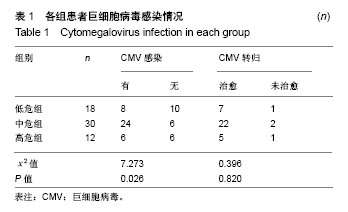
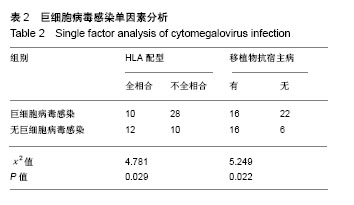
| [1] Goldstein G, Rutenberg TF, Mendelovich SL, et al. The role of immunoglobulin prophylaxis for prevention of cytomegalovirus infection in pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2017;64(7):e26420.[2] Rustia E, Violago L, Jin Z, et al. Risk Factors and Utility of a Risk-Based Algorithm for Monitoring Cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr Virus, and Adenovirus Infections in Pediatric Recipients after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016;22(9): 1646-1653.[3] Borchers S, Luther S, Lips U, et al. Tetramer monitoring to assess risk factors for recurrent cytomegalovirus reactivation and reconstitution of antiviral immunity post allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Transpl Infect Dis. 2011;13(3):222-236.[4] Robin C, Hémery F, Dindorf C, et al. Economic burden of preemptive treatment of CMV infection after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a retrospective study of 208 consecutive patients. BMC Infect Dis. 2017;17(1):747.[5] 曹伟杰,万鼎铭,李丽,等.异基因造血干细胞移植后巨细胞病毒感染和抢先治疗临床研究[J].中国实验血液学杂志, 2016,24(4): 1143-1148. [6] 卢岳,吴彤,曹星玉,等.抢先治疗减少异基因造血干细胞移植后早期巨细胞病毒疾病的临床研究[J].临床血液学杂志, 2011,24(11): 655-661.[7] 李乐,王昱,闫晨.等.异基因造血干细胞移植后低载量巨细胞病毒血症抢先治疗时机的临床研究[J].中华内科杂志, 2018,57(3): 191-195.[8] 王晓宁,张梅,贺鹏程,等.异基因造血干细胞移植中巨细胞病毒潜伏感染的防治[J].临床血液学杂志,2013,26(5):298-304.[9] Camargo JF, Kimble E, Rosa R, et al. Impact of Cytomegalovirus Viral Load on Probability of Spontaneous Clearance and Response to Preemptive Therapy in Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Recipients. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018;24(4):806-814.[10] 吴亚妹,曹永彬,李晓红,等.膦甲酸钠预防及抢先治疗造血干细胞移植中巨细胞病毒感染的临床研究[J]. 白血病•淋巴瘤, 2017, 26(6):331-335.[11] El Chaer F, Shah DP, Chemaly RF. How I treat resistant cytomegalovirus infection in hematopoietic cell transplantation recipients. Blood. 2016;128(23):2624-2636. [12] Razonable RR. Role of letermovir for prevention of cytomegalovirus infection after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2018; 31(4):286-291.[13] Bowman LJ, Melaragno JI, Brennan DC. Letermovir for the management of cytomegalovirus infection. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2017;26(2):235-241.[14] Ong SY, Truong HT, Diong CP, et al. Use of Valacyclovir for the treatment of cytomegalovirus antigenemia after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. BMC Hematol. 2015;15:8.[15] Gary R, Aigner M, Moi S, et al. Clinical-grade generation of peptide-stimulated CMV/EBV-specific T cells from G-CSF mobilized stem cell grafts. J Transl Med. 2018;16(1):124.[16] La Rosa C, Longmate J, Martinez J, et al. MVA vaccine encoding CMV antigens safely induces durable expansion of CMV-specific T cells in healthy adults. Blood. 2017;129(1): 114-125.[17] Yong MK, Cameron PU, Slavin M, et al. Identifying Cytomegalovirus Complications Using the Quantiferon-CMV Assay After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. J Infect Dis. 2017;215(11):1684-1694.[18] Schaenman JM, Shashidhar S, Rhee C, et al. Early CMV viremia is associated with impaired viral control following nonmyeloablative hematopoietic cell transplantation with a total lymphoid irradiation and antithymocyte globulin preparative regimen. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2011; 17(5):693-702.[19] 邹秉含,张钦,许亚茹,等.异基因造血干细胞移植后人巨细胞病毒感染的危险因素分析[J].中国实验血液学杂志, 2016,24(2): 551-555.[20] Valadkhani B, Kargar M, Ashouri A, et al.The risk factors for cytomegalovirus reactivation following stem cell transplantation. J Res Pharm Pract. 2016;5(1):63-69.[21] Janeczko M, Mielcarek M, Rybka B, et al. Immune recovery and the risk of CMV/ EBV reactivation in children post allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2016;41(3):287-296.[22] Vaezi M, Kasaeian A, Souri M, et al. How Do Donor-Recipient CMV Serostatus and Post-Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation CMV Reactivation Affect Outcomes in Acute Leukemia Patients. Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res. 2017; 11(3):199-208.[23] Kalra A, Williamson T, Daly A, et al. Impact of Donor and Recipient Cytomegalovirus Serostatus on Outcomes of Antithymocyte Globulin-Conditioned Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016;22(9): 1654-1663.[24] Ramanathan M, Teira P, Battiwalla M, et al. Impact of early CMV reactivation in cord blood stem cell recipients in the current era. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016;51(8):1113-1120. [25] Servais S, Dumontier N, Biard L, et al. Response to antiviral therapy in haematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients with cytomegalovirus (CMV) reactivation according to the donor CMV serological status. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016;22(3): 289.e1-7.[26] Ogonek J, Varanasi P, Luther S, et al. Possible Impact of Cytomegalovirus-Specific CD8+ T Cells on Immune Reconstitution and Conversion to Complete Donor Chimerism after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017;23(7):1046-1053.[27] Hilal T, Slone S, Peterson S, et al. Cytomegalovirus reactivation is associated with a lower rate of early relapse in myeloid malignancies independent of in-vivo T cell depletion strategy. Leuk Res. 2017;57:37-44.[28] Teira P, Battiwalla M, Ramanathan M, et al. Early cytomegalovirus reactivation remains associated with increased transplant-related mortality in the current era: a CIBMTR analysis. Blood. 2016;127(20):2427-2438.[29] Bao X, Zhu Q, Xue S, et al. Cytomegalovirus induces strong antileukemic effect in acute myeloid leukemia patients following sibling HSCT without ATG-containing regimen. Am J Transl Res. 2016;8(2):653-661.[30] Yong MK, Ananda-Rajah M, Cameron PU, et al. Cytomegalovirus Reactivation Is Associated with Increased Risk of Late-Onset Invasive Fungal Disease after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Multicenter Study in the Current Era of Viral Load Monitoring. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017;23(11):1961-1967. |
.jpg)
.jpg)