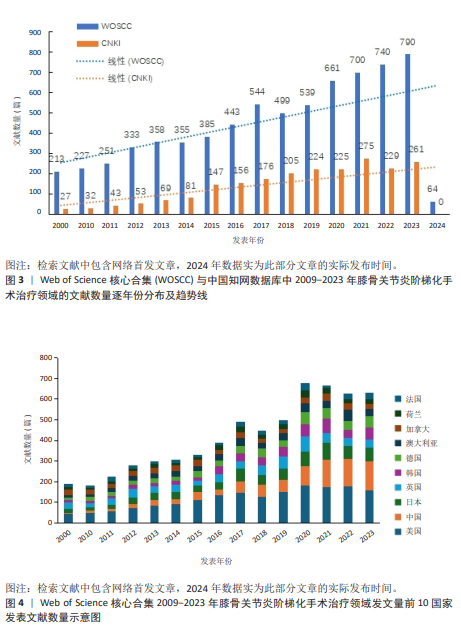
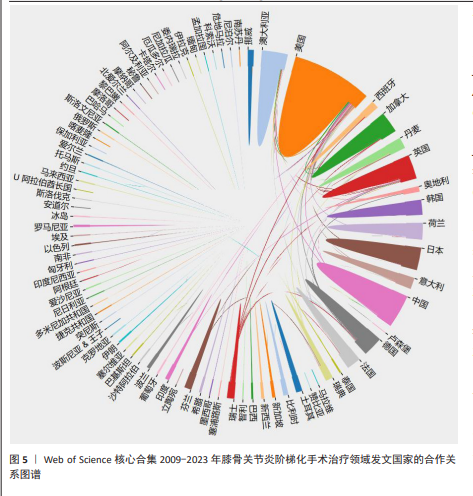
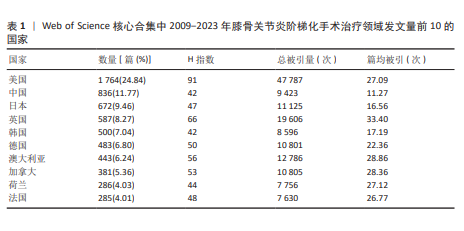
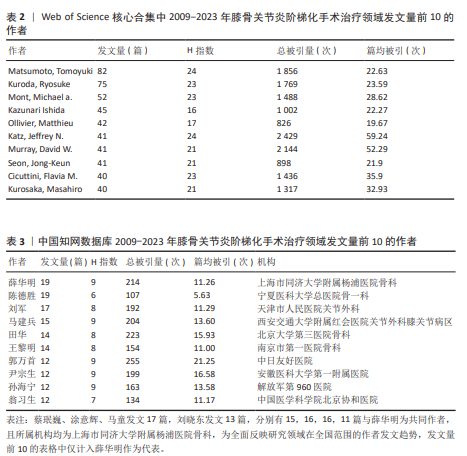
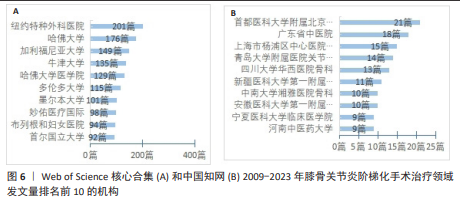
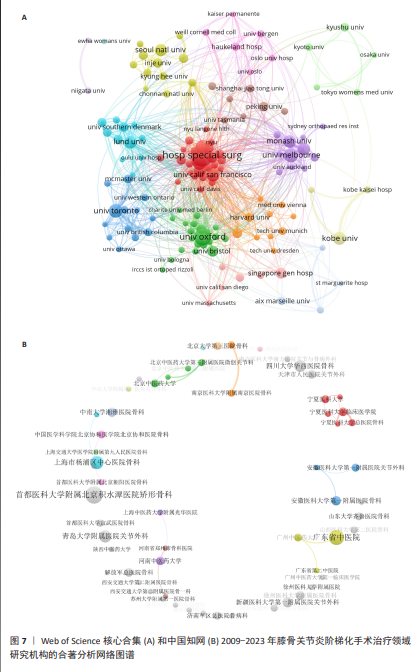
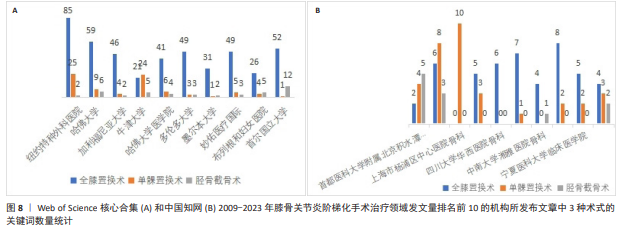
[1] 中国骨关节炎诊疗指南专家组,中国老年保健协会疼痛病学分会,黄东,等. 中国骨关节炎诊疗指南(2024版)[J]. 中华疼痛学杂志,2024,20(3):323-338.
[2] KATZ JN, ARANT KR, LOESER RF. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review. JAMA. 2021; 325(6):568-578.
[3] SKOU ST, ROOS EM, LAURSEN MB, et al. A Randomized, Controlled Trial of Total Knee Replacement. New Eng J Med. 2015; 373(17):1597-1606.
[4] BESWICK AD, WYLDE V, GOOBERMAN-HILL R, et al. What proportion of patients report long-term pain after total hip or knee replacement for osteoarthritis? A systematic review of prospective studies in unselected patients. BMJ Open. 2012;2(1):e000435.
[5] SIPAHI S, ÇELIK KEK, DOĞAN N, et al. Global Trends and Developments in Diet and Longevity Research: A Bibliometric Analysis. Nutrients. 2025;17(13):2119.
[6] SUN HL, BAI W, LI XH, et al. Schizophrenia and Inflammation Research: A Bibliometric Analysis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:907851.
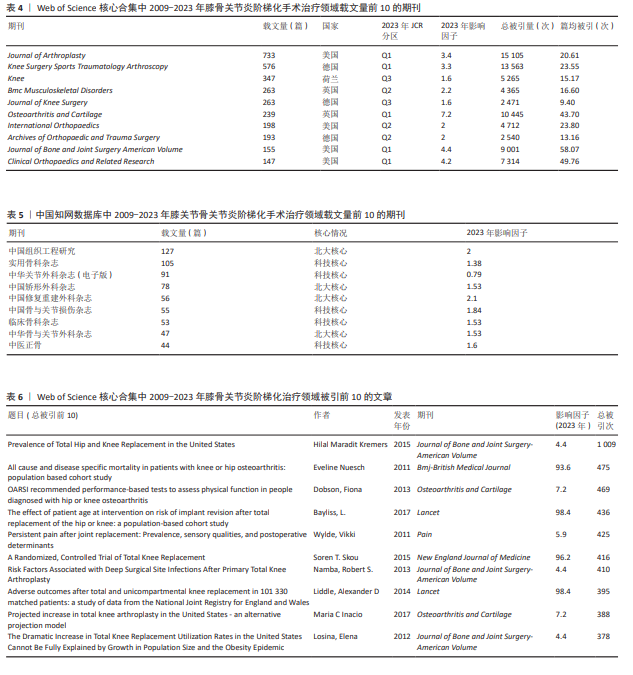
[7] MARADIT KH, LARSON DR, CROWSON CS, et al. Prevalence of Total Hip and Knee Replacement in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(17):1386-1397.
[8] NÜESCH E, DIEPPE P, REICHENBACH S, et al. All cause and disease specific mortality in patients with knee or hip osteoarthritis: population based cohort study. BMJ. 2011; 342:d1165.
[9] DOBSON F, HINMAN RS, ROOS EM, et al. OARSI recommended performance-based tests to assess physical function in people diagnosed with hip or knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(8): 1042-1052.
[10] BAYLISS LE, CULLIFORD D, MONK AP, et al. The effect of patient age at intervention on risk of implant revision after total replacement of the hip or knee: a population-based cohort study. Lancet. 2017;389(10077):1424-1430.
[11] WYLDE V, HEWLETT S, LEARMONTH ID, et al. Persistent pain after joint replacement: prevalence, sensory qualities, and postoperative determinants. Pain. 2011;152(3):566-572.
[12] NAMBA RS, INACIO MC, PAXTON EW. Risk factors associated with deep surgical site infections after primary total knee arthroplasty: an analysis of 56,216 knees. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(9):775-782.
[13] LIDDLE AD, JUDGE A, PANDIT H, et al. Adverse outcomes after total and unicompartmental knee replacement in 101,330 matched patients: a study of data from the National Joint Registry for England and Wales. Lancet. 2014;384(9952): 1437-1445.
[14] INACIO MCS, PAXTON EW, GRAVES SE, et al. Projected increase in total knee arthroplasty in the United States - an alternative projection model. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(11):1797-1803.
[15] LOSINA E, THORNHILL TS, ROME BN, et al. The dramatic increase in total knee replacement utilization rates in the United States cannot be fully explained by growth in population size and the obesity epidemic. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(3):201-107.
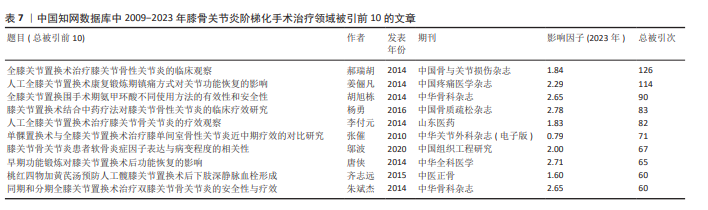
[16] 郝瑞胡,郭林,李丽丽,等.全膝关节置换术治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的临床观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2014,29(6): 544-546.
[17] 姜俪凡,冯艺,安海燕.人工全膝关节置换术康复锻炼期镇痛方式对关节功能恢复的影响[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2014, 20(2):90-94.
[18] 胡旭栋,周宗科,裴福兴,等.全膝关节置换围手术期氨甲环酸不同使用方法的有效性和安全性[J].中华骨科杂志,2014, 34(6):599-604.
[19] 杨勇,赵良虎,黄金.膝关节置换术结合中药疗法对膝关节骨性关节炎的临床疗效研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2016, 22(7):837-841.
[20] 李付元,冯世庆,周恒星,等.人工全膝关节置换术治疗膝关节骨关节炎的疗效观察[J].山东医药,2014,54(5):71-73.
[21] 张催,陈游,张春雷,等.单髁置换术与全膝关节置换术治疗膝单间室骨性关节炎近中期疗效的对比研究[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2010,4(2):192-197.
[22] 邬波,马旭,柳椰,等.膝关节骨关节炎患者软骨炎症因子表达与病变程度的相关性[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(2): 236-241.
[23] 唐侠.早期功能锻炼对膝关节置换术后功能恢复的影响[J].中华全科医学,2014, 12(8):1331-1332+1343.
[24] 齐志远,陈秀民,王在斌,等.桃红四物加黄芪汤预防人工髋膝关节置换术后下肢深静脉血栓形成[J].中医正骨,2015, 27(3):71-72+75.
[25] 朱斌杰, 陈哲峰, 刘锋, 等. 同期和分期全膝关节置换术治疗双膝关节骨关节炎的安全性与疗效 [J] . 中华骨科杂志,2014, 34(6): 619-623.
[26] ZHAO R, REN H, LI P, et al. Research trends and frontiers in rehabilitation after total knee arthroplasty: based on bibliometric and visualization analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024;19(1):897.
[27] HE J, HE L, GENG B, et al. Bibliometric Analysis of the Top-Cited Articles on Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2021;36(5):1810-1818.e3.
[28] HOU W, XIAO F, PENG P, et al. Osteotomy for treating knee osteoarthritis from 2012 to 2023: Bibliometric analysis and global trends. Medicine. 2024; 103(7):e37036.
[29] KOW RY, ABDUL RR, MOHAMAD NAZARALLAH MH, et al. Robotic-Assisted Hip and Knee Arthroplasty: A Bibliometric Analysis Using the Scopus Database. Cureus. 2024;16(3):e56617.
[30] LIU P, ZHANG C, LU Z, et al. Global research status and trends of UKA for knee osteoarthritis: a bibliometric analysis. Arthroplasty (London, England). 2020; 2(1):20.
[31] 庞凤祥,龚水帝,陈立新,等.胫骨高位截骨术研究现状的文献计量学和可视化分析[J].骨科,2020,11(2):131-139.
[32] HUANG C, HOU Y, YANG Y, et al. A bibliometric analysis of the application of physical therapy in knee osteoarthritis from 2013 to 2022. Front Med. 2024;11:1418433
[33] 赵盾,祁令臣,徐金凡,等.膝骨关节炎疼痛领域热点与前沿的可视化分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(15): 3280-3289. |