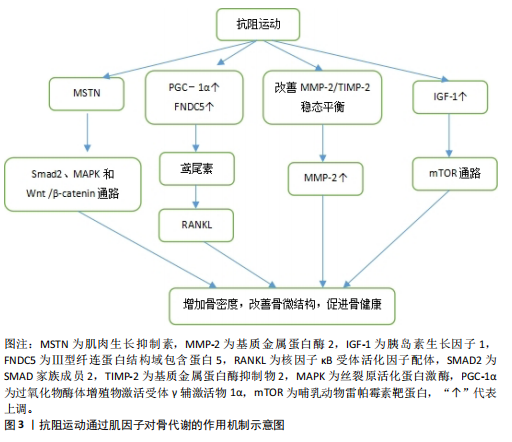
[1] 马剑雄,匡明杰,何伟伟,等.肌肉减少症与骨质疏松的相关性:研究与应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(32):5222-5227.
[2] BINKLEY N, BUEHRING B. Beyond FRAX: it’s time to consider “sarco-osteopenia”. J Clin Densitom. 2009;12(4):413-416.
[3] KIRK B, FEEHAN J, LOMBARDI G, et al. Muscle, Bone, and Fat Crosstalk: the Biological Role of Myokines, Osteokines, and Adipokines. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020;18(4):388-400.
[4] GOMARASCA M, BANFI G, LOMBARDI G. Myokines: The endocrine coupling of skeletal muscle and bone. Adv Clin Chem. 2020;94:155-218.
[5] ZHANG L, LV J, WANG C, et al. Myokine, a key cytokine for physical exercise to alleviate sarcopenic obesity. Mol Biol Rep. 2023;50(3):2723-2734.
[6] 徐帅,徐道明,沈飞.肌骨系统中运动干预肌肉与骨骼交互功能的机制研究进展[J].山东体育学院学报,2022,38(2):91-99.
[7] RINDERKNECHT E, HUMBEL RE. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1978;253(8):2769-2776.
[8] OKADA Y, NAGASE H, HARRIS ED. Matrix metalloproteinases 1, 2, and 3 from rheumatoid synovial cells are sufficient to destroy joints. J Rheumatol. 1987;14 Spec No:41-42.
[9] CANALIS E, CENTRELLA M, BURCH W, et al. Insulin-like growth factor I mediates selective anabolic effects of parathyroid hormone in bone cultures. J Clin Invest. 1989;83(1):60-65.
[10] WAGNER KR, COHEN JS. Myostatin-Related Muscle Hypertrophy-RETIRED CHAPTER, FOR HISTORICAL REFERENCE ONLY. 2005 Oct 5 [updated 2013 Jul 3].//Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, et al. editors. GeneReviews®[Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2025.
[11] BORST E, DE HOYOS DV, GARZARELLA L, et al. Effects of resistance training on insulin-like growth factor-I and IGF binding proteins. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2001;33(4):648-653.
[12] ROTH SM, MARTEL GF, FERRELL RE, et al. Myostatin gene expression is reduced in humans with heavy-resistance strength training: a brief communication. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2003;228(6):706-709.
[13] MOSIG RA, DOWLING O, DIFEO A, et al. Loss of MMP-2 disrupts skeletal and craniofacial development and results in decreased bone mineralization, joint erosion and defects in osteoblast and osteoclast growth. Hum Mol Genet. 2007;16(9):1113-1123.
[14] PEDERSEN BK. Muscles and their myokines. J Exp Biol. 2011;214(Pt 2):337-346.
[15] BOSTRÖM P, WU J, JEDRYCHOWSKI MP, et al. A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature. 2012;481(7382):463-468.
[16] SOUZA MV, LEITE RD, SOUZA LINO AD, et al. Resistance training improves body composition and increases matrix metalloproteinase 2 activity in biceps and gastrocnemius muscles of diet-induced obese rats. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2014;69(4):265-270.
[17] QIN Y, PENG Y, ZHAO W, et al. Myostatin inhibits osteoblastic differentiation by suppressing osteocyte-derived exosomal microRNA-218: A novel mechanism in muscle-bone communication. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(26):11021-11033.
[18] KIM H, WRANN CD, JEDRYCHOWSKI M, et al. Irisin Mediates Effects on Bone and Fat via αV Integrin Receptors. Cell. 2018;175(7):1756-1768.e17.
[19] RICE JC, WEEKLEY BH, KANHOLM T, et al. MMP-2 is a novel histone H3 N-terminal protease necessary for myogenic gene activation. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2021; 14(1):23.
[20] LI M, LIU Q, XIE S, et al. LncRNA TCONS_00323213 Promotes Myogenic Differentiation by Interacting with PKNOX2 to Upregulate MyoG in Porcine Satellite Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(7):6773.
[21] JU CR, CHEN C. Serum myostatin levels and skeletal muscle wasting in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Med. 2012;106(1):102-108.
[22] WU L, ZHU D, WANG B, et al. Relative abundance of mature myostatin rather than total myostatin is negatively associated with bone mineral density in Chinese. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(2):1329-1336.
[23] SHANAZARI Z, FARAMARZI M, BANITALEBI E, et al. Effect of moderate and high-intensity endurance and resistance training on serum concentrations of MSTN and IGF-1 in old male Wistar rats. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2019;38(2):/j/hmbci.2019.38.issue-2/hmbci-2018-0066/hmbci-2018-0066.xml. doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2018-0066.
[24] OMOSULE CL, PHILLIPS CL. Deciphering Myostatin’s Regulatory, Metabolic, and Developmental Influence in Skeletal Diseases. Front Genet. 2021;12:662908.
[25] WU Z, PUIGSERVER P, ANDERSSON U, et al. Mechanisms controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and respiration through the thermogenic coactivator PGC-1. Cell. 1999; 98(1):115-124.
[26] STORLINO G, COLAIANNI G, SANESI L, et al. Irisin Prevents Disuse-Induced Osteocyte Apoptosis. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(4):766-775.
[27] ZHU X, LI X, WANG X, et al. Irisin deficiency disturbs bone metabolism. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(1):664-676.
[28] ESTELL EG, LE PT, VEGTING Y, et al. Irisin directly stimulates osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption in vitro and in vivo. Elife. 2020;9:e58172.
[29] LUO Y, QIAO X, MA Y, et al. Disordered metabolism in mice lacking irisin. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):17368.
[30] KOLKENBROCK H, ORGEL D, HECKER-KIA A, et al. The complex between a tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP-2) and 72-kDa progelatinase is a metalloproteinase inhibitor. Eur J Biochem. 1991;198(3): 775-781.
[31] 任磊,苗杰,秦永生,等.自主跑轮运动调控MMP-2/TIMP-2稳态平衡改善去卵巢大鼠心脏重塑[J].天津体育学院学报, 2019,34(4):330-336.
[32] VANATKA R, ROUZIER C, LAMBERT JC, et al. Winchester syndrome: the progression of radiological findings over a 23-year period. Skeletal Radiol. 2011;40(3):347-351.
[33] NI X, XIA T, ZHAO Y, et al. Downregulation of miR-106b induced breast cancer cell invasion and motility in association with overexpression of matrix metalloproteinase 2. Cancer Sci. 2014;105(1):18-25.
[34] DERIGGI-PISANI GF, STOTZER US, MARQUETI RC, et al. Role of resistance training in bone macro and micro damages in an estrogen absence animal model. Life Sci. 2023;317:121417.
[35] ZHOU M, GRAVES DT. Impact of the host response and osteoblast lineage cells on periodontal disease. Front Immunol. 2022;13:998244.
[36] DELAGRANGE M, ROUSSEAU V, CESSANS C, et al. Low bone mass in Noonan syndrome children correlates with decreased muscle mass and low IGF-1 levels. Bone. 2021;153:116170.
[37] SHENG MHC, ZHOU XD, BONEWALD LF, et al. Disruption of the insulin-like growth factor-1 gene in osteocytes impairs developmental bone growth in mice. Bone. 2013;52(1):133-144.
[38] DRISSI H, LOMRI A, LASMOLES F, et al. Skeletal unloading induces biphasic changes in insulin-like growth factor-I mRNA levels and osteoblast activity. Exp Cell Res. 1999; 251(2):275-284.
[39] SHIMONTY A, BONEWALD LF, HUOT JR. Metabolic Health and Disease: A Role of Osteokines? Calcif Tissue Int. 2023;113(1): 21-38.
[40] EHRNBORG C, LANGE KHW, DALL R, et al. The growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor-I axis hormones and bone markers in elite athletes in response to a maximum exercise test. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003; 88(1):394-401.
[41] KOK HJ, CROWDER CN, KOO MIN CHEE L, et al. Muscle insulin-like growth factor-I modulates murine craniofacial bone growth. Eur Cell Mater. 2021;42:72-89.
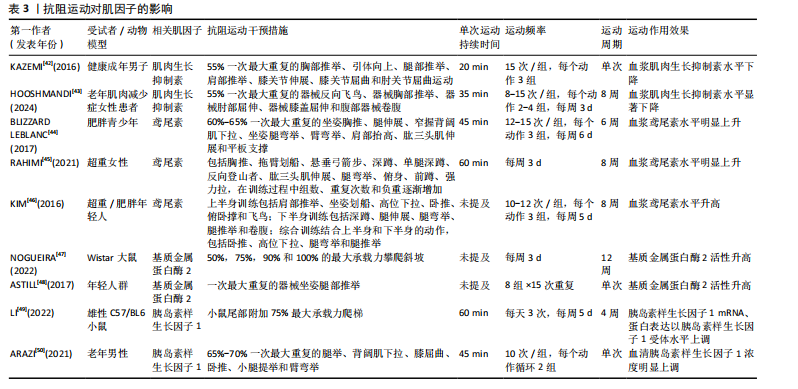
[42] KAZEMI F. The correlation of resistance exercise-induced myostatin with insulin resistance and plasma cytokines in healthy young men. J Endocrinol Invest. 2016; 39(4):383-388.
[43] HOOSHMANDI Z, DARYANOOSH F, AHMADI HEKMATIKAR A H, et al. Highlighting the effect of reduced training volume on maintaining hormonal adaptations obtained from periodized resistance training in sarcopenic older women. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. 2024;19(2):187-197.
[44] BLIZZARD LEBLANC DR, RIOUX BV, PELECH C, et al. Exercise-induced irisin release as a determinant of the metabolic response to exercise training in obese youth: the EXIT trial. Physiol Rep. 2017;5(23):e13539.
[45] RAHIMI M, NAZARALI P, ALIZADEH R. Pilates and TRX training methods can improve insulin resistance in overweight women by increasing an exercise-hormone, Irisin. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2021;20(2):1455-1460.
[46] KIM HJ, LEE HJ, SO B, et al. Effect of aerobic training and resistance training on circulating irisin level and their association with change of body composition in overweight/obese adults: a pilot study. Physiol Res. 2016;65(2):271-279.
[47] NOGUEIRA ME, SOUSA NETO IV, MOTTA-SANTOS D, et al. High-protein diet associated with resistance training reduces cardiac TNF-α levels and up-regulates MMP-2 activity in rats. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2022;128(6):1630-1636.
[48] ASTILL BD, KATSMA MS, CAUTHON DJ, et al. Sex-based difference in Achilles peritendinous levels of matrix metalloproteinases and growth factors after acute resistance exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017;122(2):361-367.
[49] LI B, FENG L, WU X, et al. Effects of different modes of exercise on skeletal muscle mass and function and IGF-1 signaling during early aging in mice. J Exp Biol. 2022; 225(21):jeb244650.
[50] ARAZI H, BABAEI P, MOGHIMI M, et al. Acute effects of strength and endurance exercise on serum BDNF and IGF-1 levels in older men. BMC Geriatr. 2021;21(1):50.
[51] TANG L, ZHAO T, KANG Y, et al. MSTN is an important myokine for weight-bearing training to attenuate bone loss in ovariectomized rats. J Physiol Biochem. 2022;78(1):61-72.
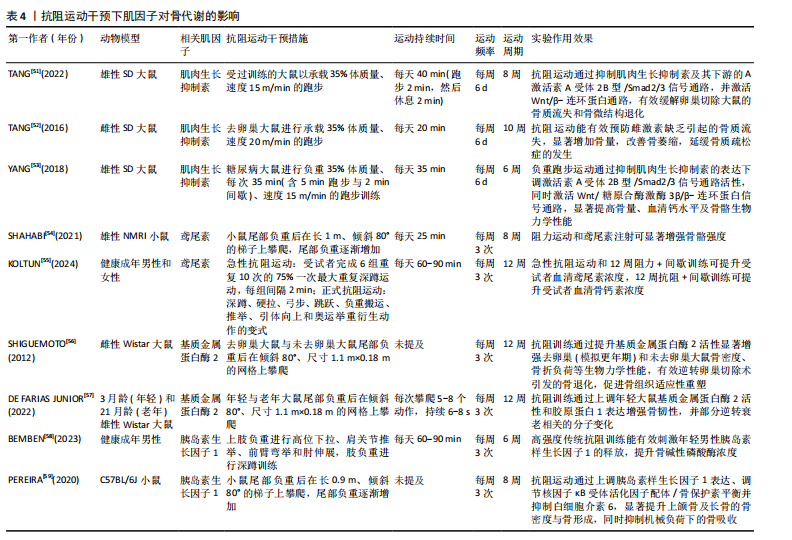
[52] TANG L, GAO X, YANG X, et al. Ladder-Climbing Training Prevents Bone Loss and Microarchitecture Deterioration in Diet-Induced Obese Rats. Calcif Tissue Int. 2016; 98(1):85-93.
[53] YANG J, SUN L, FAN X, et al. Effect of exercise on bone in poorly controlled type 1 diabetes mediated by the ActRIIB/Smad signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(4):3686-3693.
[54] SHAHABI S, ESFARJANI F, REISI J, et al. The Effects of 8-Week Resistance and Endurance Trainings on Bone Strength Compared to Irisin Injection Protocol in Mice. Adv Biomed Res. 2021;10:40.
[55] KOLTUN KJ, STERCZALA AJ, SEKEL NM, et al. Effect of acute resistance exercise on bone turnover in young adults before and after concurrent resistance and interval training. Physiol Rep. 2024;12(3):e15906.
[56] SHIGUEMOTO GE, PRESTES J, LEITE RD, et al. Effects of resistance training on matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity and biomechanical and physical properties of bone in ovariectomized and intact rats. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2012;22(5):607-617.
[57] DE FARIAS JUNIOR GC, DE SOUSA NETO IV, GUZZONI V, et al. Remodeling process in bone of aged rats in response to resistance training. Life Sci. 2020;256:118008.
[58] BEMBEN DA, SHERK VD, BUCHANAN SR, et al. Acute and chronic bone marker and endocrine responses to resistance exercise with and without blood flow restriction in young men. J Strength Cond Res. 2023; 37(4):893-901.
[59] PEREIRA LJ, MACARI S, COIMBRA CC, et al. Aerobic and resistance training improve alveolar bone quality and interferes with bone-remodeling during orthodontic tooth movement in mice. Bone. 2020;138:11549.
|