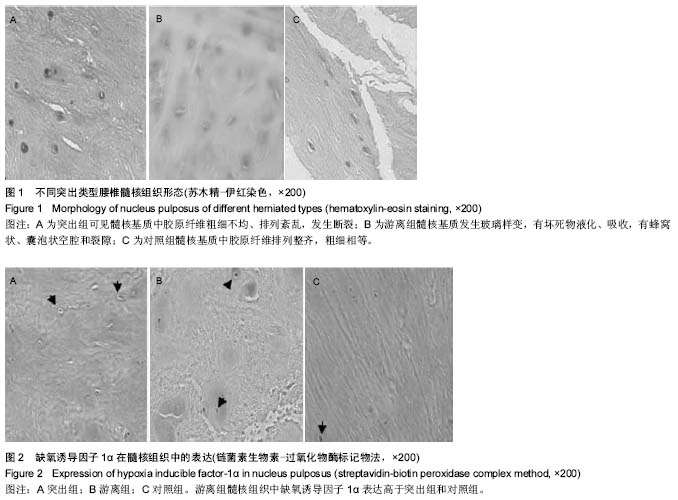
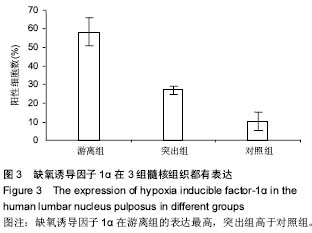
| [1] 郭鑫,皮国富,刘宏建,等.通道下经椎间孔腰椎椎体间融合术治疗单节段腰椎间盘突出症[J].中华实验外科杂志,2015,32(3): 650-652.
[2] Kang SK,Cho NS,Jang S. N-(5-Sulfanyl-idene-4,5-dihydro- l,3,4-thia-diazol-2-yl) acetamide dimethyl sulfoxide disolvate. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Onl- ine. 2012;68(Pt 1):224.
[3] Rodtiguez AG,Rodtiguez-Soto AE,Rurghardt AJ,et al. Morphology of the human vertebral endplate.J Orthop Res. 2012;30(2):280-287.
[4] Jeong JW,Bae MK,Ahn MY,et al.Regulation and destabilization of HIF-1 alpha b- y ARD1-mediated acetylation. Cell.2002;111(5):709-720.
[5] Mabjeesh NJ,Amir S.Hypoxia-inducible factor(HIF) in human tumorigenesis. Hi- stol Histopathol[R].2007;22(5): 559-572.
[6] Ratcliffe PJ.HIF-1 and HIF-2:working alone or together in hypoxia?.J Clin Invest.2007;117(4):862-865.
[7] Apeldoorn AT,Bosmans JE,Ostelo RW,et al.Cost- effectiveness of a classifycat-ion-based system for sub-acute and chronic low back pain.Eur spine.2012;21 (11):1290-1300.
[8] Guo T M,Liu M,Zhang Y G,et al.Association between caspase-9 promoter region poly morphisms and discogenic low back pain.Connect Tissue Res.2011;52(2):133-138.
[9] Anderson DG,Tannoury C.Molecular pathogenic factors in ymptomatic disc degener- ation.Spine J.2005;5(6 Suppl): 260-266.
[10] Sakamoto T,Seiki M.Mint3 enhances the activity of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in macrophages by suppressing the activity of factor inhibiting HIF-1.Biol Chen. 2009;9(2): 1-15.
[11] Lin CW,Haas M,Maher CG,et al.Cost-effectiveness of guideline-endorsed trea- tments for low back pain:a systematic review.Eur Spine.2011;20(12):1024-10 38.
[12] Gassmann M,Chilov D,Wenger RH.Regulation of the hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha. ARNT is not necessary for hypoxic induction of HIF-1 alpha in the nucle- us.Adv Exp Med Biol.2000;475:87-99.
[13] Yang Y,Bai J,Shen R,et al.Polo-like kinase 3 functions as a tumor supperssor and is a negative regulator of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha under hypoxic condit- ions.Cancer Res.2008;68(11):4077-4085.
[14] Singh N,Sharma G,Mishra V.Hypoxia inducible factor-1:its potential role in cerebral ischemia.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2012;32(4):491-507.
[15] Lancaster DE,McNeill LA,McDonough MA,et al.Disruption of dimerization and substrate phosphorylation inhibit factor inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor(FIH) activity. Bio- chem J. 2004;383(pt.3):429-437.
[16] Schaile EV,Windschugl J,Bobkiewicz W,et al. 2-Methoxyestradiol confers neuro- protection and inhibits a maladaptive HIF-1α reponse after traumatic brain inju- ry in mice.J Neurochem.2014;129(6):940-954.
[17] Loboda A,Jozkowicz A,Dulak J.HIF-1 and HIF-2 transcription factors-similar but not identical.Molecules and cells. 2010; 29(5):435-442.
[18] Ramamoorthy P,Shi H.Ischemia induces different levels of hypoxia inducible factor-1α protein expression in interneurons and pyramidal neurons.Acta ne- uropathol Commun.2014;2:51.
[19] Higgins DF,Biju MP,Akai Y,et al.Hypoxic induction of Ctgf is directly mediated by Hif-1.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.2004; 287:F1223-1232.
[20] Marin-Hernandez A,Gallardo-perez JC,Ralph SJ,et al.HIF-1alpha modulates ene- rgy metabolism in cancer cells by inducing overexpression of specific glycolytic isoforms.Mini Rev Med Chem.2009;9(9):1084 -1101 .
[21] Karuppagounder SS,Ratan RR.Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhib- ition:robust new target or another big bust for stroke therapeutics.J Cere Blood Flow Metab. 2012;32(7): 1347-1361.
[22] Singh N,Sharma G,Mishra V.Hypoxia inducible factor-1:its potential role in cerebral ischemia.J Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2012;32(4):491-507.
[23] 韩毅力,程永毅,徐永刚.低氧条件下HIF-1α对HGF表达影响的观察[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志,2012,18(18):1377-1379.
[24] Lando D,Peet DJ,Gorman JJ,et al. FIH-1 is an asparaginyl hydroxyllase enzyme that regulates the transcriptional activity of hypoxia- inducible Factor.Genes Dev. 2002;16(12): 1466-1471.
[25] Carrozza MJ,Utley RT,Wrkman JL,et al. The diverse functions of histone acetyit- ransferase complexes.Trends Genet. 2003; 19(6): 321 -329.
[26] 王俊丰,贾长青,刘洪亮,等.缺氧诱导因子-1α和血管内皮生长因子在突出腰椎间盘中的表达及意义[J].中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志,2008,17(1):65-69.
[27] Bishop T,Gallagher D,Pascual A,et al.Abnormal sympathoadrenal development and systemic hypotension in PHD3-/-mice.Mol Cell Biol.2008;28:3386-3400.
[28] Chandel NS,Simon MC.Hypoxia-inducible factor:roles in development, physiol- ogy, and disease.Cell Death Differ. 2008;15(4):619-620.
[29] Vengellur A,Lapres JJ.The role of hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha in cobalt chl-oride induced cell death in mouse embryonic fibroblasts.Toxicol Sci.2004; 82(2):638-646. |