| [1] Abdallah BM, Kassem M. Human mesenchymal stem cells: from basic biology to clinical applications. Basic Biol. 2008; 15(5):109-116.
[2] Le Blanc K, Tammik C, Sundberg B, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit and stimulate mixed lymphocyte cultures and mitogenic responses independently of the major histocompatibility system. Scand J Immunol.2003;57(1) : 11-20.
[3] 郭璇,霍然,吕仁荣,等.兔骨髓间充质干细胞培养及向成软骨细胞的诱导分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(6):963-966.
[4] Gaiba S, França LP, França JP, et al. Characterization of human adipose-derived stem cells. Acta Cir Bras. 2012;27(7):471-476.
[5] 李宝军,邓展生,高嵩涛,等.脂肪干细胞向软骨细胞诱导分化能力的研究[J].中国现代医学杂志, 2010,20(4):505-514.
[6] 吴家昌,杨彤涛,许啸,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞体外向软骨细胞分化的实验研究[J] 医学研究生学报,2010,23(2)128-132.
[7] 江逊,段小红,狄静芳,等.体外培养人鼻中隔软骨细胞合成硫酸糖胺多糖的检测[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008, 12(46): 9041-9044.
[8] 李卿,刘伟,夏万尧,等.爱茜蓝法检测组织工程化软骨及软骨细胞中蛋白聚糖的含量[J].中华实验外科杂志,2003,20(1):89.
[9] Cavallo C, Cuomo C, Fantini S. Comparison of alternative mesenchymal stem cell sources for cell banking and musculoskeletal advanced therapies. J Cell Biochem. 2011; 112(5): 1418-1430.
[10] Pittenger MF, Maekay AM, Beek SC, et al.Multilineage potential of adult human mesenehymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.
[11] Zohar R,Sodek J,McCulloch CA.Characterization of stromal progenitor cells enriched by flow cytometry. Blood.1997; 90(9):3471.
[12] 徐鹏,舒畅,赵子义,等.免疫磁珠法分离纯化骨髓间充质干细胞及向神经细胞定向分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007, 11(20):3872-3875.
[13] Krinner A,Zscharnack M,Bader A,et al.Impact of oxygen environment on mesenchymal stem cell expansion and chondrogenic differentiation. Cell Prolif.2009;42:471-484.
[14] 赵林,冯智慧,焦淑贤,等.全骨髓贴壁法分离培养大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞及其生物学特性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(32):5923-5927
[15] Boiret N, Rapatel C, Veyrat-Masson R, et al. Characterization of nonexpanded mesenchymal progenitor cells from normal adult human bone marrow. Exp Hematol. 2005;33:219-225.
[16] Maijenburg MW, Kleijer M, Vermeul K, et al. The composition of the mesenchymal stromal cell compartment in human bone marrow changes during development and aging. Haematologica. 2012;97(2):179-183.
[17] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy.2006;8(4):315-317.
[18] Huang CY, Hagar KL, Frost LE, et al. Effects of Cyclic Compressive Loading on Chondrogenesis of Rabbit Bone-Marrow Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells. 2004;22(3):313-323.
[19] Zscharnack M, Poesel C, Galle J, et al. Low oxygen expansion improves subsequent chondrogenesis of ovine bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in collagen type I hydrogel. Cells Tissues Organs. 2009;190(2):81-93.
[20] Linkhart TA, Mohan S, Baylink DJ. Growth factors for bone growth and repair: IGF, TGF-β and BMP. Bone. 1996;19(1): S1-S12.
[21] Phornphutkul C, Wu KY, Yang X, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I signaling is modified during chondrocyte differentiation. Endocrinol. 2004;183(3): 477-486.
[22] Schmidt MB, Chen EH, Lynch SE. A review of the effects of insulin-like growth factor and platelet derived growth factor on in vivo cartilage healing and repair. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006;14(5):403-412.
[23] Park H, Temenoff JS, Tabata Y, et al. Injectable biodegradable hydrogel composites for rabbit marrow mesenchymal stem cell and growth factor delivery for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2007;28:3217-3227.
[24] 俞猛,于方,付胜良.兔骨髓间充质干细胞体外培养定向诱导分化为软骨细胞[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(27): 4951-4954.
[25] Bi X,Yang X,Bostrom MP,et al. Fourier transform infrared imaging spectroscopy investigations in the pathogenesis and repair of cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006; 1758(7): 934-941.
[26] Johnstone B, Yoo JU. Autologous mesenchymal progenitor cells in articular cartilage repair. Clin Orthop. 1999;367(10) :156.
[27] Sasano Y,Mizoguchi I,Kagayama M,et al. Distribution of type I collagen, type II collagen and PNA binding glycoconjugates during chondrogenesis of three distinct embryonic cartilages. Anat Embroyol. 1992;186(3):205-213.
[28] Schmitz N, Laverty S, Kraus V, et al. Basic methods in histopathology of joint tissues. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010; 18 (3): S113-116.
[29] Sridharan G, Shankar AA. Toluidine blue: A review of its chemistry and clinical utility. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2012; 16(2): 251-255.
[30] 张波,杨述华,张宇坤,等. CDMP-1 促进成人骨髓间充质干细胞成软骨分化的研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011, 26(3): 217-220.
[31] 周静萍,陶德韬,施六霞.兔骨髓间充质干细胞体外软骨向诱导的实验研究[J].皖南医学院学报,2008,27 (1):9-15.
[32] Tang X, Sheng L, Xie F, et al. Differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells into chondrocytes using chondrocyte extract. Mol Med Report. 2012;6(4): 745-749.
[33] 李丽艳,黄金中,杜江. 转化生长因子β1诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨细胞分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(1): 38-41.
[34] 寇建强,王昌耀,王英振.外源性透明质酸对兔骨髓间充质干细胞定向分化为软骨细胞的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(3):381-385.
[35] 张清林,吕惠成,吴一民.转化生长因子β1 联合骨形态发生蛋白2 诱导骨髓间充质干细胞体外向软骨细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(24):4371-4375.
[36] 李中华,栾保华.体外诱导兔骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨细胞分化的实验研究[J].山东大学学报:医学版,2008,46(2):159-162.
[37] 尹其翔,沈铁城,黄永辉.人骨髓间充质干细胞体外成软骨诱导研究[J].江苏大学学报:医学版,2008,18(2):118-121.
[38] 吕晶,柯杰,王琳,等.与软骨细胞共培养和条件培养液诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨细胞分化的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(19) :3421-3426. |
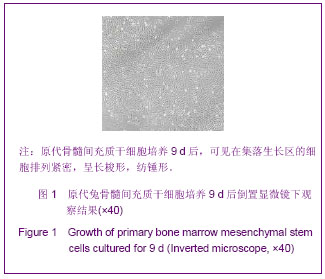
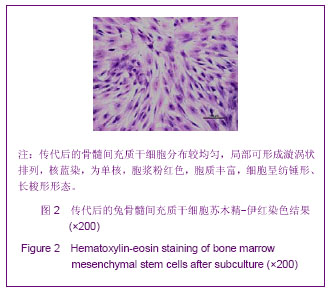

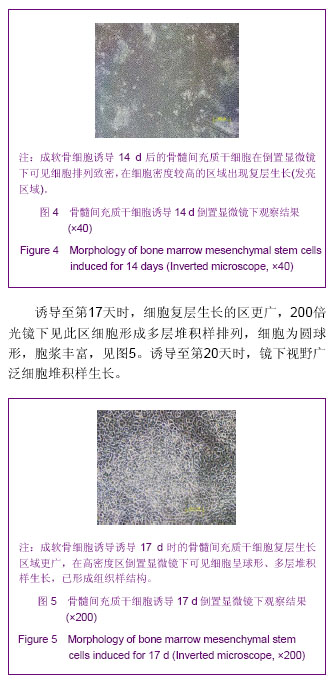
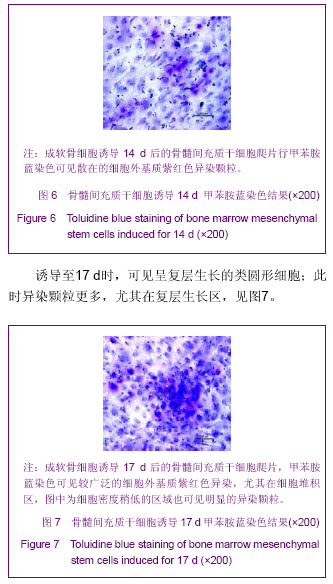

.jpg)