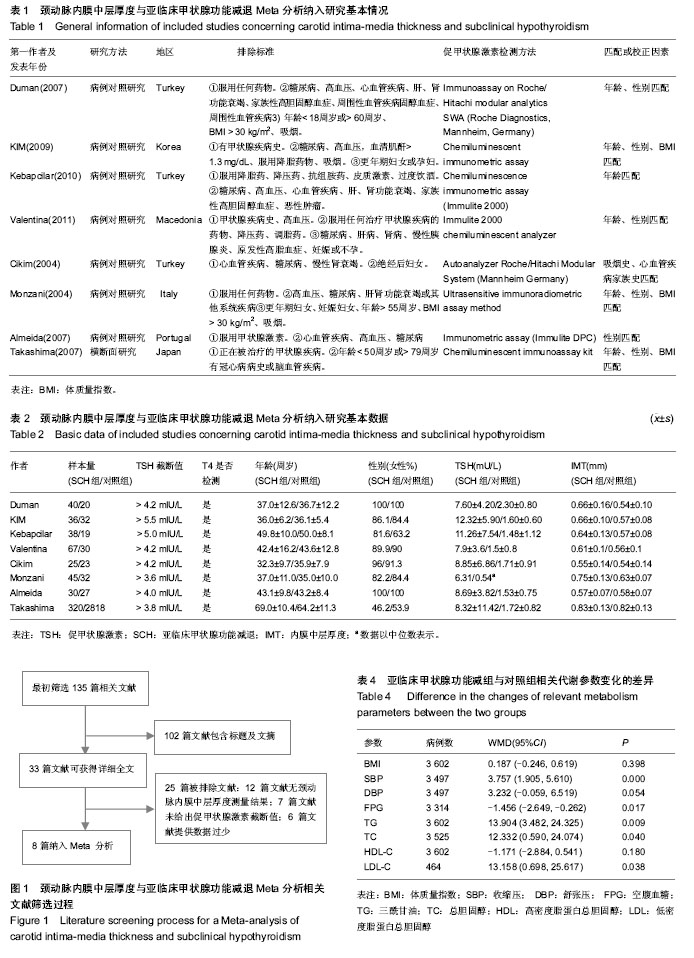
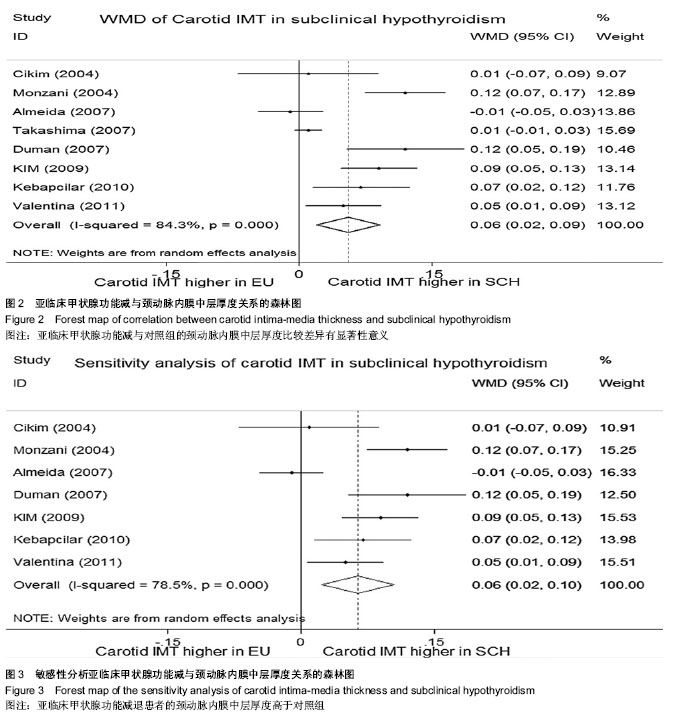
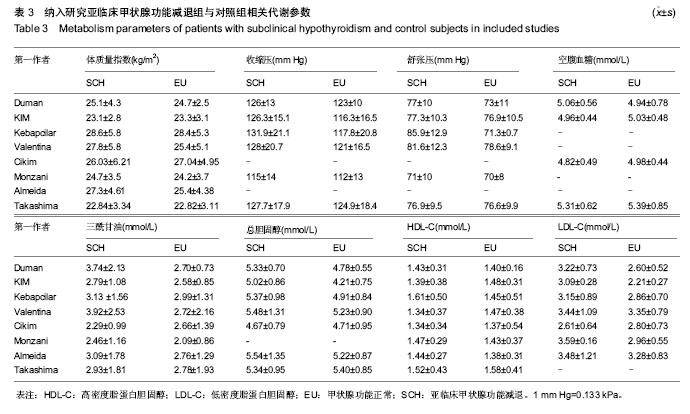
| [1] Helfand M. Screening for subclinical thyroid dysfunction in nonpregnant adults: a summary of the evidence for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force.Ann Intern Med.2004; 140: 128-41.
[2] Canaris GJ, Manowitz NR, Mayor G,et al. The Colorado thyroid disease prevalence study. Arch Intern Med.2000;160: 526-34.
[3] Gharib H, Tuttle RM, Baskin HJ, et al. Subclinical thyroid dysfunction: a joint statement on management from the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists,the American Thyroid Association, and the Endocrine Society.J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2005;90:581-585. discussion 586-587.
[4] Hak AE, Pols HA, Visser TJ, et al. Subclinical hypothy-roidism is an independent risk factor for atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction in elderly women: the Rotterdam Study. Ann Intern Med.2000;132:270-278.
[5] O’Leary DH, Polak JF. Intima-media thickness: a tool for atherosclerosis imaging and event prediction. Am J Cardiol. 2002;90:18L-21L.
[6] Baldassarre D, Amato M, Bondioli A,et al. Carotid artery intima-media thickness measured by ultrasonography in normal clinical practice correlates well with atherosclerosis risk factors. Stroke.2000;31:2426-30.
[7] Lorenz MW, Markus HS, Bots ML, et al. Prediction of clinicalcardiovascular events with carotid intima-media thickness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Circulation. 2007;115:459-467.
[8] Monzani F, Caraccio N, Kozàkowà M, et al. Effect of levothyroxine replacement on lipid profile and intima-media thickness in subclinical hypothyroidism: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004;89: 2099-3106.
[9] Duman D, Demirtunc R, Sahin S, et al. The effects of simvastatin and levothyroxine on intima-media thickness of the carotid artery in female normolipemic patients with subclinical hypothyroidism: a prospective,randomized-controlled study. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2007;8:1007-1011.
[10] Kim SK, Kim SH, Park KS,et al. Regression of the increased common carotid artery-intima media thickness in subclinical hypothyroidism after thyroid hormone replacement. Endocr J.2009;56:753-758.
[11] Kebapcilar L, Comlekci A, Tuncel P, et al. Effect of levothyroxine replacement therapy on paraoxonase-1 and carotid intima-media thickness in subclinical hypothyroidism. Med Sci Monit.2010;16:CR41-7.
[12] Valentina VN, Marijan B, Chedo D,et al. Subclinical hypothyroidism and risk to carotid atherosclerosis. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol.2011;55:475-80.
[13] Cikim AS, Oflaz H, Ozbey N, et al. Evaluation of endothelial function in subclinical hypothyroidism and subclinical hyperthyroidism.Thyroid 2004;14:605-609.
[14] Almeida CA, Teixeira Pde F, Soares DV, et al. Carotid intima-media thickness as a marker of cardiovascular risk in patients with subclinical hypothyroidism.Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol.2007;51:472-477.
[15] Takashima N, Niwa Y, Mannami T, et al. Characterization of subclinical thyroid dysfunction from cardiovascular and metabolic viewpoints: the Suita study. Circ J.2007;71: 191-195.
[16] Huston P, Naylor CD. Health services research: reporting on studies using secondary data sources. CMAJ.1996;155:1697- 709.
[17] Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA.2000;283:2008e12.
[18] Surks MI, Ortiz E, Daniels GH, et al. Subclinical thyroid disease: scientificreview and guidelines for diagnosis and management. JAMA.2004;291:228-38.
[19] Haugen B. When isn’t the TSH normal and why? Clinical implications and causes. Paper presented at the 12th annual meeting of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE). 2003, San Diego, Calif.
[20] Lee S. When is the TSH normal? New criteria for diagnosis and management. Paper presented at the 12th annual meeting of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE).2003, San Diego, Calif.
[21] Ochs N, Auer R, Bauer DC, et al. Meta-analysis: subclinical thyroid dysfunction and the risk for coronary heart disease and mortality. Ann Intern Med. 2008;148:832-45.
[22] Christ-Crain M, Meier C, Guglielmetti M, et al. Elevated C-reactive protein and homocysteine values: cardiovascular risk factors in hypothyroidism? A crosssectional and a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Atherosclerosis. 2003; 166:379-86.
[23] Zhang W, Tian LM, Han Y, et al. Presence of thyrotropin receptor in hepatocytes:not a case of illegitimate transcription. J Cell Mol Med.2009;13:4636e42.
[24] Cai Y, Ren Y, Shi J. Blood pressure levels in patients with subclinical thyroid dysfunction: a meta-analysis of cross-sectional data. Hypertens Res. 2011;34:1098-105.
[25] Gumieniak O, Perlstein TS, Hopkins PN, et al. Thyroid function and blood pressure homeostasis in euthyroid subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:3455-61.
[26] Marcisz C, Jonderko G, Kucharz EJ. Influence of short-time application of a low sodium diet on blood pressure in patients with hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism during therapy. Am J Hypertens.2001;14:995-1002.
[27] Maratou E, Hadjidakis DJ, Kollias A, et al. Studies of insulin resistance in patients with clinical and subclinical hypothyroidism. Eur J Endocrinol. 2009;160:785-790. |