342.
[4] Huda R,Solanki D R,Mathru M.Inflammatory and redox responses to ischaemia reperfusion in human skeletal muscle. Clin Sci(Lond).2004;107(5):497-503.
[5] Pedowitz RA. Tourniquet-induced neuromuscular injury. A Recent review of rabbit and clinical experiments.ACTA Orthopaedica Scandinavica.1991:1-33.
[6] Murry C,Jennings R,Reimer K. Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myoeardium. Circulation.1986;1124-1136.
[7] Bushell AJ, Klenerman L, Taylor S, et al.Ischaemic preconditioning of skeletal muscle.1.Protection against the structural changes induced by ischaemia/reperfusion injury. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84(8):1184-1188.
[8] Harkin DW, Barros D'Sa AA, McCallion K,et al. Ischemic preconditioning before lower limb ischemia--reperfusion protects against acute lung injury. J Vasc Surg. 2002;35(6):1264-1273.
[9] Kunkel SL,Remick DG,Stricter RM. Mechanisms that regulate the production and effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Crit Rev Immunol. 1989;9(2):93-117.
[10] Pang CY,Zhong AG,Xu N. Protective effect of ischemic preconditioning (IPC) and adenosine in skeletal muscle ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury.Faseb journal.1993;(7):A494.
[11] 胡跃林,中间季雄,于长隆,等.止血带缺血预处理对大鼠骨骼肌缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用--组织病理学研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2003,22(2):153-155.
[12] Brumback R,Feeback D,Leech R.Rhabdomyolysis in childhood.A primer on normal muscle function and selected metabolic myopathies characterized by disordered energy production. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1992 Aug;39(4):821-858.
[13] Birnbaum Y, Hale SL, Kloner RA. Ischmic preconditioning at adistance: reduction of myocardina infarct size by partial reduction of blood suppy combined with rapid stimulation of the gastroncncemius muscle in the rabbit. Circulation.1997;96(5):1641-1646.
[14] Liem DA , Verdrouw PD , Ploeg H, et al. Sites of action of adenosine in interorgan preconditioning of the heat . Am J Phyisol Heat Cric Physiol.2002;283(1):H29-37.
[15] Hu S, Dong H, Zhang H, et al. Noninvasive limb remote ischemic preconditioning contributes neuroprotective effscts via activation of adenosine Al receptor and redox status after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rate. Brain Res.2012; 1459:81-90.
[16] Tsubote H,Marui A, Eskai J,et al . Remote postconditioning may attenuate ischaemia-receperfusion injury in the murine hindlimb through adenosine receptol activation.Vasc Endovasc Surg.2010;40(6):804-809.
[17] Heusch G, Musiolik J, Kottenberg E, et al. STAT5 activation and cardioprotection by remote ischemic preconditioning in humans. Circulation Res.2011;110(1):111-115.
[18] Masitskaya S, Marina N, Gourine A, et al . Cardioprotection evoked by remote ischaemic preconditioning is critically dependent on the activity of vagal pre-ganglionic. Cardiovasc Res.2012;95(4) :487-494.
[19] Loukogeorgais SP,Williams R, Panagiotidou AT, et al. Transient limb ischemia induces remote preconditioning and remote postcondi-tioning in humans by a K (ATP)-channel dependent mechanism. Circulation.2007;116(12): 1386-1395.
[20] Cai ZP, Parajuli N, Zheng X, et al. Remote ischemic precondial ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice by upregulating interleukin-10. Basic Res Caidnaol.2012;107(4): 277.
[21] Wang Q, Zhang X, Ding Q, et al. Limb remote postconditioning alleviates cerbral reperfusion injury through reactive oxyren species-mediated inhibition of delta protein kinase C in rate. Anesth Analg.2011;113(5):1180-1187.
[22] Peng B, Guo QL, He ZL, et al. remot ischemic postconditioning protecs the brain from global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by up-regulating endothelial nitric oxide synthase through the P13K/Akt pathway . Brain Res. 2012;1445: 92-102.
[23] Zhou Y, Fathali N, Lekic T, et al. remote limb ischemic postcon-ditioning protects agains neonatal hypoxic-ischemic postcon-ditioning protects against neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in rat pups by the opioid receptor/Akt pathway. Stroke.2011;42 (2):439-444.
[24] Abu-Amary M,Yang SY, Quaglia A, et al. The hepatic soluble guanylyl cyclase-eyeclic guanosine monophosphate pathway mediates the protection of remote ischemic preconditioning on the microcircu-lation in live ischemia-reperfusion injury. Thansplantaion.2012;93(9): 880-886.
[25] Czeiger D , Dukhno O, Douvdevani A, et al . Transient extremity ischemia augments CD34+ progenitor cell availability. Stem Cell Rev.2011;7(3):639-645.
[26] Yassin MM, Harkin DW, Barros D'Sa AA, et al.Lower Limb Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Triggers a Systemic Inflammatory Response and Multiple Organ Dysfunction. World J Surg. 2002;26: 115-121.
[27] 金海丰,潘景业,陈洁,等.失血性休克血清对内皮细胞t-PA 和 PAI-1mRNA表达的影响.中国急救复苏与灾害医学杂志, 2011,6(4): 309-312.
[28] Spillert C R, Sun S, PonnuduraiT,et a.l Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induced necrosis: a monocyte-mediated hyper-coagulable effect. J NatlMed Assoc.1995;87: 508-509.
[29] Akyol A,Ulsoy H,Imamoglu M,et al.Does propofol or caffeic acid phenethyl ester prevent lung injury after hindlimb ischaemia reperfusion in ventilated rats.Injury.2006;37(5): 380-387.
[30] Fujita N,Manabe H,Yoshida N. Inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme protects endothelial cell against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury.Biofactors.2000; (4): 257-266.
[31] Loukogeorgais SP,Williams R , Panagiotidou AT, et al. Transient limb ischemia induces remote preconditioning and remote postcondi-tioning in humans by a K (ATP)-channel dependent mechanism. Circulation.2007;116(12):1386-1395.