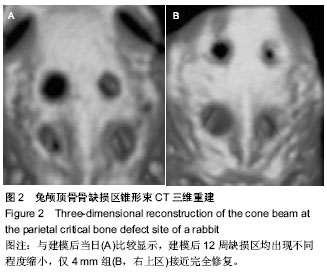
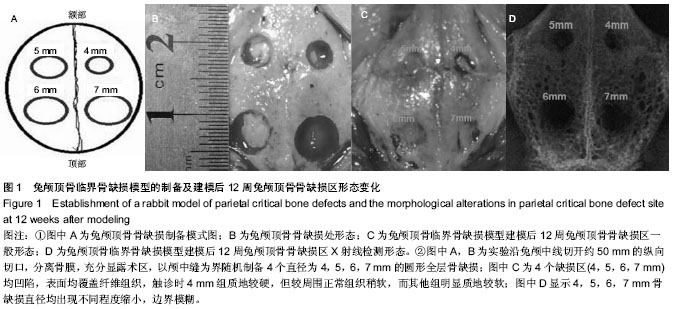
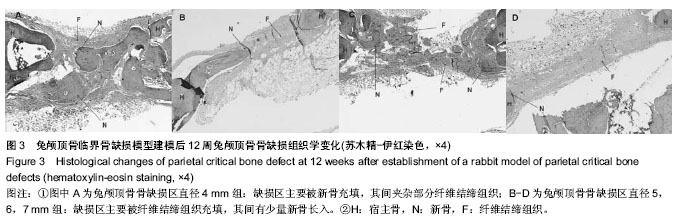
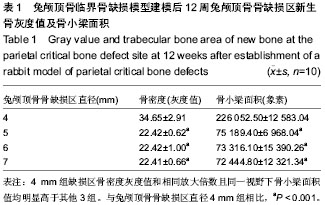
| [1] Chiapasco M, Casentini P, Zaniboni M. Bone augmentation procedures in implant dentistry. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:237-259.
[2] Kessler P, Thorwarth M, Bloch-Birkholz A, et al. Harvesting of bone from the iliac crest-comparison of the anterior and posterior sites. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005;43(1):51-56.
[3] Moore WR, Graves SE, Bain GI. Synthetic bone graft Substitutes. Aust N Z J Surg. 2001;71(6):354-361.
[4] Schmitz JP, Hollinqer JO. The critical size defect as anexperimental model for craniomandibulofacial nonunions. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1986;(205):299-308.
[5] Gosain AK, Song L, Yu P, et al. Osteogenesis in cranial defects: reassessment of the concept of critical size and the expression of TGF-beta isoforms. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000; 106(2):360-371.
[6] Jiang ZQ, Liu HY, Zhang LP, et al. Repair of calvarial defects in rabbits with platelet-rich plasma as the scaffold for carrying bone marrow stromal cells. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2012;113(3):327-333.
[7] Yun JH, Yoo JH, Choi SH, et al. Synergistic effect of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and platelet-rich plasma on bone regeneration of calvarial defects in rabbits. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2012;9(1):17-23.
[8] Borie E, FuentesR, Del Sol M, et al. The influence of FDBA and autogenous bone particles on regeneration of calvaria defects in the rabbit: a pilot study. Ann Anat. 2011;193(5): 412-417.
[9] Lin CY, Chang YH, Kao CY, et al. Augmented healing of critical-size calvarial defects by baculovirus-engineered MSCs that persistently express growth factors. Biomaterials. 2012;33(14):3682-3692.
[10] Lin CY, ChangYH, Li KC, et al. The use of ASCs engineered to express BMP2 or TGF-b3 within scaffold constructs to promote calvarial bone repair. Biomaterials. 2013;34(37): 9401-9412.
[11] Naitoa Y, Terukina T, Gallic S, et al. The effect of simvastatin-loaded polymeric microspheres in a critical size bone defect in the rabbit calvaria. Int J Pharm. 2014; 461(1-2): 157-162.
[12] El Backly RM, Zaky SH, Canciani B, et al. Platelet rich plasma enhances osteoconductive properties of a hydroxyapatite-β-tricalcium phosphate scaffold (Skelite ) for late healing of critical size rabbit calvarial defects. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2013.
[13] Fok TC, Jan A, Peel SA, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen results in increased vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) protein expression in rabbit calvarial critical-sized defects. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008;105(4): 417-422.
[14] Tuusa SM, Peltola MJ, Tirri T, et al. Reconstruction of critical size calvarial bone defects in rabbits with glass-fiber-reinforced composite with bioactive glass granule coating. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2008;84(2): 510-519.
[15] Li G, Wang X, Cao J, et al. Coculture of peripheral blood CD34+ cell and mesenchymal stem cell sheets increase the formation of bone in calvarial critical-size defects in rabbits. Br J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2014;52(2):134-139.
[16] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30.
[17] Rapp SJ, Jones DC, Gerety P, et al. Repairing critical-sized rat calvarial defects with progenitor cell-seeded acellularperiosteum: a novel biomimetic scaffold. Surgery. 2012;152(4):595-605.
[18] Amorosa LF, Lee CH, Aydemir AB, et al. Physiologic load-bearing characteristics of autografts, allografts, and polymer-based scaffolds in a critical sized segmental defect of long bone: an experimental study. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8: 1637-1643.
[19] Chatterjea A, van der Stok J, Danoux CB, et al. Inflammatory response and bone healing capacity of two porous calcium phosphate ceramics in critical size cortical bone defects. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(5):1399-1407.
[20] Pang L, Hao W, Jiang M, et al. Bony defect repair in rabbit using hybrid rapid prototyping polylactic-co-glycolic acid/β-tricalciumphosphate collagen I/apatite scaffold and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Indian J Orthop. 2013;47(4):388-394.
[21] Zhang X, Xu M, Song L, et al. Effects of compatibility of deproteinized antler cancellous bone with various bioactive factors on their osteogenic potential. Biomaterials. 2013; 34(36):9103-9114.
[22] Yang P, Huang X, Wang C, et al. Repair of bone defects using a new biomimetic construction fabricated by adipose-derived stem cells, collagen I, and porous beta-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2013;238(12):1331- 1343.
[23] Kang SH, Chung YG, Oh IH, et al. Bone regeneration potential of allogeneic or autogeneic mesenchymal stem cells loaded onto cancellous bone granules in a rabbit radial defect model. Cell Tissue Res. 2014;355(1):81-88.
[24] Bi L, Cheng W, Fan H, et al. Reconstruction of goat tibial defects using an injectable tricalcium phosphate/chitosan in combination with autologous platelet-rich plasma. Biomaterials. 2010;31(12):3201-3211.
[25] Berner A, Reichert JC, Woodruff MA, et al. Autologous vs. allogenic mesenchymal progenitor cells for the reconstruction of critical sized segmental tibial bone defects in aged sheep. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(8):7874-7884.
[26] Liu T, Wu G, Wismeijer D, et al. Deproteinized bovine bone functionalized with the slow delivery of BMP-2 for the repair of critical-sized bone defects in sheep. Bone. 2013;56(1): 110-118.
[27] Bergmann CJ, Odekerken JC, Welting TJ, et al. Calcium phosphate based three-dimensional cold plotted bone scaffolds for critical size bone defects. Biomed Res Int. 2014; 2014:852610.
[28] Wehrhan F, Amann K, Molenberg A, et al. Critical size defect regeneration using PEG-mediated BMP-2 gene delivery and the use of cell occlusive barrier membranes–the osteopromotive principle revisited. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2013; 24(8):910-920.
[29] Schubert T, Lafont S, Beaurin G, et al.Critical size bone defect reconstruction by an autologous 3D osteogenic-like tissue derived from differentiated adipose MSCs. Biomaterials. 2013; 34(18):4428-4438.
[30] Asamura S, Mochizuki Y, Yamamoto M, et al. Bone regeneration using a bone morphogenetic protein-2 saturated slow-release gelatin hydrogel sheet: evaluation in a canine orbital floor fracture model. Ann Plast Surg. 2010;64(4): 496-502.
[31] Chiu HC, Chiang CY, Tu HP, et al. Effects of bone morphogenetic protein-6 on periodontal wound healing/regeneration in supraalveolar periodontal defects in dogs. J Clin Periodontol. 2013;40(6):624-630.
[32] Lee JS, Kim YW, Jung UW, et al. Bone regeneration and collagen fiber orientation around calcium phosphate-coated implants with machined or rough surfaces: a short-term histomorphometric study in dog mandibles. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2013;28(5):1395-1402.
[33] Choi S, Liu IL, Yamamoto K, et al. Implantation of tetrapod-shaped granular artificial bones or β-tricalcium phosphate granules in a canine large bone-defect model. J Vet Med Sci. 2014;76(2):229-235.
[34] Seeherman HJ, Li XJ, Smith E, et al. rhBMP-2/calcium phosphate matrix induces bone formation while limiting transient bone resorption in a nonhuman primate core defect model. J Bone Joint surg Am. 2012;94(19):1765-1776.
[35] Schlegel KA, Lang FJ, DonathK, et al. The monocortical critical size bone defect as an alternative experimental model in testing bone substitute materials. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;102(1):7-13.
[36] Hollinger JO, Kleinschmidt JC. The critical size defect as an experimental model to test bone repair materials. J Craniofac Surg. 1990;1(1):60-68.
[37] Lee HE, Kim JY, Kweon HY, et al. A combination graft of low-molecular-weight silk fibroin with Choukroun platelet-rich fibrin for rabbit calvarialdefect. OralSurg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010;109(5):e33-e38.
[38] Dumas JE, Brown Baer PB, Prieto EM, et al. Injectable reactive biocomposites for bone healing in critical-size rabbit calvarial defects. Biomed Mater. 2012;7(2):024112.
[39] Liu Y, Lu Y, TianX, et al. Segmental bone regeneration using an rhBMP-2-loaded gelatin/nanohydroxyapatite/fibrin scaffold in a rabbit model. Biomaterials. 2009;30(31):6276-6285.
[40] Humber CC, Sandor GK, Davis JM, et al. Bone healing with an in situ–formed bioresorbable polyethylene glycol hydrogel membrane in rabbit calvarial defects. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010;109(3):372-384.
[41] Pripatnanont P, Nuntanaranont T, Vongvatcharanon S, et al. The primacy of platelet-rich fibrin on bone regeneration of various grafts in rabbit’s calvarial defects. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2013;41(8):e191-200.
[42] Biguetti CC, Filho EJ, de Andrade Holgado L, et al. Effect of low-level laser therapy on intramembranous and endochondral autogenous bone grafts healing. Microse Res Tech. 2012;75(9):1237-1244.
[43] Guo Z, Iku S, Mu L, et al. Implantation with new three-dimensional porous titanium web for treatment of parietal bone defect in rabbit. Artif Organs. 2013;37(7): 623-628. |