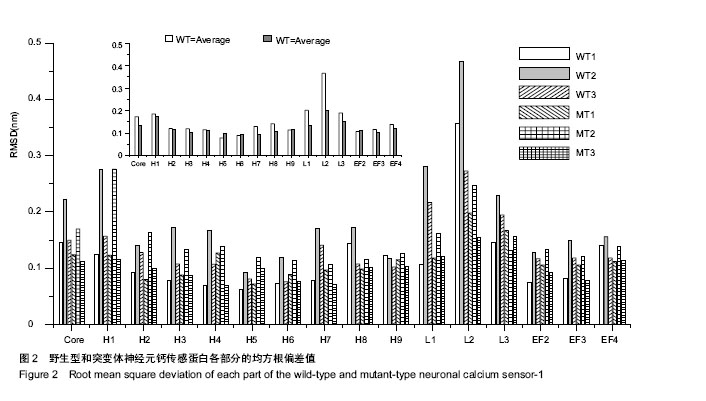
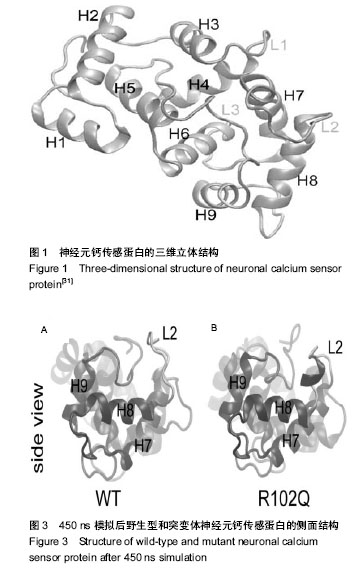
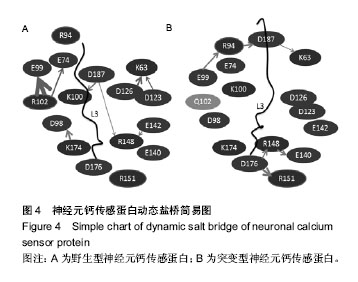
| [1] Nagamatsu LS, Flicker L, Kramer AF, et al. Exercise is medicine, for the body and the brain. Br J Sports Med. 2014; 48: 943-944.
[2] Drumond LE, Mourao FA, Leite HR, et al. Differential effects of swimming training on neuronal calcium sensor-1 expression in rat hippocampus/cortex and in object recognition memory tasks. Brain Res bulletin.2012;88:385-391.
[3] Czurko A, Hirase H, Csicsvari J,et al. Sustained activation of hippocampal pyramidal cells by 'space clamping' in a running wheel.Eur Neurosci. 1999;11:344-352.
[4] Berchtold NC, Chinn G, Chou M, et al. Exercise primes a molecular memory for brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein induction in the rat hippocampus.Neuroscience. 2005; 133:853-861.
[5] Cotman CW, Berchtold NC. Exercise: a behavioral intervention to enhance brain health and plasticity.Trends in neurosciences.2002;25:295-301.
[6] Chodzko-Zajko WJ,Moore KA. Physical fitness and cognitive functioning in aging.Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 1994;22:195-220.
[7] Etgen T, Sander D, Huntgeburth U,et al.Physical activity and incident cognitive impairment in elderly persons: the INVADE study.Archives of internal medicine. 2010;170:186-193.
[8] Geda YE, Roberts RO, Knopman DS,et al. Physical exercise, aging, and mild cognitive impairment: a population-based study. Arch Neurol. 2010;67:80-86.
[9] Haapala EA. Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Motor Skills in Relation to Cognition and Academic Performance in Children-A Review. J Hum Kinet. 2013;36:55-68.
[10] Ardoy DN, Fernandez-Rodriguez JM, Jimenez-Pavon D, et al. A Physical Education trial improves adolescents' cognitive performance and academic achievement: the EDUFIT study. Scandinavian Journal Of Medicine & Science In Sports. 2014; 24: e52-e61.
[11] 朱玉珍,张庆文.神经元钙传感蛋白研究前沿与热点分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(42):6856-6862.
[12] Saab BJ. The synaptic role of neuronal calcium sensor 1 in dentate gyrus plasticity, curiousity and spatial memory, In Department of Molecular Genetics, University of Toronto. 2010.
[13] Piton A, Michaud JL, Peng H, et al. Mutations in the calcium-related gene IL1RAPL1 are associated with autism. Hum Mol Genet.2008;17:3965-3974.
[14] Heidarsson PO, Bjerrum-Bohr IJ, Jensen GA, et al. The C-terminal tail of human neuronal calcium sensor 1 regulates the conformational stability of the Ca2+- activated state.J Mol Biol. 2012;417:51-64.
[15] Handley MT, Lian LY, Haynes LP, et al. Structural and functional deficits in a neuronal calcium sensor-1 mutant identified in a case of autistic spectrum disorder.PLoS One. 2010;5:e10534.
[16] Bellucci L, Corni S, Di Felice R, et al. The Structure of Neuronal Calcium Sensor-1 in SolutionRevealed by Molecular Dynamics Simulations.PLoS One. 2013;8:e74383.
[17] Duan Y, Kollman PA. Pathways to a protein folding intermediate observed in a 1-microsecond simulation in aqueous solution.Science. 1998;282:740-744.
[18] Shrivastava IH, Sansom MS. Simulations of ion permeation through a potassium channel: molecular dynamics of KcsA in a phospholipid bilayer.Biophys J. 2000;78:557-570.
[19] Zhong Q,Jiang Q,Moore PB, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation of a synthetic ion channel.Biophys J.1998;74:3-10.
[20] Hess B,Kutzner C,Van der Spoel D,et al.Erik GROMACS 4: Algorithms for highly efficient, load-balanced, and scalable molecular simulation.J Chem Theory Comput. 2008;4:435-447.
[21] Bjelkmar P, Larsson P, Cuendet MA,et al.Implementation of the CHARMM force field in GROMACS: analysis of protein stability effects from correction maps, virtual interaction sites, and water models.J Chem Theory Comput. 2010;6:459-466
[22] Bussi G, Donadio D,Parrinello M.Canonical sampling through velocity rescaling.J Chem Phys.2007;126:014101.
[23] Parrinello MR.A Polymotphic transitions in single-crystals-a new molecular-dynamics method.J Appl Phys.1981;52:7182-7190.
[24] Hess, B. B., H ; Berendsen, HJC ; Fraaije, JGEM. LINCS:A linear constraint solver for molecular simulations.J Comput Chem.1997;18:1463-1472.
[25] Miyamoto SK, PA. Settle- an analytical version of the shake and rattle algorithm for rigid water models. J. Comput. Chem. 1992; 13: 952-962.
[26] 张占军,李澎,邱蕾,等.神经元钙传感蛋白的研究进展及其在脑缺血中的作用[J].中国药理学通报,2009,25(1):12-15.
[27] Burgoyne RD,Weiss JL.The neuronal calcium sensor family of Ca2+-binding proteins.Biochem J 2001;353:1-12.
[28] Bourne Y,Dannenberg J,Pollmann V,et al. Immunocytochemical localization and crystal structure of human frequenin (neuronal calcium sensor 1).J Biol Chem. 2001;276:11949-11955.
[29] Kumar S, Ma B, Tsai CJ,et al. Contribution of Salt Bridges Toward Protein Thermostability.J Biomol Struc. and Dynamics. 2000;conversation 11:79-85.
[30] Kumar S, Ma B, Tsai CJ,et al. Electrostatic strengths of salt bridges in thermophilic and mesophilic glutamate dehydrogenase monomers.Proteins. 2000;38:368-383.
[31] van Wijk SJ, Melquiond AS, de Vries SJ,et al. Dynamic control of selectivity in the ubiquitination pathway revealed by an ASP to GLU substitution in an intra-molecular salt-bridge network.PLoS Comput Biol. 2012;8:e1002754.
[32] Mohan S, Sheena A, Poulose N, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation studies of GLUT4: substrate-free and substrate-induced dynamics and ATP-mediated glucose transport inhibition.PloS one. 2010;5:e14217.
[33] Chebaro Y, Amal I, Rochel N, et al. Phosphorylation of the retinoic acid receptor alpha induces a mechanical allosteric regulation and changes in internal dynamics.PLoS Comput Biol. 2013;9:e1003012.
[34] Zhu Y, Wu Y, Luo Y, et al.R102Q Mutation Shifts the Salt-bridge Network and Reduces the Structural Flexibility of Human Neuronal Calcium Sensor-1 Protein.Jour Phys Chem B. J Phys Chem B. 2014;118(46):13112-13122. |