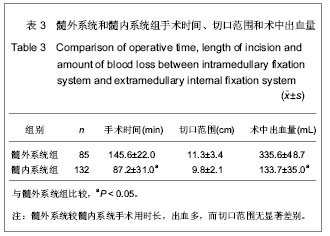
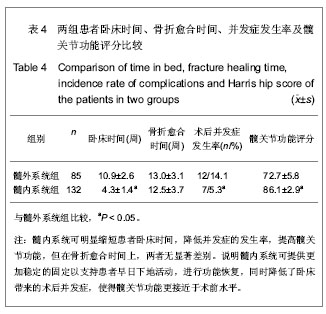
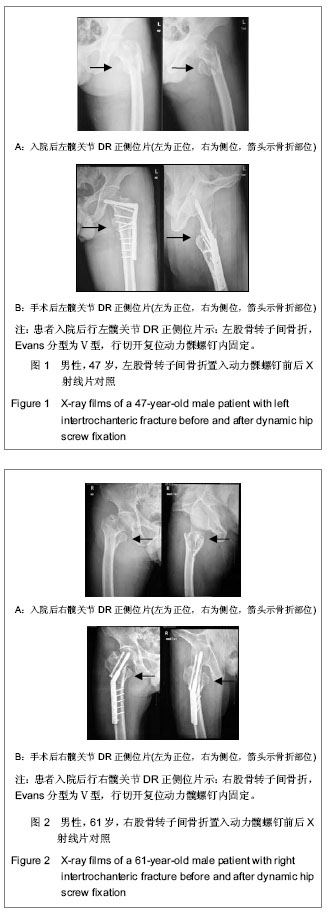
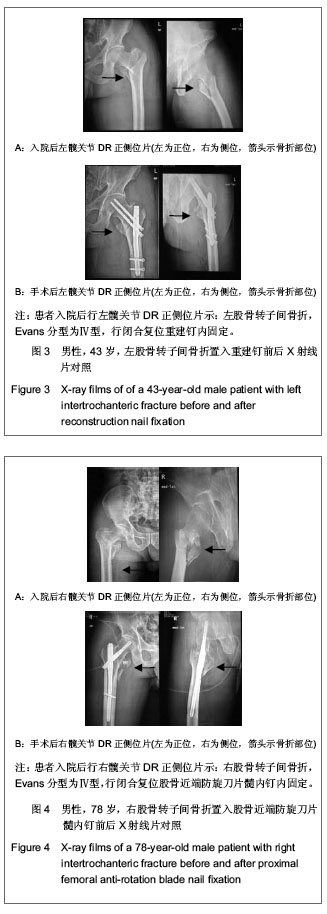
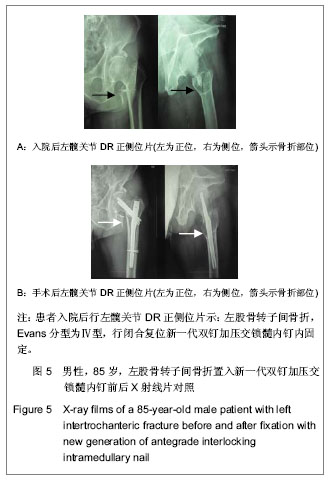
| [1] 危杰.股骨转子间骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2004,6(5):554- 557.[2] 梅浩,袁艾东,李文锐.股骨转子间骨折治疗的研究现状[J].中华创伤杂志,2012,28(5):419-421 .[3] 杨惠林,王根林.股骨转子间骨折治疗方法的选择[J].中华创伤杂志,2012,28(5):385-387 .[4] 胥少汀,葛宝丰,徐印坎.实用骨科学[M].3版.北京:人民军医出版社,2005:710-711.[5] 邱贵兴,戴尅戎.骨科手术学(上册)[M]. 3版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2010:313.[6] Maxwell MJ, Moran CG, Moppett IK.Development and validation of a preoperative scoring system to predict 30 day mortality in patients undergoing hip fracture surgery.Br J Anaesth. 2008;101(4):511-517. [7] Norvell DC,王簕,杨云峰.闭合性髋部骨折或长骨骨折围手术期抗生素预防性应用的疗效分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2009, 11(11): 1072-1078.[8] 孙可. 抗生素在骨科围手术期的预防性应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(19):1473-1475.[9] 林金矿,李毅中,俞海明,等.利伐沙班预防老年人髋部骨折术后下肢深静脉血栓形成的研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2011,13(9): 885-887.[10] 中华医学会骨科学分会创伤骨科学组.中国骨科创伤患者围手术期静脉血栓栓塞症预防的专家共识[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2012,14(6):461-463.[11] 焦竞,黄玉成,李涛,等.不同内固定方式结合康复训练治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折患者的疗效观察[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志, 2012,34(4):300-302.[12] 林石明,郑玉堂,陈联源,等.DCS治疗股骨粗隆间不稳定骨折36例[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2005,20(11):778.[13] 谢瑞卿,张云飞,牛滕峰,等. 动力髁螺钉治疗不稳定性股骨粗隆间骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2006,21(1):66-67.[14] 张宏宇,魏春生.DHS与DCS治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折体会[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2008,23(10):868-869.[15] 童松林,高益斌,陆文杰,等.微创动力髋螺钉与动力髋螺钉治疗高龄粉碎性股骨转子间骨折的疗效比较[J].中华创伤杂志,2010, 26(3):231-233.[16] 兰玉平,殷光义,钟风林,等.股骨重建钉治疗股骨干合并同侧股骨转子周围骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2006,8(7):688-689.[17] 张朝,滕云升,郭永明,等.股骨重建钉治疗股骨不稳定粗隆间骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2005,20(10):699-700.[18] 陈雁西,梅炯,毕刚,等.PFNA治疗股骨转子间伴或不伴外侧壁骨折的疗效分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,32(7):614-620.[19] 唐佩福,姚琦,黄鹏,等.股骨近端髓内钉-螺旋刀片治疗高龄骨质疏松性股骨转子间骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2007, 9(7): 622-624.[20] 洪全明,王平,刘军,等.DHS与Intertan髓内钉治疗股骨粗隆间骨折疗效分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(4):311-313.[21] 蒋恺,秦涛,麻文谦,等.PFNA-Ⅱ及InterTan系统治疗股骨粗隆间骨折疗效评价[J].实用骨科杂志,2012,18(2):123-126.[22] Harris WH.Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969;51(4):737-755.[23] 梁吉华,史源欣,邵伟忠,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉与动力髋螺钉治疗股骨转子间骨折的疗效比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2011, 13(9): 888-890.[24] 方大标,王秋根. 95° DCS治疗股骨粗隆间及粗隆下粉碎性不稳定骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2005,20(8):518-520.[25] 顾军,王明海,唐坚,等.多功能股骨近端重建钉治疗老年人股骨粗隆间骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2008,23(8):638-640.[26] 刘贵明,孙德毅.闭合复位股骨重建钉治疗老年股骨粗隆下骨折[J].长治医学院学报,2011,25(1):34-36.[27] 陈洪强,戴颖,赵滨,等.股骨重建钉治疗股骨不稳定粗隆间骨折39例分析[J].局解手术学杂志,2010,19(6):523.[28] 王瑞,孔晓川,柳伟,等.微创短重建钉内固定治疗老年股骨转子间骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2010,13(1):69-70.[29] 俞光荣,王树青,饶志涛,等.防旋股骨近端髓内钉治疗不稳定性转子间骨折33例[J].中华创伤杂志,2007,23(2):83-86.[30] 高翔.股骨近端防旋髓内钉微创治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效观察[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(16):1463-1466.[31] 李慧武,孙月华,史定伟,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗老年股骨转子间骨折112例[J].中华创伤杂志, 2011,27(11):990-994.[32] 李玉茂,赵勇,李平生,等.股骨近端防旋髓内针(PFNA)治疗老年骨质疏松性股骨粗隆周围骨折[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究, 2011,8(3):53-55.[33] 曾展鹏,苏博源,黄学员,等.微创股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗股骨转子间骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2008,10(4):309-312. [34] 汤欣,刘谟震,于利,等. 新一代髓内钉InterTAN在股骨转子间骨折治疗中的应用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2010,12(9):814-818 .[35] 张巍,罗从风,曾炳芳.髓内钉INTERTAN治疗股骨近端骨折的回顾性分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2010,16(10):731-734.[36] 周利均,屠文华,李杭.双钉加压交锁髓内钉在高龄股骨粗隆间骨折中的应用[J].浙江创伤外科,2012,17(2):185-186.[37] 张培训,党育,薛峰,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗股骨转子间骨折中显性和隐性失血量分析[J].中华创伤杂志,2011,27(9): 755-788.[38] 冯刚,潘志军,叶有晨.股骨转子间骨折围手术期隐性失血的比较研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,32(7):648-653. |