| [1] Friedenstein AJ, Petrakova KV, Kurolesova AI, et al. Heterotopic of bone marrow. Analysis of precursor cells for osteogenic and hematopoietic tissues. Transplantation. 1968; 6(2):230-247.
[2] Liechty KW, MacKenzie TC, Shaaban AF, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells engraft and demonstrate site-specific differentiation after in utero transplantation in sheep. Nat Med. 2000;6(11):1282-1286.
[3] Reyes M, Lund T, Lenvik T, et al. Purification and ex vivo expansion of postnatal human marrow mesodermal progenitor cells. Blood. 2001;98(9):2615-2625.
[4] Siegel G, Schäfer R, Dazzi F. The immunosuppressive properties of mesenchymal stem cells. Transplantation. 2009; 87(9 Suppl):S45-49.
[5] Bernardo ME, Pagliara D, Locatelli F. Mesenchymal stromal cell therapy: a revolution in Regenerative Medicine. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2012;47(2):164-171.
[6] Pasquinelli G, Tazzari P, Ricci F, et al. Ultrastructural characteristics of human mesenchymal stromal (stem) cells derived from bone marrow and term placenta. Ultrastruct Pathol. 2007;31(1):23-31.
[7] Toyama K, Honmou O, Harada K, et al. Therapeutic benefits of angiogenetic gene-modified human mesenchymal stem cells after cerebral ischemia. Exp Neurol. 2009;216(1):47-55.
[8] Liao W, Xie J, Zhong J, et al. Therapeutic effect of human umbilical cord multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells in a rat model of stroke. Transplantation. 2009;87(3):350-359.
[9] Tang YL, Zhao Q, Qin X, et al. Paracrine action enhances the effects of autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on vascular regeneration in rat model of myocardial infarction. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005;80(1):229-236.
[10] Williams AR, Hare JM. Mesenchymal stem cells: biology, pathophysiology, translational findings, and therapeutic implications for cardiac disease. Circ Res. 2011;109(8): 923-940.
[11] Huang J, Zhang Z, Guo J, et al. Genetic modification of mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing CCR1 increases cell viability, migration, engraftment, and capillary density in the injured myocardium. Circ Res. 2010;106(11):1753-1762.
[12] 苟文丽. 胎儿附属物的形成与功能[A]//妇产科学[M]. 8版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2013:33.
[13] 中华人民共和国国务院.医疗机构管理条例.1994-09-01.
[14] 沙文琼,王自能,王冬菊.人胚胎滋养细胞和胎盘间充质干细胞的分离与纯化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(10): 1833-1837.
[15] 付洪兰.实用电子显微镜技术[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2004.
[16] 沙文琼,王自能,苏放明.人胎盘间充质干细胞雌、孕激素受体的表达[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14 (45):8390-8393.
[17] Kim DH, Yoo KH, Choi KS, et al. Gene expression profile of cytokine and growth factor during differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell. Cytokine. 2005; 31(2):119-126.
[18] Kögler G, Radke TF, Lefort A, et al. Cytokine production and hematopoiesis supporting activity of cord blood-derived unrestricted somatic stem cells. Exp Hematol. 2005;33(5): 573-583.
[19] Liu CH, Hwang SM. Cytokine interactions in mesenchymal stem cells from cord blood. Cytokine. 2005;32(6):270-279.
[20] Majumdar MK, Thiede MA, Haynesworth SE, et al. Human marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) express hematopoietic cytokines and support long-term hematopoiesis when differentiated toward stromal and osteogenic lineages. J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 2000; 9(6):841-848.
[21] Manochantr S, U-pratya Y, Kheolamai P, et al. Immunosuppressive properties of mesenchymal stromal cells derived from amnion, placenta, Wharton's jelly and umbilical cord. Intern Med J. 2013;43(4):430-439.
[22] Hwang JH, Lee MJ, Seok OS, et al. Cytokine expression in placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells in patients with pre-eclampsia and normal pregnancies. Cytokine. 2010;49(1): 95-101.
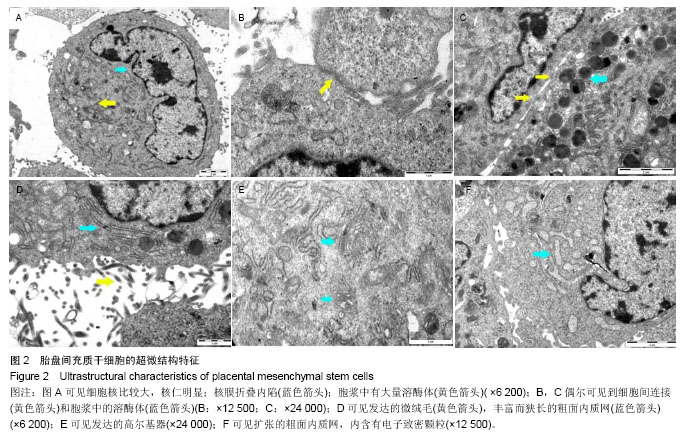
[23] 钟志年,卢国辉,朱少芳,等.人胎盘间充质干细胞的生物学特性及超微结构[J]. 中华生物医学工程杂志, 2011,17(5):416-419.
[24] Settembre C, Fraldi A, Medina DL, et al. Signals from the lysosome: a control centre for cellular clearance and energy metabolism. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14(5):283-296.
[25] Luzio JP, Parkinson MD, Gray SR, et al. The delivery of endocytosed cargo to lysosomes. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009; 37(Pt 5):1019-1021.
[26] Kaushik S, Cuervo AM. Chaperone-mediated autophagy: a unique way to enter the lysosome world. Trends Cell Biol. 2012;22(8):407-417.
[27] Mijaljica D, Prescott M, Devenish RJ. Microautophagy in mammalian cells: revisiting a 40-year-old conundrum. Autophagy. 2011;7(7):673-682.
[28] Verhage M, Toonen RF. Regulated exocytosis: merging ideas on fusing membranes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007;19(4):402- 408.
[29] Chandra A, Barillas S, Suliman A, et al. A novel fluorescence- based cellular permeability assay. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 2007;70(3):329-333.
[30] Geissmann F, Manz MG, Jung S, et al. Development of monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Science. 2010; 327(5966):656-661.
[31] Abbas AK, Lichtman AH. Cellular and Molecular Immunology. 5th ed. Beijing: Pekong University Medial Press. 2005:281- 283.
[32] Stich S, Loch A, Leinhase I, et al. Human periosteum-derived progenitor cells express distinct chemokine receptors and migrate upon stimulation with CCL2, CCL25, CXCL8, CXCL12, and CXCL13. Eur J Cell Biol. 2008;87(6):365-376.
[33] Romieu-Mourez R, François M, Boivin MN, et al. Cytokine modulation of TLR expression and activation in mesenchymal stromal cells leads to a proinflammatory phenotype. J Immunol. 2009;182(12):7963-7973.
[34] Gordon S. Pattern recognition receptors: doubling up for the innate immune response. Cell. 2002;111(7):927-930.
[35] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999; 284(5411):143-147.
[36] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.
[37] Krampera M, Glennie S, Dyson J, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibit the response of naive and memory antigen-specific T cells to their cognate peptide. Blood. 2003;101(9):3722-3729.
[38] Di Nicola M, Carlo-Stella C, Magni M, et al. Human bone marrow stromal cells suppress T-lymphocyte proliferation induced by cellular or nonspecific mitogenic stimuli. Blood. 2002;99(10):3838-3843.
[39] Glennie S, Soeiro I, Dyson PJ, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induce division arrest anergy of activated T cells.Blood. 2005 1;105(7):2821-2827. |
.jpg)
.jpg)