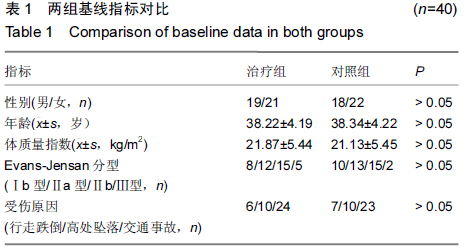
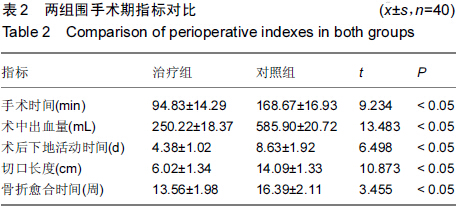
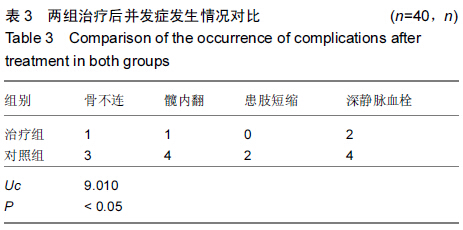
[2] 王东,王起奎,周君琳.股骨近端防旋髓内钉与InterTan髓内钉治疗股骨转子间骨折疗效比较的Meta分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2014,16(8):668-673.
[3] van Embden D, Stollenwerck GA, Koster LA, et al. The stability of fixation of proximal femoral fractures: a radiostereometric analysis. Bone Joint J. 2015;97(3):391-397.
[4] 任军,曾兆辉,佘军,等.微创锁定钢板技术在股骨转子周围骨折治疗中的应用[J].中国乡村医药,2011,18(10):17-18.
[5] 高建生,汤骏.PFNA治疗成人股骨转子周围骨折的疗效分析[J].浙江创伤外科,2010,15(4):463-464.
[6] 李青忠,姚志宏,王君,等.闭合手法复位小切口PFNA治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折临床分析[J].浙江创伤外科,2014,4(11): 584-585.
[7] Konstantinidis L, Grünewald H, Hauschild O, et al. Sliding of the load carrier in third-generation intramedullary nails for proximal femur fractures: An in vitro mechanical comparison study. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2015;229(2):110-114.
[8] 李成付,陈晓艺,边瑜健.PFNA治疗不稳定股骨转子间骨折的临床疗效比较[J].中国现代医生,2014,52(10):135-136.
[9] 冯金海.三种方法治疗股骨粗隆间骨折疗效比较[J].中国实用医刊,2014,41(10):73-75.
[10] 吴国林,陈红卫,张根福,等.PFNA内固定治疗老年股骨转子间骨折38例疗效分析[J].浙江医学,2014,4(12):325-327.
[11] 邓军荣.锁定接骨板治疗股骨转子间骨折42例临床分析[J].临床外科杂志,2011,19(10):728.
[12] 易先宏,潘骏,翁益民,等.加长型股骨近端髓内钉治疗青年股骨转子下骨折[J].中医正骨,2010,22(6):38-39.
[13] Hoshi M, Oebisu N, Takada J, et al. Case report demonstrating effectiveness of sorafenib in multiple lung and bone metastases of renal cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2015; 9(3):1409-1411.
[14] 王小洪.股骨近端髓内钉在股骨转子周围骨折中的应用[J].中医学报,2014,29(1):34-35.
[15] 张敬东,项良碧,祖启明,等.人工股骨头置换治疗高龄股骨转子间不稳定型骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,35(7):6514-6518.
[16] 荣忠美,杨明,荣建辉.股骨近端髓内钉(PFN)治疗股骨转子周围骨折[J].江西医药,2012,47(12):1071-1072.
[17] Choy WS, Kim KJ, Lee SK, et al. Surgical treatment of pathological fractures occurring at the proximal femur. Yonsei Med J. 2015;56(2):460-465.
[18] Wei J, Qin DA, Guo XS. [Curative effect analysis on proximal frmoral nail antirotation for the treatment of femoral intertrochanteric fracture and integrity of lateral trochanteric wall].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2015;28(6):572-575.
[19] Lin YB, Li RB, Xiong GS, et al. Treatment of Middle-up Part Long-segment Femoral Fracture with Long Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation.Orthop Surg. 2015;7(2):138-145.
[20] Nicolaou D, Watson JT. Nailing proximal femur fractures: how to choose starting point and proximal screw configuration. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29 Suppl 4:S22-27.
[21] Shi Y, Li F, Tan W, et al. [Effectiveness comparison of proximal femoral nail anti-rotation and locking compression plate for intertrochanteric fractures with lateral unsubstantial femoral wall in elderly patients]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014;28(10):1199-1203.
[22] Guerra MT, Pasqualin S, Souza MP, et al. Functional recovery of elderly patients with surgically-treated intertrochanteric fractures: preliminary results of a randomised trial comparing the dynamic hip screw and proximal femoral nail techniques. Injury. 2014;45 Suppl 5:S26-31.
[23] Ma KL, Wang X, Luan FJ, et al. Proximal femoral nails antirotation, Gamma nails, and dynamic hip screws for fixation of intertrochanteric fractures of femur: A meta-analysis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100(8):859-866.
[24] Chen Y, Liu S, Lin P, et al. Comparative biomechanical study of reversed less invasive stabilization system and proximal femoral nail antirotation for unstable intertrochanteric fractures. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(23):4124-4129.
[25] Turgut A, Kalenderer Ö, Günayd?n B, et al. Fixation of intertrochanteric femur fractures using Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA) in the lateral decubitus position without a traction table. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2014;48(5): 513-520.
[26] Li M, Wu L, Liu Y, et al. Clinical evaluation of the Asian proximal femur intramedullary nail antirotation system (PFNA-II) for treatment of intertrochanteric fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2014;9:112.
[27] Zhang K, Zhang S, Yang J, et al. Proximal femoral nail vs. dynamic hip screw in treatment of intertrochanteric fractures: a meta-analysis. Med Sci Monit. 2014;20:1628-1633.