| [1] Turner PR. Roles of amyloid precursor protein and its fragments inr regulating neural activity, plasticity and memory. Prog Neurobiol. 2003; 70:1-32.[2] Giacchino J, Criado JR, Games D, et al. In vivo synaptic transmission in young and aged amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice. Brain Res. 2000;876:185-190.[3] Terry RD, Masliah E, Salmon DP, et al. Physical basis of cognitive alterations in Alzheimer’s disease: synapse loss is the major correlate of cognitive impairment. Ann Neurol. 1991;30:572-580.[4] Terry RD, Katzman R. Life span and synapses: will there be a primary senile dementia? Neurobiol Aging. 2001;22(3):347-348.[5] Peters A, Sethares C, Luebke JI. Synapses are lost during aging in the primate prefrontal cortex. Neuroscience. 2008;152(4):970-981. [6] Baum ML, Kurup P, Xu J, et al. A STEP forward in neural function and degeneration. Commun Integr Biol. 2010;3:419-422.[7] Boulanger LM, Lombroso PJ, Raghunathan A, et al. Cellular and molecular characterization of a brain-enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase. J Neurosci. 1995;15(2):1532-1544.[8] Oyama T, Goto S, Nishi T, et al. Immunocytochemical localization of the striatal enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase in the rat striatum: a light and electron microscopic study with a complementary DNA-generated polyclonal antibody. Neuroscience 1995;69(3): 869-880.[9] Baum ML, Kurup P, Xu J, et al. A STEP forward in neural function and degeneration. Commun Integr Biol. 2010;3(5):419-422.[10] Paul S, Olausson P, Venkitaramani DV, et al. The protein tyrosine phosphatase step gates long-term potentiation and fear memory in the lateral amygdala. Biol Psychiat. 2007;61:1049-1061.[11] Venkitaramani DV, Paul S, Zhang Y, et al. Knockout of striatal enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase in mice results in increased ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Synapse. 2009;63(1):69-81.[12] Floden AM, Li S, Combs CK. Beta-amyloid-stimulated microglia induce neuron death via synergistic stimulation of tumor necrosis factor alpha and NMDA receptors. J Neurosci. 2005;25(10):2566-2575.[13] Frank AW, Randy JA, Fengju BA. Proteomic survey of rat cerebral cortical synaptosomes. Proteomics. 2005;5(8):2177-2201.[14] Snyder EM, Nong Y, Almeida CG, et al. Regulation of NMDA receptor trafficking by amyloid-beta. Nat Neurosci 2005;8:1051-1058.[15] Costa-Mattioli M, Sossin WS, Klann E, et al. Translational control of long-lasting synaptic plasticity and memory. Neuron. 2009;61(1):10-26.[16] Sweatt JD. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in synaptic plasticity and memory. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2004;14(3):311-317.[17] Paul S, Nairn AC, Wang P, et al. NMDA-mediated activation of the tyrosine phosphatase STEP regulates the duration of ERK signaling. Nat Neurosci 2003;6:34-42.[18] Schafe GE, Atkins CM, Swank MW, et al. Activation of ERK/MAP kinase in the amygdala is required for memory consolidation of pavlovian fear conditioning. J Neurosci. 2000;20(21):8177-8187.[19] Valjent E, Pascoli V, Svenningsson P, et al. Regulation of a protein phosphatase cascade allows convergent dopamine and glutamate signals to activate ERK in the striatum. PNAS. 2005;102:491-496.[20] English JD, Sweatt JD. A requirement for the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in hippocampal long term potentiation. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:19103-19106.[21] Impey S, Smith DM, Obrietan K, et al. Stimulation of cAMP response element(CRE)-mediated transcription during contextual learning. Nat Neurosci. 1998;1(7):595-601.[22] Davis S, Vanhoutte P, Pages C, et al. The MAPK/ERK cascade targets both Elk-1 and cAMP response element-binding protein to control long-term potentiation-dependent gene expression in the dentate gyrus in vivo. J Neurosci. 2000;20:4563-4572.[23] Swank MW, Sweatt JD. Increased histone acetyltransferase and lysine acetyltransferase activity and biphasic activation of the ERK/RSK cascade in insular cortex during novel taste learning. J Neurosci. 2001;21:3383-3391.[24] Dineley KT, Westerman M, Bui D, et al. Beta-amyloid activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade via hippocampal alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: In vitro and in vivo mechanisms related to Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci. 2001;21(12):4125-4133.[25] Carlezon WA Jr, Duman RS, Nestler EJ. The many faces of CREB. Trends. Neurosci 2005;28:436-445.[26] Bitner RS, Bunnelle WH, Anderson DJ, et al. Broad-spectrum efficacy across cognitive domains by alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonism correlates with activation of ERK1/2 and CREB phosphorylation pathways. J Neurosci. 2007;27(39):10578-10587.[27] Dineley KT, Westerman M, Bui D, et al. Beta-amyloid activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade via hippocampal alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: in vitro and in vivo mechanisms related to Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci. 2001;21(12):4125-4133.[28] Adams JP, Sweatt JD. Molecular psychology: roles for the ERK MAP kinase cascade in memory. Annu. Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2002;42: 135-163.[29] Selcher JC, Atkins CM, Trzaskos JM, et al. A necessity for MAP kinase activation in mammalian spatial learning. Learn Mem. 1999;6:478-490.[30] Zhang L, Xie JW, Yang J, et al. The Tyrosine Phosphatase STEP61 Negtively Regulates Aβ-mediated ERK/CREB Signaling Pathways via α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. J Neurosci Res. 2013;91(12): 1581-1590. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
β淀粉样蛋白:β淀粉样蛋白(Aβ)全长为Aβ1-40或Aβ1-42,是老年斑的主要结构物质,Aβ的沉积是阿尔茨海默病理的始发因素和中心环节,是多种因素导致阿尔茨海默发生发展的共同通路。
纹状体富集的酪氨酸磷酸酶:其位于后突触末端,影响突触增强的形成,可能的机制是使关键性信号蛋白如MAPK激酶ERK1/2,p38和Fyn去磷酸化并失活。
文题释义:
β淀粉样蛋白:β淀粉样蛋白(Aβ)全长为Aβ1-40或Aβ1-42,是老年斑的主要结构物质,Aβ的沉积是阿尔茨海默病理的始发因素和中心环节,是多种因素导致阿尔茨海默发生发展的共同通路。
纹状体富集的酪氨酸磷酸酶:其位于后突触末端,影响突触增强的形成,可能的机制是使关键性信号蛋白如MAPK激酶ERK1/2,p38和Fyn去磷酸化并失活。.jpg) 文题释义:
β淀粉样蛋白:β淀粉样蛋白(Aβ)全长为Aβ1-40或Aβ1-42,是老年斑的主要结构物质,Aβ的沉积是阿尔茨海默病理的始发因素和中心环节,是多种因素导致阿尔茨海默发生发展的共同通路。
纹状体富集的酪氨酸磷酸酶:其位于后突触末端,影响突触增强的形成,可能的机制是使关键性信号蛋白如MAPK激酶ERK1/2,p38和Fyn去磷酸化并失活。
文题释义:
β淀粉样蛋白:β淀粉样蛋白(Aβ)全长为Aβ1-40或Aβ1-42,是老年斑的主要结构物质,Aβ的沉积是阿尔茨海默病理的始发因素和中心环节,是多种因素导致阿尔茨海默发生发展的共同通路。
纹状体富集的酪氨酸磷酸酶:其位于后突触末端,影响突触增强的形成,可能的机制是使关键性信号蛋白如MAPK激酶ERK1/2,p38和Fyn去磷酸化并失活。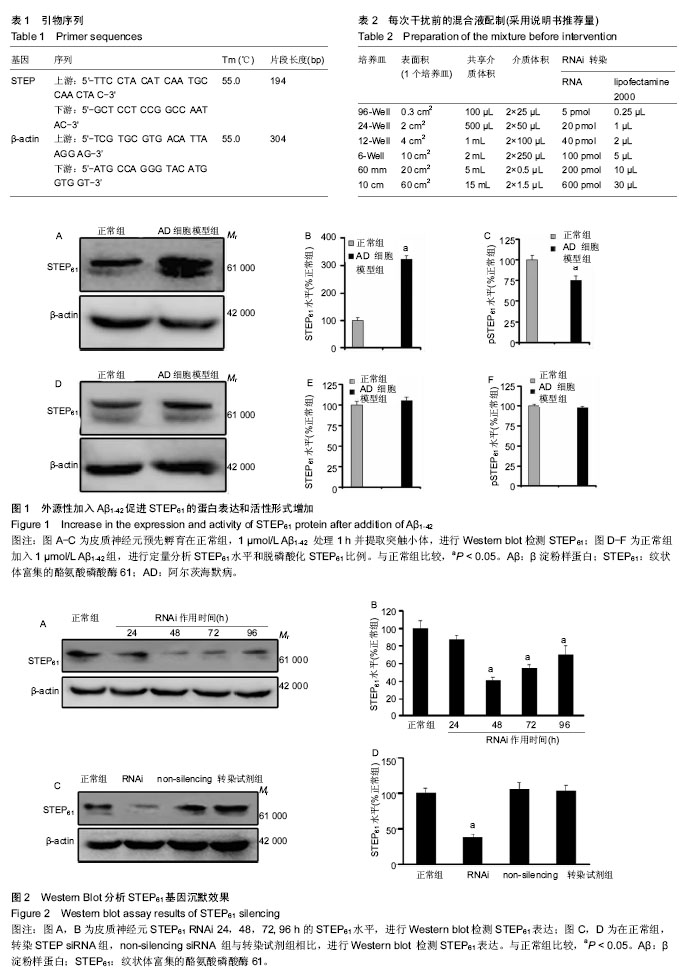
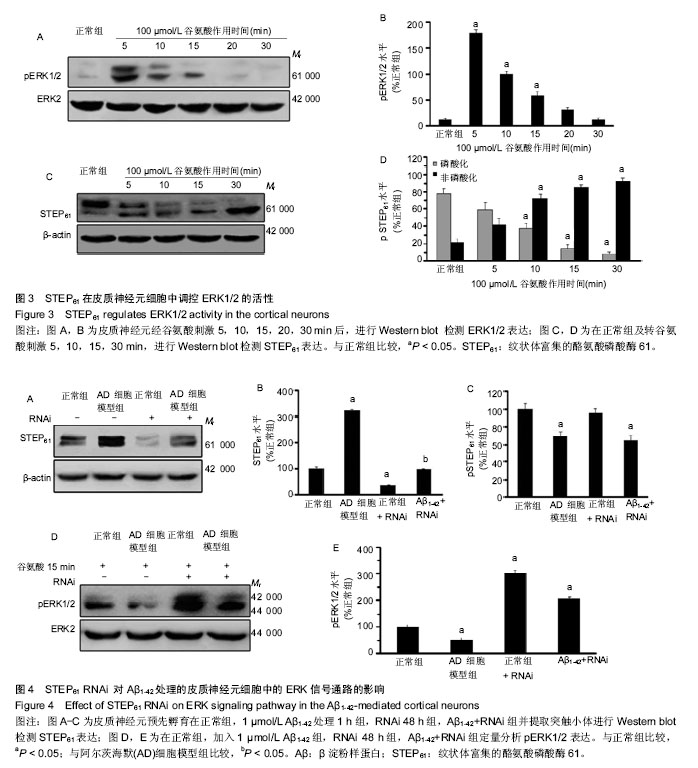
.jpg) 文题释义:
β淀粉样蛋白:β淀粉样蛋白(Aβ)全长为Aβ1-40或Aβ1-42,是老年斑的主要结构物质,Aβ的沉积是阿尔茨海默病理的始发因素和中心环节,是多种因素导致阿尔茨海默发生发展的共同通路。
纹状体富集的酪氨酸磷酸酶:其位于后突触末端,影响突触增强的形成,可能的机制是使关键性信号蛋白如MAPK激酶ERK1/2,p38和Fyn去磷酸化并失活。
文题释义:
β淀粉样蛋白:β淀粉样蛋白(Aβ)全长为Aβ1-40或Aβ1-42,是老年斑的主要结构物质,Aβ的沉积是阿尔茨海默病理的始发因素和中心环节,是多种因素导致阿尔茨海默发生发展的共同通路。
纹状体富集的酪氨酸磷酸酶:其位于后突触末端,影响突触增强的形成,可能的机制是使关键性信号蛋白如MAPK激酶ERK1/2,p38和Fyn去磷酸化并失活。