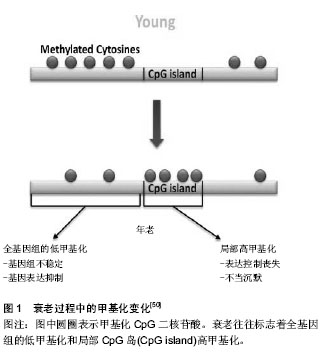
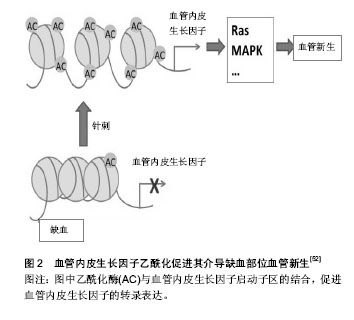
| [1] Ademokun A, Wu YC, Dunn-Walters D. The ageing B cell population: composition and function. Biogerontology. 2010; 11(2):125-137.
[2] Solana R, Tarazona R, Gayoso I, et al. Innate immunosenescence: effect of aging on cells and receptors of the innate immune system in humans. Semin Immunol. 2012; 24(5):331-341.
[3] Hajishengallis G. Too old to fight? Aging and its toll on innate immunity. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2010;25(1):25-37.
[4] Weiskopf D, Weinberger B, Grubeck-Loebenstein B. The aging of the immune system. Transpl Int. 2009;22(11):1041-1050.
[5] Weksler ME, Pawelec G, Franceschi C. Immune therapy for age-related diseases. Trends Immunol. 2009;30(7):344-350.
[6] 骆永珍,张燕华,周荣兴.针灸与免疫[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2002.
[7] Mills KH. Designer adjuvants for enhancing the efficacy of infectious disease and cancer vaccines based on suppression of regulatory T cell induction. Immunol Lett. 2009;122(2):108-111.
[8] Dimitrijevi? M, Stanojevi? S, Kuštrimovi? N, et al. The influence of aging and estradiol to progesterone ratio on rat macrophage phenotypic profile and NO and TNF-α production. Exp Gerontol. 2013;48(11):1243-1254.
[9] Camous X, Pera A, Solana R, et al. NK cells in healthy aging and age-associated diseases. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012; 2012:195956.
[10] Gayoso I, Sanchez-Correa B, Campos C, et al. Immunosenescence of human natural killer cells. J Innate Immun. 2011;3(4):337-343.
[11] Campos C, Pera A, Sanchez-Correa B, et al. Effect of age and CMV on NK cell subpopulations. Exp Gerontol. 2014;54: 130-137.
[12] Solana R, Mariani E. NK and NK/T cells in human senescence. Vaccine. 2000;18(16):1613-1620.
[13] DelaRosa O, Pawelec G, Peralbo E, et al. Immunological biomarkers of ageing in man: changes in both innate and adaptive immunity are associated with health and longevity. Biogerontology. 2006;7(5-6):471-481.
[14] Grubeck-Loebenstein B, Della Bella S, Iorio AM, et al. Immunosenescence and vaccine failure in the elderly. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2009;21(3):201-209.
[15] Nomellini V, Brubaker AL, Mahbub S, et al. Dysregulation of neutrophil CXCR2 and pulmonary endothelial icam-1 promotes age-related pulmonary inflammation. Aging Dis. 2012;3(3):234-247.
[16] Sapey E, Greenwood H, Walton G, et al. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibition restores neutrophil accuracy in the elderly: toward targeted treatments for immunosenescence. Blood. 2014;123(2):239-248.
[17] George AJ, Ritter MA. Thymic involution with ageing: obsolescence or good housekeeping? Immunol Today. 1996; 17(6):267-272.
[18] Mocchegiani E, Giacconi R, Cipriano C, et al. Are zinc-bound metallothionein isoforms (I+II and III) involved in impaired thymulin production and thymic involution during ageing? Immun Ageing. 2004;1(1):5.
[19] Griffith AV, Fallahi M, Nakase H, et al. Spatial mapping of thymic stromal microenvironments reveals unique features influencing T lymphoid differentiation. Immunity. 2009; 31(6): 999-1009.
[20] Chen L, Xiao S, Manley NR. Foxn1 is required to maintain the postnatal thymic microenvironment in a dosage-sensitive manner. Blood. 2009;113(3):567-574.
[21] Gray DH, Seach N, Ueno T, et al. Developmental kinetics, turnover, and stimulatory capacity of thymic epithelial cells. Blood. 2006;108(12):3777-3785.
[22] Lynch HE, Goldberg GL, Chidgey A, et al. Thymic involution and immune reconstitution. Trends Immunol. 2009;30(7): 366-373.
[23] Malaguarnera L, Cristaldi E, Lipari H, et al. Acquired immunity: immunosenescence and physical activity. Eur Rev Aging Phys Act. 2008;5(2):61–68.
[24] Linton PJ, Dorshkind K. Age-related changes in lymphocyte development and function. Nat Immunol. 2004;5(2): 133-139.
[25] Naylor K, Li G, Vallejo AN, et al. The influence of age on T cell generation and TCR diversity. J Immunol. 2005;174(11): 7446-7452.
[26] Nikolich-Zugich J, Slifka MK, Messaoudi I. The many important facets of T-cell repertoire diversity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4(2):123-132.
[27] Richardson BC. Role of DNA methylation in the regulation of cell function: autoimmunity, aging and cancer. J Nutr. 2002; 132(8 Suppl):2401S-2405S.
[28] Mendez S, Reckling SK, Piccirillo CA, et al. Role for CD4(+) CD25(+) regulatory T cells in reactivation of persistent leishmaniasis and control of concomitant immunity. J Exp Med. 2004;200(2):201-210.
[29] Sharma S, Dominguez AL, Lustgarten J. High accumulation of T regulatory cells prevents the activation of immune responses in aged animals. J Immunol. 2006;177(12):8348-8355.
[30] Garg SK, Delaney C, Toubai T, et al. Aging is associated with increased regulatory T-cell function. Aging Cell. 2014;13(3): 441-448.
[31] Gregg R, Smith CM, Clark FJ, et al. The number of human peripheral blood CD4+ CD25high regulatory T cells increases with age. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005;140(3):540-546.
[32] Colonna-Romano G, Bulati M, Aquino A, et al. B cell immunosenescence in the elderly and in centenarians. Rejuvenation Res. 2008;11(2):433-439.
[33] Geiger H, Van Zant G. The aging of lympho-hematopoietic stem cells. Nat Immunol. 2002;3(4):329-333.
[34] Nicoletti C. Antibody protection in aging: influence of idiotypic repertoire and antibody binding activity to a bacterial antigen. Exp Mol Pathol. 1995;62(2):99-108.
[35] Hasler P, Zouali M. Immune receptor signaling, aging, and autoimmunity. Cell Immunol. 2005;233(2):102-108.
[36] 朱梅,金华,孙晓冬,等.针刺“足三里”、“关元”穴区对老年大鼠肝脏内巨噬细胞形态计量学影响[J].中国老年学杂志, 2004, 24(5):454-455.
[37] 朱梅,高洪泉,刘瑞丰,等.针刺“足三里”、“关元”穴区对老年大鼠肝脏内巨噬细胞功能影响的实验研究[J].针灸临床杂志, 2003, 19(6):54-55.
[38] 高希言,王燕.艾灸强壮要穴对衰老小鼠免疫功能的影响[J].河南中医,2005,25(11):24-26.
[39] 李艳梅,宋立中,陈少宗.择时温针灸关元、足三里对老年人超氧化物歧化酶、T细胞亚群的影响[J].辽宁中医杂志, 2014,41(4): 779-781.
[40] Pavão TS, Vianna P, Pillat MM, et al. Acupuncture is effective to attenuate stress and stimulate lymphocyte proliferation in the elderly. Neurosci Lett. 2010;484(1):47-50.
[41] Zhang CY, Yang L, Chen HP, et al. Clinical study on anti-aging action of herbal cake-partition moxibustion. J Acupunct Tuina Sci. 2009,7(1):37-40.
[42] 肖凌,明平红,宁勇,等.针灸调节衰老大鼠对疫苗反应性的实验研究[J].湖北中医药大学学报,2012,14(2):10-12.
[43] Esteller M. The necessity of a human epigenome project. Carcinogenesis. 2006;27(6):1121-1125.
[44] Yano S, Ghosh P, Kusaba H, et al. Effect of promoter methylation on the regulation of IFN-gamma gene during in vitro differentiation of human peripheral blood T cells into a Th2 population. J Immunol. 2003;171(5):2510-2516.
[45] Richardson B. Impact of aging on DNA methylation. Ageing Res Rev. 2003;2(3):245-261.
[46] Bollati V, Schwartz J, Wright R, et al. Decline in genomic DNA methylation through aging in a cohort of elderly subjects. Mech Ageing Dev. 2009;130(4):234-239.
[47] Grolleau-Julius A, Ray D, Yung RL. The role of epigenetics in aging and autoimmunity. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2010; 39(1): 42-50.
[48] Saccani S, Natoli G. Dynamic changes in histone H3 Lys 9 methylation occurring at tightly regulated inducible inflammatory genes. Genes Dev. 2002;16(17):2219-2224.
[49] Salminen A, Huuskonen J, Ojala J, et al. Activation of innate immunity system during aging: NF-kB signaling is the molecular culprit of inflamm-aging. Ageing Res Rev. 2008; 7(2):83-105.
[50] Johnson AA, Akman K, Calimport SR, et al. The role of DNA methylation in aging, rejuvenation, and age-related disease. Rejuvenation Res. 2012;15(5):483-494.
[51] Foulks JM, Parnell KM, Nix RN, et al. Epigenetic drug discovery: targeting DNA methyltransferases. J Biomol Screen. 2012;17(1):2-17.
[52] Wang ZG, Wu JX. DNA methyltransferases: classification, functions and research progress. Yi Chuan. 2009;31(9): 903-912.
[53] Li KK, Li F, Li QS, et al. DNA methylation as a target of epigenetic therapeutics in cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013;13(2):242-247.
[54] Yang X, Lay F, Han H, et al. Targeting DNA methylation for epigenetic therapy. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2010;31(11):536-546.
[55] Leppert S, Matarazzo MR. De novo DNMTs and DNA methylation: novel insights into disease pathogenesis and therapy from epigenomics. Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(11): 1812-1818.
[56] Berletch JB, Andrews LG, Tollefsbol TO. A method to detect DNA methyltransferase I gene transcription in vitro in aging systems. Methods Mol Biol. 2007;371:73-80.
[57] Jin B, Robertson KD. DNA methyltransferases, DNA damage repair, and cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;754:3-29.
[58] Luczak MW, Jagodziński PP. The role of DNA methylation in cancer development. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2006;44(3): 143-154.
[59] 孔叶平.组蛋白乙酰化在艾灸抗大运动量后心肌细胞自由基中的作用机制研究[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2013.
[60] Fu SP, He SY, Xu B, et al. Acupuncture promotes angiogenesis after myocardial ischemia through H3K9 acetylation regulation at VEGF gene. PLoS One. 2014;9(4):e94604.
[61] 项洋.衰老小鼠巨噬细胞microRNA表达及其调控机制研究[D].北京:北京协和医学院,2011.
[62] Bruniquel D, Schwartz RH. Selective, stable demethylation of the interleukin-2 gene enhances transcription by an active process. Nat Immunol. 2003;4(3):235-240.
[63] García-Domínguez P, Dell'aversana C, Alvarez R, et al. Synthetic approaches to DNMT inhibitor SGI-1027 and effects on the U937 leukemia cell line. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013;23(6):1631-1635.
[64] Oike T, Komachi M, Ogiwara H, et al. C646, a selective small molecule inhibitor of histone acetyltransferase p300, radiosensitizes lung cancer cells by enhancing mitotic catastrophe. Radiother Oncol. 2014;111(2):222-227. |