| [1]Mouriño V, Boccaccini AR. Bone tissue engineering therapeutics: controlled drug delivery in three-dimensional scaffolds. J R Soc Int. 2010; 7(43):209.[2]Jones AC, Arns CH, Sheppard AP, et al. Assessment of bone ingrowth into porous biomaterials using MICRO-CT. Biomaterials. 2007;28(15):2491-2504.[3]Seitz H, Rieder W, Irsen S, et al. Three-dimensional printing of porous ceramic scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2005;74B(2):782-788.[4]Behnia H, Khojasteh A, Esmaeelinejad M, et al. Effects of Different Growth Factors on New Bone Formation:, A Systematic Review. J Islam Dent Assoc Iran. 2012.[5]Hassani A, Khojasteh A, Alikhasi M. Anterior Palate of the Maxilla as a Donor Site for Oral and Maxillofacial Reconstructive Procedures. Asian J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;20(3):135-138.[6]Olender E, Brubaker S, Uhrynowskatyszkiewicz I, et al. Autologous osteoblast transplantation, an innovative method of bone defect treatment: role of a tissue and cell bank in the process. Transplant Proc.2014;46(8):2867-2872.[7]Faldini C, Traina F, Perna F, et al. Surgical treatment of aseptic forearm nonunion with plate and opposite bone graft strut. Autograft or allograft? Int Orthop. 2015;39(7): 1343-1349.[8]Amini AR, Laurencin CT, Nukavarapu SP. Bone Tissue Engineering: Recent Advances and Challenges. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2012;40(5):363.[9]Derby B. Printing and prototyping of tissues and scaffolds. Science. 2012;338(6109):921-926.[10]Ozbolat IT, Hospodiuk M. Current advances and future perspectives in extrusion-based bioprinting. Biomaterials. 2016;76(37):321-343.[11]Derby B. Bioprinting: inkjet printing proteins and hybrid cell-containing materials and structures. J Mat Chem. 2008; 18(47):5717-5721.[12]Pati F, Jang J, Ha DH, et al. Printing three-dimensional tissue analogues with decellularized extracellular matrix bioink.Nat Commun. 2014;5:3935. [13]Murphy SV, Atala A. 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32(8):773-785.[14][14] Mironov V, Kasyanov V, Markwald RR. Organ printing: From bioprinter to organ biofabrication line. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2011;22(5): 667-673.[15]Pati F, Gantelius J, Svahn HA. 3D Bioprinting of Tissue/Organ Models. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2016;55(15):4650-4665. [16]Murphy SV, Atala A. 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Nat Biotechnol. 2014; 32(8):773-785.[17]Zhang X, Zhang Y. Tissue Engineering Applications of Three-Dimensional Bioprinting. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015; 72(3):777-782.[18]Gasperini L, Maniglio D, Motta A, et al. An Electrohydrodynamic Bioprinter for Alginate Hydrogels Containing Living Cells. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2015; 21(2):123.[19]Mézel C, Souquet A, Hallo L, et al. Bioprinting by laser-induced forward transfer for tissue engineering applications: jet formation modeling. Biofabrication. 2010;2(1): 014103.[20]Nakamura M, Nishiyama Y, Henmi C, et al. Ink jet three-dimensional digital fabrication for biological tissue manufacturing: analysis of alginate microgel beads produced by ink jet droplets for three dimensional tissue fabrication. J Imaging Sci Tech. 2008;52(6):060201–060201-6.[21]Khalil S, Nam J, Sun W. Multi‐nozzle deposition for construction of 3D biopolymer tissue scaffolds. Rapid Prot J. 2005;11(1):9-17(9).[22]Park JH, Jang J, Lee JS, et al. Three-Dimensional Printing of Tissue/Organ Analogues Containing Living Cells. Ann Biomed Eng. 2017;45(1):180.[23]Skoog SA, Goering PL, Narayan RJ. Stereolithography in tissue engineering. J Mat Sci. 2014;25(3):845-56.[24]Fashion’s Biological Future Is Now.www.Biofabricate.Co/[25]Skardal A, Atala A. Biomaterials for Integration with 3-D Bioprinting. Ann Biomed Eng. 2015;43(3):730-746.[26]Ozbolat IT, Hospodiuk M. Current advances and future perspectives in extrusion-based bioprinting. Biomaterials. 2016;76(37):321.[27]Panwar A, Tan LP. Current Status of Bioinks for Micro- Extrusion-Based 3D Bioprinting. Molecules. 2016;21 (6):685.[28]Lei M, Wang X. Biodegradable Polymers and Stem Cells for Bioprinting. Molecules. 2016;21(5):539.[29]Trappmann B, Chen CS. How cells sense extracellular matrix stiffness: a material's perspective. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2013;24(5):948-953.[30]schumperlin DJ, Liu F, Tager AM. Biomechanical regulation of mesenchymal cell function. Curr Opin Rheumatol.2013;25(1): 92-100.[31]Lee KY, Mooney DJ. Alginate: properties and biomedical applications. Prog Polym Sci. 2012;37(1):106-126.[32]Giri TK, Thakur D, Alexander A, et al. Alginate based hydrogel as a potential biopolymeric carrier for drug delivery and cell delivery systems: present status and applications. Curr Drug Deliv. 2012;9(6):539-555.[33]Garg T, Goyal AK. Biomaterial-based scaffolds – current status and future directions. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2014; 11(5):767-789.[34]Dong C, Lv Y. Application of Collagen Scaffold in Tissue Engineering: Recent Advances and New Perspectives. Polymers. 2016;8(2):42.[35]Aamodt JM, Grainger DW. Extracellular matrix-based biomaterial scaffolds and the host response. Biomaterials. 2016;86:68-82.[36]Klotz BJ, Gawlitta D, Rosenberg AJ, et al. Gelatin-Methacryloyl Hydrogels: Towards Biofabrication-Based Tissue Repair. Trends Biotechnol. 2016;34(5):394.[37]Seok J, Warren HS, Cuenca AG, et al. Genomic responses in mouse models poorly mimic human inflammatory diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(9):3507-3512. [38]Shim JH, Lee JS, Kim JY, et al. Bioprinting of a mechanically enhanced three-dimensional dual cell-laden construct for osteochondral tissue engineering using a multi-head tissue/organ building system. J Micromechanics Microengineering. 2012;22(8):85014-85024(11).[39]Duan B, Hockaday LA, Kang KH, et al. 3D Bioprinting of Heterogeneous Aortic Valve Conduits with Alginate/Gelatin Hydrogels. J Biomed Mat Res. 2013;101A(5):1255-1264.[40]Pinar Z, Hyun JJ, Kong H, et al. Stereolithography‐Based Hydrogel Microenvironments to Examine Cellular Interactions. Adv Funct Mat. 2011;21(19):3597-3597.[41]Mandrycky C, Wang Z, Kim K, et al. 3D Bioprinting for Engineering Complex Tissues. Biotechnol Adv. 2016;34(4): 422-434.[42]Mironov V, Visconti R P, Kasyanov V, et al. Organ printing: tissue spheroids as building blocks. Biomaterials. 2009; 30(12):2164.[43]Ozbolat IT. Bioprinting scale-up tissue and organ constructs for transplantation. Trends in Biotechnology. 2015;33(7): 395-400.[44]Poldervaart MT, Wang H, Van d SJ, et al. Sustained release of BMP-2 in bioprinted alginate for osteogenicity in mice and rats. Plos One. 2013;8(8):e72610.[45]Ahn S, Lee H, Lee EJ, et al. A direct cell printing supplemented with low-temperature processing method for obtaining highly porous three-dimensional cell-laden scaffolds. J Mat Chem. 2014;2(18):2773-2782.[46]Bose S, Vahabzadeh S, Bandyopadhyay A. Bone tissue engineering using 3D printing. Mat Today. 2013;16(12): 496-504.[47]Wüst S, Godla ME, Müller R, et al. Tunable hydrogel composite with two-step processing in combination with innovative hardware upgrade for cell-based three-dimensional bioprinting. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(2): 630-640. [48]薛世华,王勇,赵雨,等.人牙髓细胞三维生物打印的初步研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2012,12(17):4103-4107.[49]薛世华,吕培军,王勇,等. 人牙髓细胞共混物三维生物打印技术[J]. 北京大学学报医学版, 2013,45(1):105-108.[50]宋杨,王晓飞,王宇光,等. 人脂肪间充质干细胞与生物材料共混物三维打印体的体内成骨[J]. 北京大学学报医学版, 2016, 48(1):45-50.[51]宋杨,王晓飞,王宇光,等. 纳米羟基磷灰石对人脂肪干细胞共混物三维生物打印影响的初步研究[J]. 北京大学学报医学版, 2016,48(5):894-899.[52]Bendtsen ST, Quinnell SP, Mei W. Development of a novel alginate‐polyvinyl alcohol‐hydroxyapatite hydrogel for 3D bioprinting bone tissue engineered scaffolds. J Biomed Mat Res.2017;105(5):1457.[53]Gao G, Schilling AF, Yonezawa T, et al. Bioactive nanoparticles stimulate bone tissue formation in bioprinted three-dimensional scaffold and human mesenchymal stem cells. Biotechno J. 2014;9(10):1304.[54]Daly AC, Cunniffe GM, Sathy BN, et al. 3D Bioprinting: 3D Bioprinting of Developmentally Inspired Templates for Whole Bone Organ Engineering (Adv. Healthcare Mater. 18/2016). Adv Health Mat. 2016;5(18):2353.[55]Kang HW, Lee SJ, Ko IK, et al. A 3D bioprinting system to produce human-scale tissue constructs with structural integrity]. Nature Biotechnol. 2016;34(3):312.[56]Mercado-Pagán ÁE, Stahl AM, Shanjani Y, et al. Vascularization in Bone Tissue Engineering Constructs. Ann Biomed Eng. 2015;43(3):718-729.[57]Ju YP, Shim JH, Choi SA, et al. 3D printing technology to control BMP-2 and VEGF delivery spatially and temporally to promote large-volume bone regeneration. J Mat Chem. 2015;3(27):5415-5425.[58]Daly AC, Critchley SE, Rencsok EM, et al. A comparison of different bioinks for 3D bioprinting of fibrocartilage and hyaline cartilage. Biofabrication. 2016;8(4):045002. |
.jpg)
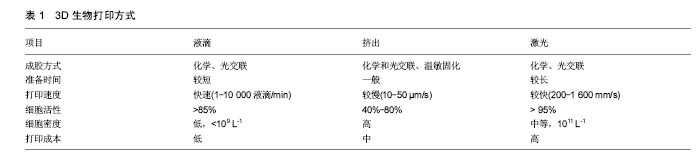
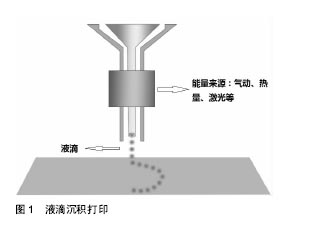
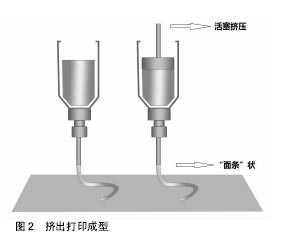
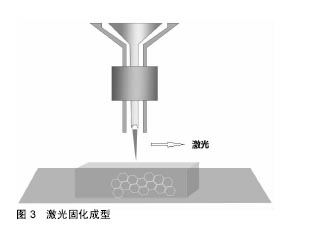
.jpg)