中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (3): 444-449.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0045
• 骨与关节图像与影像 bone and joint imaging • 上一篇 下一篇
骨盆CT三维重建指导髂骨钉置入
李春光,田 宁,李丕宝,石恩东,崔海银,阴祖栋,程 林
- 山东省立第三医院急诊科,山东省济南市 250031
Three-dimensional reconstruction of pelvic CT in guiding iliac nail implantation
Li Chun-guang, Tian Ning, Li Pi-bao, Shi En-dong, Cui Hai-yin, Yin Zu-dong, Cheng Lin
- Department of Emergency, Shandong Provincial Third Hospital, Jinan 250031, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
骨盆CT三维重建:对患者骨盆进行CT扫描然后经过后处理,按比例生成骨盆图像,可以进行三维测量,也可以进行各个层面的切割测量,文章就是在划定的髂骨路径层面进行测量得出数据,指导髂骨钉的置入。
髂骨钉:自椎弓根钉发展而来,针对髂骨专门设计的置入髂骨内螺钉,达到固定腰骶部稳定的目的;髂骨钉置入的路径没有统一的置入点,路径,长度,直径等,在术前对骨盆髂骨钉钉路径进行测量指导手术治疗非常必要。
摘要
背景:目前行髂骨钉置入没有统一路径标准,因人体个体差异性较大,在置入前行骨盆CT三维重建,可测量出所置入髂骨钉的直径、深度、角度等,最大程度保证置入的准确性。
目的:通过骨盆的CT三维重建测量髂骨钉置入路径的相关数据,指导髂骨钉置入,使修复手术更为精确。
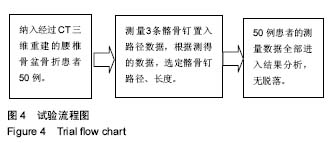
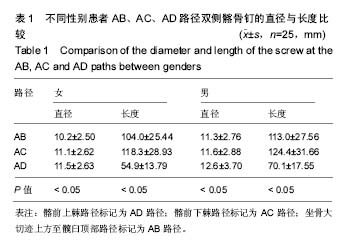
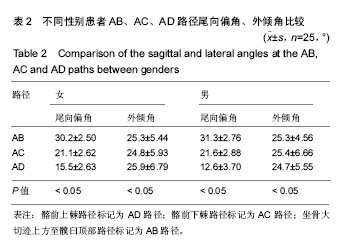
方法:选择2013年1月至2016年12月在山东省立第三医院接受骨盆病变、骨折治疗的患者50例。对患者进行骨盆CT扫描三维重建,将A点(S1骶后孔上缘连线与髂后上棘交点)位置作为髂骨钉置入点,在此点上分别测量3条路径:①髂前上棘路径标记为AD路径;②髂前下棘路径标记为AC路径;③坐骨大切迹上方至髋臼顶部路径标记为AB。在此3条路径平面上对髂骨做切面,分别在每个切面上设计髂骨钉所穿入的通道,测量出髂骨螺钉通道的直径、长度以及置入角度,根据测得的数据,选定合适的髂骨钉。
结果与结论:①同一置入路径的男性、女性髂骨钉通道长度比较,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。经配对 t 检验,AB路径与AC路径,AC路径与AD路径的髂骨钉通道长度、直径比较,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05);②同一置入路径男性、女性的尾向偏角比较,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。经配对t检验,男性、女性患者通过不同路径的尾向偏角比较,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);男性、女性患者通过不同路径的外倾角比较,差异亦有显著性意义(P < 0.05);③结果提示,骨盆CT三维重建可以测得可置入髂骨钉的长度、直径及角度,从而指导手术治疗。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-0418-1289(李春光)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)