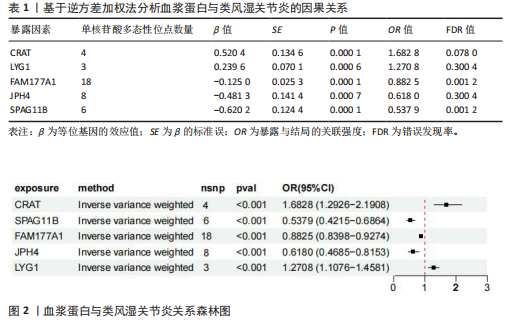
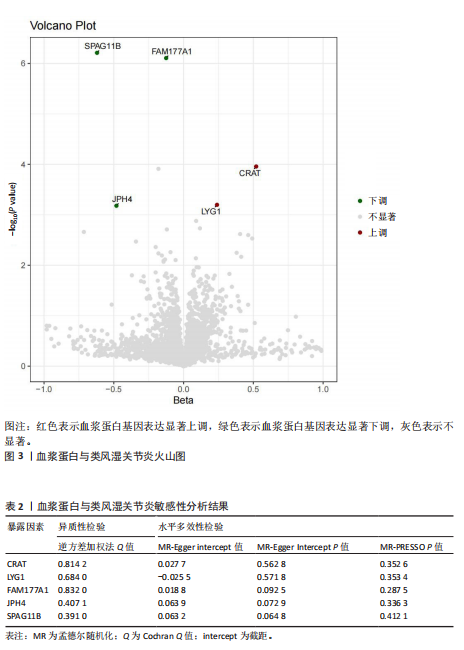
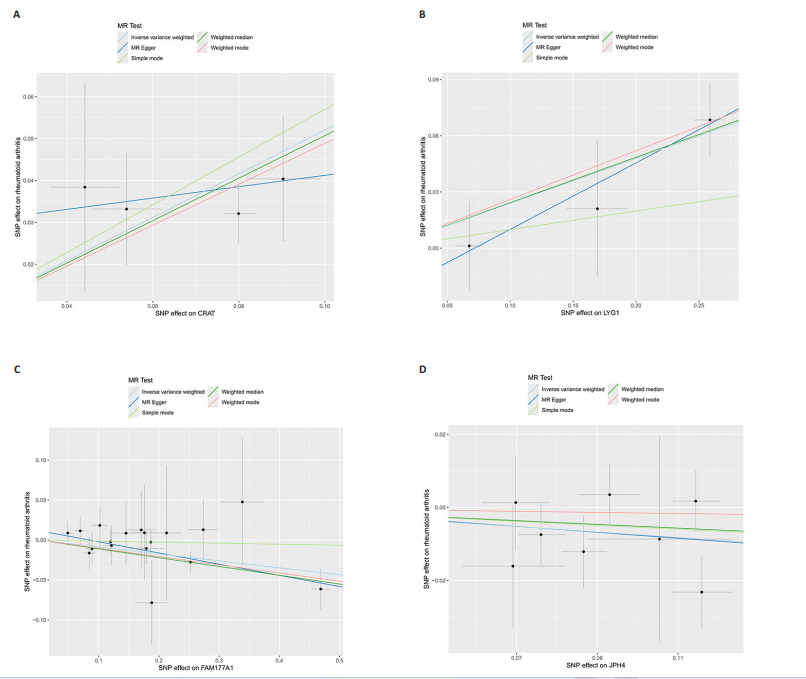
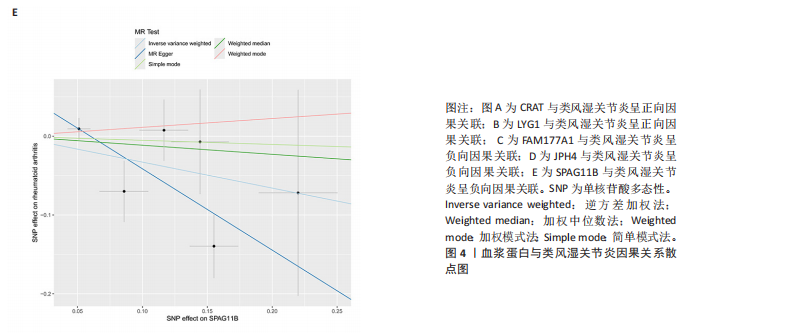
[1] MUELLER AL, PAYANDEH Z, MOHAMMADKHANI N, et al. Recent Advances in Understanding the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis: New Treatment Strategies. Cells. 2021;10(11):3017.
[2] 刘晨旭,郜娜.蛋白质组学在类风湿关节炎中发病机制及诊疗研究中的最新研究进展[J].中国现代医学杂志,2024, 34(7):49-54.
[3] JIANG N, LI Q, LI H, et al. Chinese registry of rheumatoid arthritis (CREDIT) V: sex impacts rheumatoid arthritis in Chinese patients. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022;135(18):2210-2217.
[4] BENNIKE TB. Advances in proteomics: characterization of the innate immune system after birth and during inflammation. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1254948.
[5] 郑梓桐,王美娟,冯育林,等.基于蛋白质组学筛选关节炎相关生物标志物的研究进展[J].中草药,2024,55(18):6383-6392.
[6] FIGUS FA, PIGA M, AZZOLIN I, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis: Extra-articular manifestations and comorbidities. Autoimmun Rev. 2021;20(4):102776.
[7] LABORDE CM, CASTRO-SANTOS P, DÍAZ-PEÑA R. Contribution of Multiplex Immunoassays to Rheumatoid Arthritis Management: From Biomarker Discovery to Personalized Medicine. J Pers Med. 2020;10(4):202.
[8] LOVEGROVE CE, HOWLES SA, FURNISS D, et al. Causal inference in health and disease: a review of the principles and applications of Mendelian randomization. J Bone Miner Res. 2024;39(11):1539-1552.
[9] GBD 2021 Gout Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of gout, 1990-2020, and projections to 2050: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2024;6(8):e507-e517.
[10] CHIU PC, CHATTOPADHYAY A, WU MC, et al. Elucidation of a Causal Relationship Between Platelet Count and Hypertension: A Bi-Directional Mendelian Randomization Study. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8: 743075.
[11] LI HB, WU LJ, JIANG N, et al. Treatment satisfaction with rheumatoid arthritis in patients with different disease severity and financial burden: A subgroup analysis of a nationwide survey in China. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020;133(8):892-898.
[12] SANDERSON E, GLYMOUR MM, HOLMES MV, et al. Mendelian randomization. Nat Rev Methods Primers. 2022;2:6.
[13] STUDENIC P, ALETAHA D, DEWIT M, et al. American College of Rheumatology/EULAR remission criteria for rheumatoid arthritis: 2022 revision. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023;82(1):74-80.
[14] FERKINGSTAD E, SULEM P, ATLASON BA, et al. Large-scale integration of the plasma proteome with genetics and disease. Nat Genet. 2021;53(12):1712-1721.
[15] SMOLEN JS, LANDEWÉ RBM, BERGSTRA SA, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2022 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023;82(1):3-18.
[16] BHAK Y, TENESA A. Mendelian randomization study of whole blood viscosity and cardiovascular diseases. PLoS One. 2024;19(4):e0294095.
[17] ÁLVARO-GRACIA ÁLVARO JM, DÍAZ DEL CAMPO FONTECHA P, ANDRÉU SÁNCHEZ JL, et al. Update of the Consensus Statement of the Spanish Society of Rheumatology on the use of biological and synthetic targeted therapies in rheumatoid arthritis. Reumatol Clin (Engl Ed). 2024;20(8):423-439.
[18] 缪怡,胡朝英,钱柳,等.类风湿性关节炎免疫学研究进展[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版),2011,31(7):1035-1040.
[19] BOERS M, HARTMAN L, OPRIS-BELINSKI D, et al. Low dose, add-on prednisolone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis aged 65+: the pragmatic randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled GLORIA trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022;81(7):925-936.
[20] 林滢,沈楚楚,徐森磊,等.针灸治疗类风湿关节炎的研究进展[J].中国针灸, 2024,44(12):1479-1488.
[21] ROODENRIJS NMT, KEDVES M, HAMAR A, et al. Diagnostic issues in difficult-to-treat rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic literature review informing the EULAR recommendations for the management of difficult-to-treat rheumatoid arthritis. RMD Open. 2021;7(1):e001511.
[22] HU C, DAI Z, XU J, et al. Proteome Profiling Identifies Serum Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:865425.
[23] WATANABE R, HASHIMOTO M, MURATA K, et al. Prevalence and predictive factors of difficult-to-treat rheumatoid arthritis: the KURAMA cohort. Immunol Med. 2022; 45(1):35-44.
[24] ANDONIAN BJ, KOSS A, KOVES TR, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis T cell and muscle oxidative metabolism associate with exercise-induced changes in cardiorespiratory fitness. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):7450.
[25] NAGY G, ROODENRIJS NMT, WELSING PMJ, et al. EULAR points to consider for the management of difficult-to-treat rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022; 81(1):20-33.
[26] ZHU X, LONG W, ZHANG J, et al. Integrated multi-omics revealed that dysregulated lipid metabolism played an important role in RA patients with metabolic diseases. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024;26(1):188.
[27] CONRAN C, KOLFENBACH J, KUHN K, et al. A Review of Difficult-to-Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis: Definition, Clinical Presentation, and Management. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2023;25(12):285-294.
[28] ZHAO Z, REN J, XIE S, et al. Identification of biomarkers associated with CD8+ T cells in rheumatoid arthritis and their pan-cancer analysis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1044909.
[29] VAN MULLIGEN E, WEEL AE, HAZES JM, et al. Tapering towards DMARD-free remission in established rheumatoid arthritis: 2-year results of the TARA trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(9):1174-1181.
[30] SHARMA S, SUN X, AGARWAL S, et al. Role of carnitine acetyl transferase in regulation of nitric oxide signaling in pulmonary arterial endothelial cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2012; 14(1):255-272.
[31] EULER N, HELLBACHER E, KLINT EA, et al. Diffuse large B cell lymphoma in rheumatoid arthritis patients is associated with elevated B-cell driving factors including CXCL13. Clin Immunol. 2025;275:110476.
[32] TRAGNI V, PRIMIANO G, TUMMOLO A, et al. Personalized Medicine in Mitochondrial Health and Disease: Molecular Basis of Therapeutic Approaches Based on Nutritional Supplements and Their Analogs. Molecules. 2022;27(11):3494.
[33] CHEN L, XU L, ZHANG Y, et al. Dioscin alleviates the dysfunction of fibroblast-like synoviocytes by circ_0008267/miR-942-5p/FKBP5 axis during rheumatoid arthritis. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03872-y.
[34] LEE SY, PARK JL, KIM K, et al. Identification of NIFTP-Specific mRNA Markers for Reliable Molecular Diagnosis of Thyroid Tumors. Endocr Pathol. 2023; 34(3):311-322.
[35] LI Y, PRADEEP SINGH S. Computational Screening of IL-1 and IL-6 Inhibitors for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Insights from Molecular Docking and Dynamics Analysis. Curr Pharm Des. 2025. doi: 10.2174/0113816128344776250222043907.
[36] LIU H, YU Z, TANG B, et al. LYG1 Deficiency Attenuates the Severity of Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease via Skewing Allogeneic T Cells Polarization Towards Treg Cells. Front Immunol. 2021;12:647894.
[37] SUR D, PRAMANIK R. The TIM-3/Gal-9 Pathway: A Promising Therapeutic Target for Regulation of Immune Checkpoint in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2025. doi: 10.2174/0115733971330865250312075719.
[38] GUIMARÃES ES, MARTINS JM, GOMES MTR, et al. Lack of Interleukin-6 Affects IFN-γ and TNF-α Production and Early In Vivo Control of Brucella abortus Infection. Pathogens. 2020;9(12):1040.
[39] HUANG H, WEI X. Therapeutic potential of CD20/CD3 bispecific antibodies in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Rheumatol Immunol Res. 2025;5(4): 209-216.
[40] PANG X, XU F, FAN C, et al. Global research trends of MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: bibliometrics and visualization analysis. Clin Rheumatol. 2025;44(1):53-66.
[41] ALI S, ZEHRA A, KHALID MU, et al. Role of C-reactive protein in disease progression, diagnosis and management. Discoveries (Craiova). 2023;11(4):e179.
[42] YANG C, LI D, TENG D, et al. Epigenetic Regulation in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:859400.
[43] KYRIAKIDI M, VETSIKA EK, FRAGOULIS GE, et al. Identification and Clinical Correlation of Circulating MAIT, γδ T, ILC3, and Pre-Inflammatory Mesenchymal Cells in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Spondyloarthritis. Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2023;35(2):312-315.
[44] LIAO BW, ZHANG HY, DU WT, et al. FAM177A1 Inhibits IL-1β-Induced Signaling by Impairing TRAF6-Ubc13 Association. J Immunol. 2021;207(12):3090-3097.
[45] BYKERK VP. Clinical implications of synovial tissue phenotypes in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024;10:1093348.
[46] CHEN S, WANG Q, WANG H, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in T cell-mediated diseases. Scand J Immunol. 2023; 98(3):e13307.
[47] PIGGOTT CA, JIN Y. Junctophilins: Key Membrane Tethers in Muscles and Neurons. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021;14:709390.
[48] GHODOOSIFAR S, DEHGHAN G, SAFARALIZADEH R, et al. The Association between the Expression of MicroRNA-4270 and MicroRNA-4441 with some Metabolic Factors in Iranian Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2023;22(6):536-550.
[49] NARMADHA G, YENUGU S. Molecular modeling of the human sperm associated antigen 11 B (SPAG11B) proteins. Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2015;61(2):78-88.
[50] WANG J, LIU J. Correlation between protein expression profiling of inflammation and bone metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Afr Health Sci. 2023;23(3):624-634.
[51] DENADAI-SOUZA A, RIBEIRO CM, ROLLAND C, et al. Effect of tryptase inhibition on joint inflammation: a pharmacological and lentivirus-mediated gene transfer study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):124.
|