| [1]Marei MK,El Backly RM.Dental Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Translational Regenerative Dentistry: From Artificial to Biological Replacement.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2018;6(49):1-14.[2]Rignon-Bret C,Hadida A,Aidan A,et al.Efficacy of bone substitute material in preserving volume when placing a maxillary immediate complete denture: study protocol for the PANORAMIX randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2016;17:255-266. [3]Sánchez-Siles M,Ballester-Ferrandis JF,Salazar-Sánchez N,et al.Long-term evaluation of quality of life and satisfaction between implant bar overdentures and conventional complete dentures: a 23 years retrospective study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2018;20:208-214. [4]Grabowski G,Cornett CA.Bone graft and bone graft substitutes in spine surgery:current concepts and controversies.J Am Acad Orthop Surg.2013;21:51-60.[5]Ozdemir T,Higgins AM,Brown JL.Osteoinductive biomaterial geometries for bone regenerative engineering.Curr Pharm Des.2013;19:3446-3455.[6]Calasans-Maia MD,Melo BR,Alves AT,et al.Cytocompatibility and biocompatibility of nanostructured carbonated hydroxyapatite spheres for bone repair.J Appl Oral Sci. 2015; 23(6): 599-608.[7]Hashemi-Beni B,Khoroushi M,Foroughi MR,et al.Cytotoxicity assessment of polyhydroxybutyrate/chitosan/nano- bioglass nanofiber scaffolds by stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth stem cells from dental pulp of exfoliated deciduous tooth. Dent Res J (Isfahan).2018; 15(2):136-145.[8]Anand S,Rejula F,Sam JVG,et al.Comparative Evaluation of Effect of Nano-hydroxyapatite and 8% Arginine Containing Toothpastes in Managing Dentin Hypersensitivity: Double Blind Randomized Clinical Trial.Acta Medica(Hradec Kralove). 2017;60(3):114-119.[9]Bossù M,Saccucci M,Salucci A,et al.Enamel remineralization and repair results of Biomimetic Hydroxyapatite toothpaste on deciduous teeth: an effective option to fluoride toothpaste. J Nanobiotechnol.2019;17(1):17.[10]刘琳,包广洁.牙髓牙本质组织工程生物支架材料的研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(8):1455-1460.[11]Valiense H,Barreto M,Resende RF,et al.In vitro and in vivo evaluation of strontiumcontaining nanostructured carbonated hydroxyapatite/sodium alginate for sinus lift in rabbits. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2015;104(2):274-282.[12]Khoroushi M,Foroughi MR,Karbasi S,et al.Effect of Polyhydroxybutyrate/Chitosan/Bioglass nanofiber scaffold on proliferation and differentiation of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth into odontoblast-like cells.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2018;(89):128-139.[13]Hashemibeni B,Dehghani L,Sadeghi F,et al.Bone repair with differentiated osteoblasts from adipose-derived stem cells in hydroxyapatite/Tricalcium phosphate in vivo.Int J Prev Med. 2016;7:62. [14]Khoroushi M,Eshghi A,Naderibeni F.Pit and fissure sealant retention following air abrasion preparation with bioactive glass and aluminum oxide particles.J Dent Child (Chic).2016; 83:132-138. [15]Ginebra MP,Espanol M,Montufar EB,et al.New processing approaches in calcium phosphate cements and their applications in regenerative medicine.Acta Biomater. 2010;6:2863-2873.[16]Almasri M,Altalibi M.Efficacy of reconstruction of alveolar bone using an alloplastic hydroxyapatite tricalcium phosphate graft under biodegradable chambers.Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011; 49:469-473.[17]Brandt J,Henning S,Michler G,et al.Nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite for bone repair: an animal study. J Mater Sci Mater Med.2010;21:283-294.[18]Grossardt C,Ewald A,Grover LM,et al.Passive and active in vitro resorption of calcium and magnesium phosphate cements by osteoclastic cells.Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16: 3687-3695.[19]Sunouchi K,Tsuru K,Maruta M,et al.Fabrication of solid and hollow carbonate apatite microspheres as bone substitutes using calcite microspheres as a precursor.Dent Mater J. 2012;31:549-557.[20]Lucaciu O,Sori??u O,Gheban D,et al.Dental follicle stem cells in bone regeneration on titanium implants.BMC Biotechnol. 2015;15:114.[21]Gronthos S,Mankani M,Brahim J,et al.Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.2003;97(25):13625-13630.[22]Yuan H,Fernandes H,Habibovic P,et al.Osteoinductive ceramics as a synthetic alternative to autologous bone grafting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(31):13614-13619.[23]Miron RJ,Zhang Q,Sculean A,et al.Osteoinductive potential of 4 commonly employed bone grafts. Clin Oral Investig. 2016; 20(8):2259-2265.[24]Fairbairn P,Leventis M,Mangham C,et al.Alveolar Ridge Preservation Using a Novel Synthetic Grafting Material: A Case with Two-Year Follow-Up. Case Rep Dent. 2018; 2018: 6412806. doi: 10.1155/2018/6412806. eCollection 2018.[25]Snowdon MR,Mohanty AK,Misra M.Miscibility and Performance Evaluation of Biocomposites Made from Polypropylene/Poly(lactic acid) /Poly(hydroxybutyrate- co-hydroxyvalerate) with a Sustainable Biocarbon Filler.ACS Omega.2017;2(10):6446-6454.[26]Luklinska ZB,Schluckwerder H.In vivo response to HA-polyhydroxybutyrate/polyhydroxyvalerate composite.J Microsc.2003;211:121-129. [27]Yang X,Yang F,Walboomers XF,et al.The performance of dental pulp stem cells on nanofibrous PCL/gelatin/nHA scaffolds.J Biomed Mater Res A.2010;93:247-257.[28]Ramier J,Grande D,Bouderlique T,et al.From design of bio-based biocomposite lectrospun scaffolds to osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stromal cells. J Mater Sci Mater Med.2014;25:1563-1575.[29]Toloue EB,Karbasi S,Salehi H,et al.Potential of an electrospun composite scaffold of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate)- chitosan/alumina nanowires in bone tissue engineering applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2019;99: 1075-1091. [30]Hasegawa S,Neo M,Tamura J,et al.In vivo evaluation of a porous hydroxyapatite/poly-DL-lactide composite for bone tissue engineering.J Biomed Mater Res A.2007;81:930-938. |
.jpg)
 2.2.3 RANKL/骨保护素比值 植入材料3组植入后7-21 d的RANKL/骨保护素比值均有所增高,到42 d比值开始下降,3组植入材料组内,每两组时间点的RANKL/骨保护素比值比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图4C。
2.2.3 RANKL/骨保护素比值 植入材料3组植入后7-21 d的RANKL/骨保护素比值均有所增高,到42 d比值开始下降,3组植入材料组内,每两组时间点的RANKL/骨保护素比值比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图4C。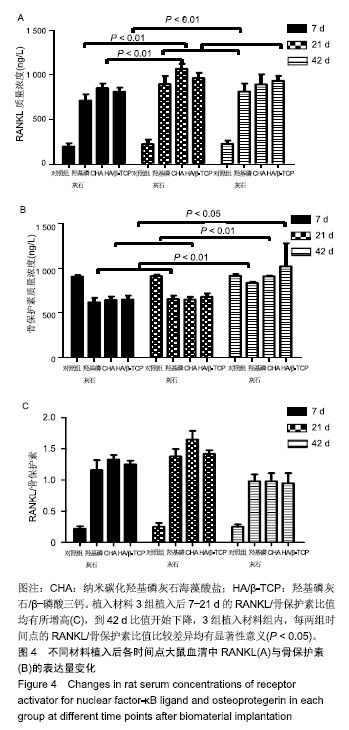
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)