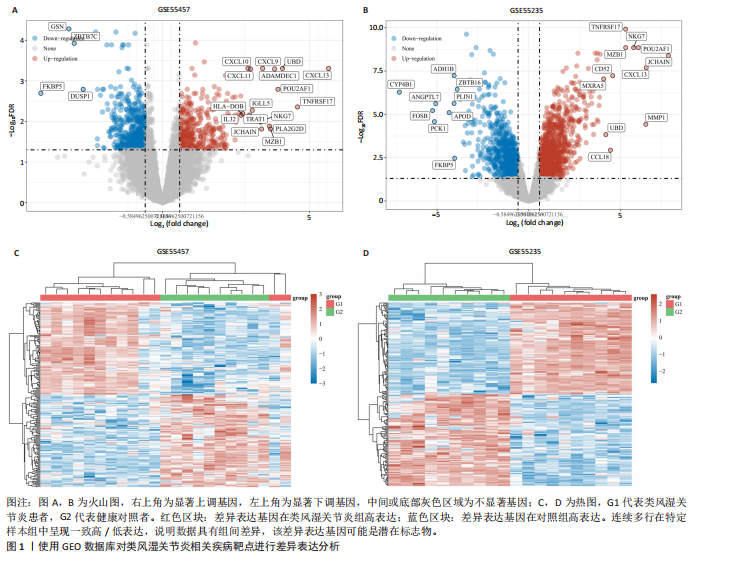
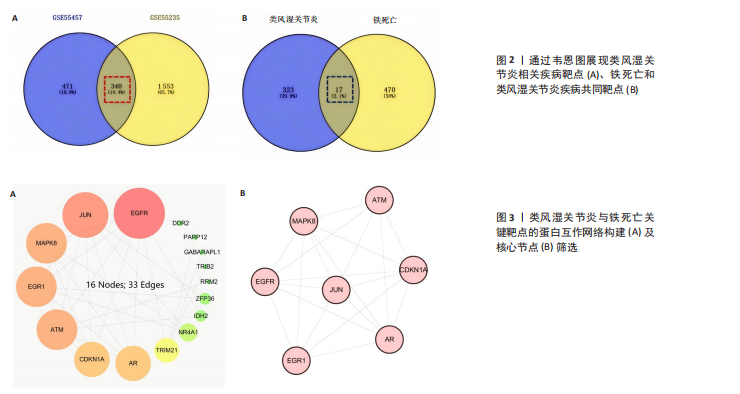
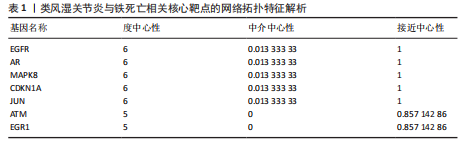
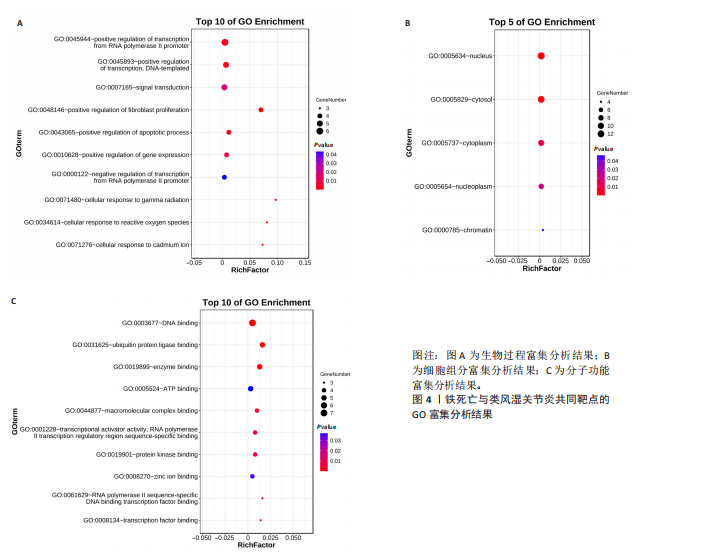
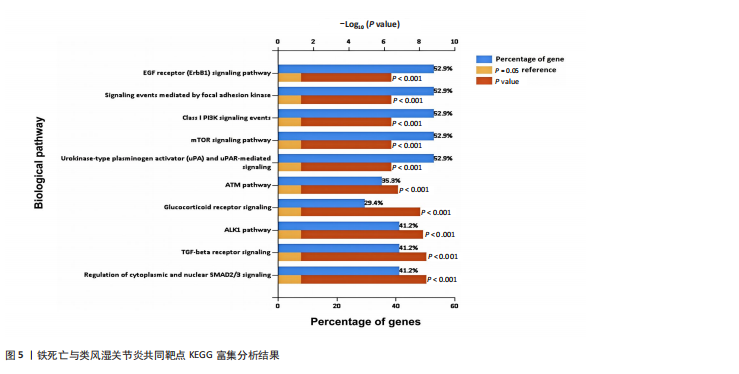
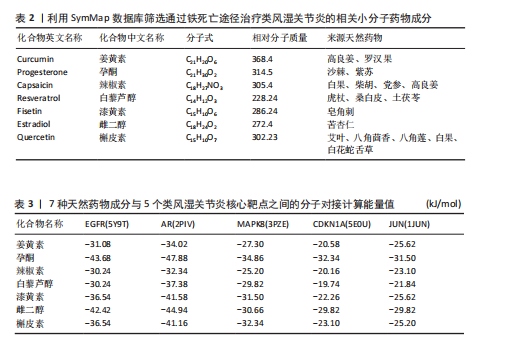
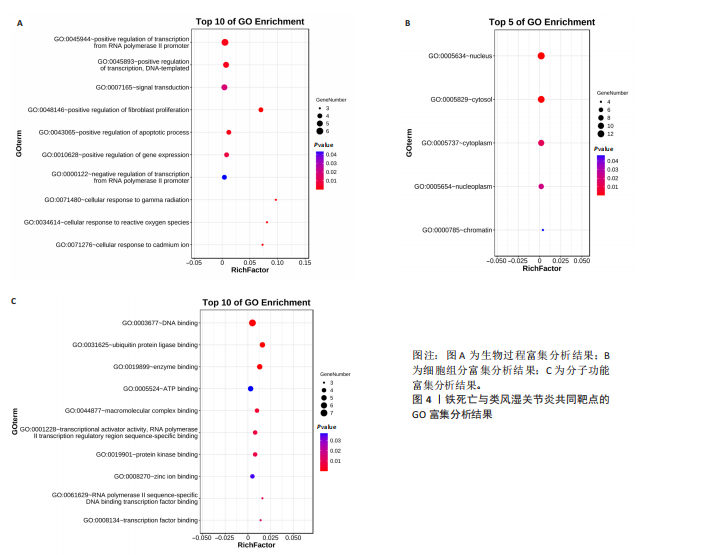
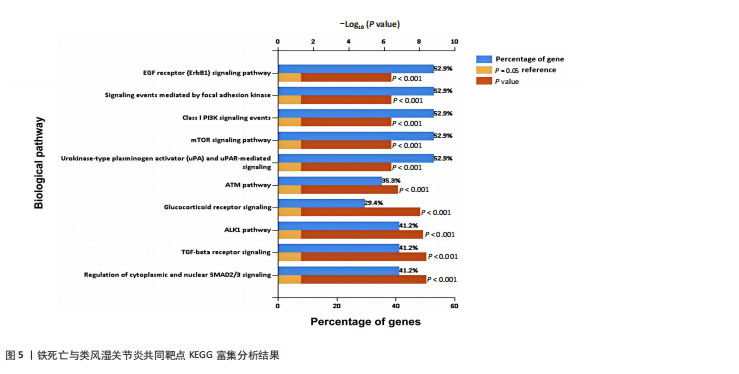
[1] 冷冬月,李旭峰,方兴刚.吴茱萸碱抑制HMGB1/TLR-4/NF-κB信号通路对类风湿关节炎大鼠的改善作用[J].河北医药, 2023,45(18):2760-2764.
[2] WEYAND CM, GORONZY JJ. The immunology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Immunol. 2021; 22(1):10-18.
[3] ALIVERNINI S, FIRESTEIN GS, MCINNES IB. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunity. 2022;55(12):2255-2270.
[4] YANG M, SU Y, XU K, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis increases the risk of malignant neoplasm of bone and articular cartilage: a two-sample bidirectional mendelian randomization study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023;25(1):219.
[5] 李杰,邓泽辉,王英,等.托珠单抗联合泼尼松和甲氨蝶呤治疗难治性中重度类风湿关节炎临床评价[J].中国药业,2024, 33(4):97-100.
[6] 彭延刚.艾拉莫德联合布洛芬治疗类风湿关节炎的临床效果[J].临床合理用药, 2023,16(7):27-29+33.
[7] BERGSTRA SA, SEPRIANO A, KERSCHBAUMER A, et al. Efficacy, duration of use and safety of glucocorticoids: a systematic literature review informing the 2022 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023;82(1):81-94.
[8] PIRMARDVAND CHEGINI S, VARSHOSAZ J, TAYMOURI S. Recent approaches for targeted drug delivery in rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis and treatment. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(sup2):502-514.
[9] STOCKWELL BR, JIANG X, GU W. Emerging Mechanisms and Disease Relevance of Ferroptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 2020;30(6):478-490.
[10] 郑恩会,钟晓琳,蒋宗哲,等.中药及其天然产物通过靶向铁死亡治疗肝癌研究进展[J.天然产物研究与开发,2025,37(8): 1578-1584+1534.
[11] 刘微微,王国辉.关于铁死亡在缺血性脑卒中中的研究进展[J].微量元素与健康研究,2025,42(2):71-74.
[12] 余伟杰,刘爱峰,陈继鑫,等.基于生物信息学及机器学习分析椎间盘退变伴铁死亡的关键基因及潜在中药预测[J].中国中药杂志,2025,50(19):5482-5497.
[13] LUO H, ZHANG R. Icariin enhances cell survival in lipopolysaccharide-induced synoviocytes by suppressing ferroptosis via the Xc-/GPX4 axis. Exp Ther Med. 2021; 21(1):72.
[14] SHA N, VANNUCCI M, BROWN PJ, et al. Gene selection in arthritis classification with large-scale microarray expression profiles. Comp Funct Genomics. 2003;4(2):171-181.
[15] 李楠,杨海芯,曾珊,等.桂枝芍药知母汤对类风湿关节炎Th17/Treg细胞失衡及JAK2/STAT3信号通路的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2023,38(6):2567-2571.
[16] DI MATTEO A, BATHON JM, EMERY P. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2023;402(10416):2019-2033.
[17] ZHANG Y, GAO Z, CHAO S, et al. Transdermal delivery of inflammatory factors regulated drugs for rheumatoid arthritis. Drug Deliv. 2022;29(1):1934-1950.
[18] HU H, LUAN L, YANG K, et al. Psychometric validation of Chinese Health Assessment Questionnaire for use in rheumatoid arthritis patients in China. Int J Rheum Dis. 2017;20(12):1987-1992.
[19] MIGUEL-LAVARIEGA D, ELIZARARRÁS-RIVAS J, VILLARREAL-RÍOS E, et al. Perfil epidemiológico de la artritis reumatoide [Epidemiological profile of rheumatoid arthritis]. Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc. 2023;61(5):574-582.
[20] ALPIZAR-RODRIGUEZ D, FINCKH A. Is the prevention of rheumatoid arthritis possible. Clin Rheumatol. 2020;39(5):1383-1389.
[21] WANG X, KONG Y, LI Z. Advantages of Chinese herbal medicine in treating rheumatoid arthritis: a focus on its anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024;11:1371461.
[22] 阚玉娜,谢佳明,马立威,等.中药活性成分改善类风湿性关节炎作用机制研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2021, 23(10):139-145.
[23] AKAGI R, AKATSU Y, FISCH KM, et al. Dysregulated circadian rhythm pathway in human osteoarthritis: NR1D1 and BMAL1 suppression alters TGF-β signaling in chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(6):943-951.
[24] VAN DER KRAAN PM. The changing role of TGFβ in healthy, ageing and osteoarthritic joints. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017;13(3): 155-163.
[25] YING J, WANG P, ZHANG S, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta1 promotes articular cartilage repair through canonical Smad and Hippo pathways in bone mesenchymal stem cells. Life Sci. 2018;192:84-90.
[26] WANG Q, TAN QY, XU W, et al. Cartilage-specific deletion of Alk5 gene results in a progressive osteoarthritis-like phenotype in mice. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017; 25(11):1868-1879.
[27] NERVIANI A, BOUTET MA, GHIRARDI GM, et al. Axl and MerTK regulate synovial inflammation and are modulated by IL-6 inhibition in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):2398.
[28] ZHAO L, LIU M, ZHENG K, et al. Fufang Duzheng tablet attenuates adjuvant rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting arthritis inflammation and gut microbiota disturbance in rats. Heliyon. 2024;10(12):e32705.
[29] WEI Y, LUO L, GUI T, et al. Targeting cartilage EGFR pathway for osteoarthritis treatment. Sci Transl Med. 2021;13(576):eabb3946.
[30] 涂华微.类风湿关节炎患者血清腺苷脱氨酶水平及外周血单个核细胞腺苷受体基因表达的研究[D].南充:川北医学院,2024.
[31] JIANG Y, QIAO Y, HE D, et al. Adaptor protein HIP-55-mediated signalosome protects against ferroptosis in myocardial infarction. Cell Death Differ. 2023;30(3):825-838.
[32] 李玉杰,吴巧萍,李情操,等.铁死亡相关基因在类风湿性关节炎中的作用机制[J].浙江医学,2024,46(24):2619-2625+2692.
[33] ZHAO C, SUN G, LI Y, et al. Forkhead box O3 attenuates osteoarthritis by suppressing ferroptosis through inactivation of NF-κB/MAPK signaling. J Orthop Translat. 2023;39:147-162.
[34] LIU Y, GU W. p53 in ferroptosis regulation: the new weapon for the old guardian. Cell Death Differ. 2022;29(5):895-910.
[35] 范丹丹.miR-126-3p与自噬相关基因对类风湿关节炎发病机制影响的研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2022.
[36] 秦齐刚.基于虚拟筛选从中药中发现抗RA药效物质基础及作用机制研究[D].重庆:重庆科技学院,2022.
[37] 伍甜,张杰.姜黄素对类风湿关节炎免疫细胞群调节机制研究进展[J].中医临床研究,2025,17(18):65-74.
[38] WANG H, ZHANG M, HU Y, et al. Deciphering the role of ferroptosis in rheumatoid arthritis: Synovial transcriptome analysis and immune infiltration correlation. Heliyon. 2024;10(13):e33648.
[39] 李维彤,谢亚,吕中阳,等.辣椒素在骨关节炎中的作用研究进展[J].实用老年医学,2024,38(2):198-202.
[40] 郑云松,皮浩吕,何子晗,等.基于AKT-HK2-NF-κB信号通路的辣椒素对CIA大鼠的作用机制[J].贵州医科大学学报,2024, 49(11):1615-1621.
[41] 李雨,王杰,陈铭勰,等.辣椒素对CIA大鼠关节滑膜组织抗炎作用及机制[J].贵州医科大学学报,2023,48(5):508-514.
[42] LIU X, WANG Z, QIAN H, et al. Natural medicines of targeted rheumatoid arthritis and its action mechanism. Front Immunol. 2022;13:945129.
[43] 陈倩雯,何奕坤,沈佳莹,等.白藜芦醇治疗类风湿关节炎研究进展[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2022,42(10):1266-1272.
[44] NANDAVE M, ACHARJEE R, BHADURI K, et al. A pharmacological review on SIRT 1 and SIRT 2 proteins, activators, and inhibitors: Call for further research. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;242(Pt 1):124581.
[45] FERNÁNDEZ-RODRÍGUEZ JA, ALMONTE-BECERRIL M, RAMIL-GÓMEZ O, et al. Autophagy Activation by Resveratrol Reduces Severity of Experimental Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2021;65(2):e2000377.
[46] 龙晨,杨硕,潘彬,等.基于网络药理学和实验验证白藜芦醇治疗类风湿性关节炎的作用机制[J].现代药物与临床, 2024,39(6):1425-1435.
[47] 李浩,姚血明,姚晓玲,等.漆黄素调控焦亡相关蛋白对人类风湿关节炎滑膜成纤维细胞增殖、迁移及周期阻滞影响[J].中国药理学通报,2024,40(10):1937-1944.
[48] 杭小雨.雌二醇对类风湿性关节炎中ASIC1a介导的关节软骨损伤的作用及其机制研究[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2021.
[49] 蒋海旭,许杰,陆清怡.槲皮素治疗类风湿关节炎的研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2021,27(5):243-250.
[50] 魏欣,王士民,孙成,等.基于网络药理学研究白仙风汤剂治疗类风湿性关节炎的药理机制[J].药物评价研究,2019, 42(5):858-868.
[51] 许义方,许文昌.基于网络药理学和分子对接技术探讨阳和汤治疗类风湿性关节炎的作用机制[J].中医临床研究, 2025,17(4):95-104.
[52] 张鸽,黄炜.尼尔雌醇联合醋酸甲羟孕酮治疗围绝经期妇女类风湿性关节炎的临床观察[J].中国药房,2014,25(24): 2275-2277.
[53] ISHIZUKA M, HATORI M, SUZUKI T, et al. Sex steroid receptors in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Sci (Lond). 2004;106(3):293-300.
[54] 李霞,张丹,赵彩虹,等.性激素、催乳素与类风湿关节炎[J].大连大学学报, 2002,23(4):102-105.
[55] CUI J, SHEN Y, LI R. Estrogen synthesis and signaling pathways during aging: from periphery to brain. Trends Mol Med. 2013;19(3):197-209.
[56] KHOSLA S, MELTON LJ 3RD, RIGGS BL. The unitary model for estrogen deficiency and the pathogenesis of osteoporosis: is a revision needed?. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(3):441-451.
[57] BASU A, SCHELL J, SCOFIELD RH. Dietary fruits and arthritis. Food Funct. 2018; 9(1):70-77.
[58] JI JJ, LIN Y, HUANG SS, et al. Quercetin: a potential natural drug for adjuvant treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2013;10(3): 418-421.
[59] 吴志鹏,张迪,高乐,等.从铁死亡探讨中药抑制类风湿关节炎的研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2025,27(9):94-100.
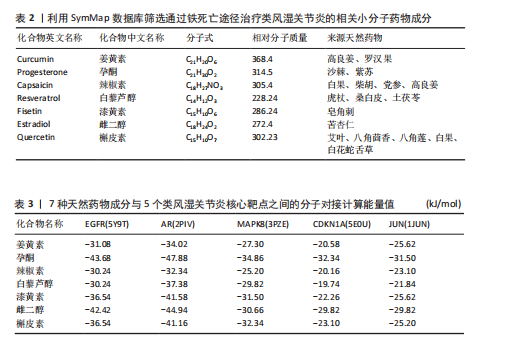
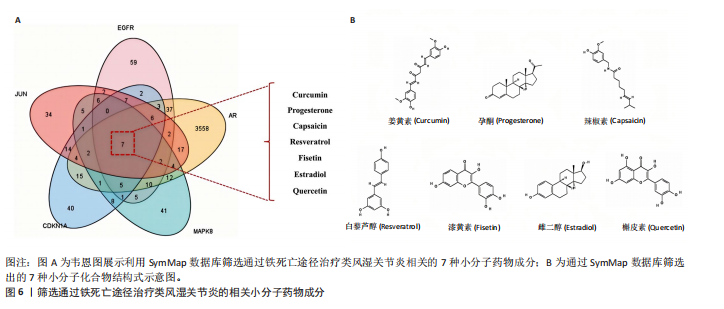
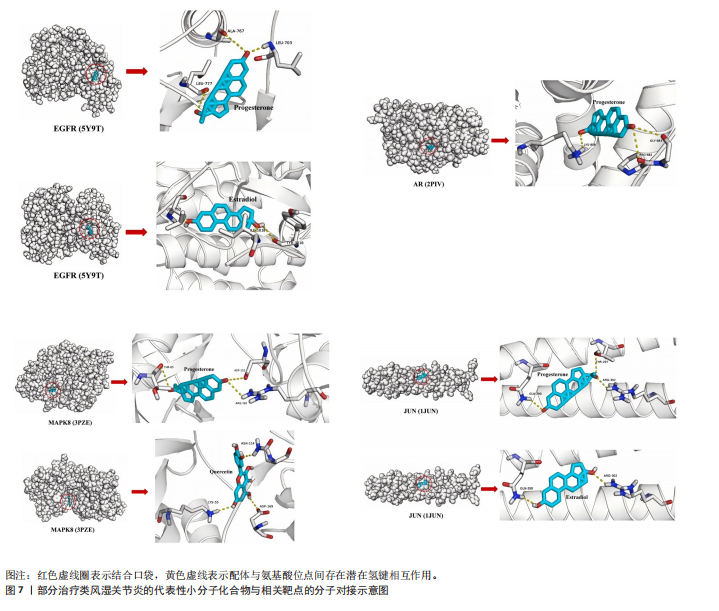
[60] 王丽娟,孟美辰,王志远,等.铁死亡在关节疾病中的作用及研究进展[J].山东第一医科大学(山东省医学科学院)学报,2024,45(10):628-631.
[61] 梁霄,李娅兰,张筠昊,等.基于TLR2/p38 MAPK/NF-κB信号通路探讨独活寄生汤对类风湿性关节炎大鼠的抗炎作用及机制[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2023,29(11):43-52.
|