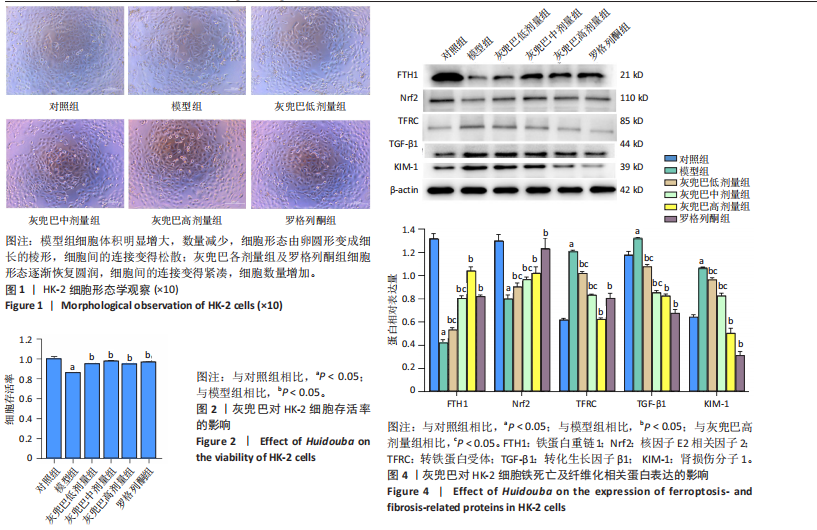
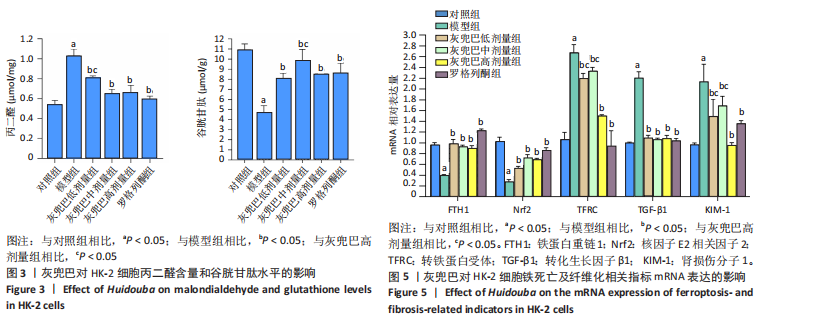
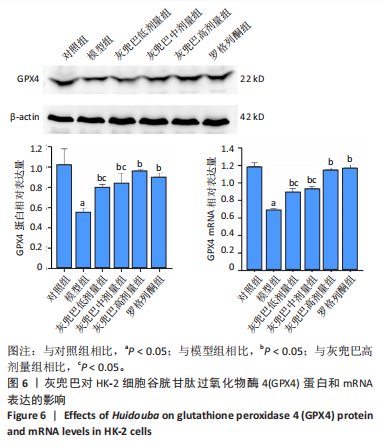
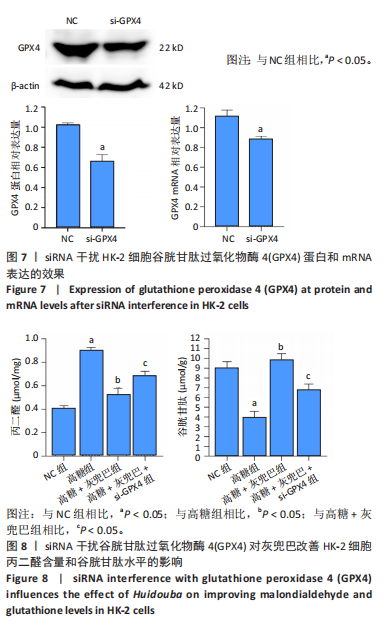
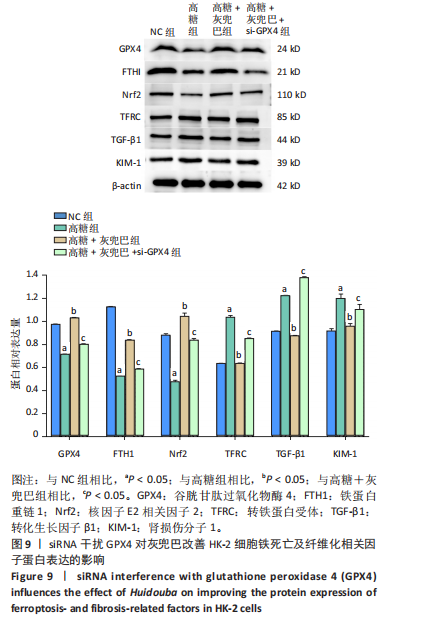
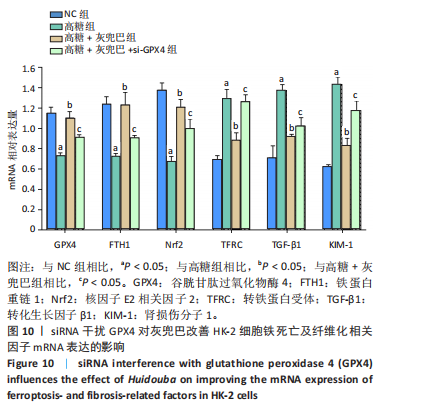
[1] SAGOO MK, GNUDI L. Diabetic Nephropathy: An Overview. Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2067:3-7.
[2] BAI S, XIONG X, TANG B, et al. hsa-miR-199b-3p Prevents the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Dysfunction of the Renal Tubule by Regulating E-cadherin through Targeting KDM6A in Diabetic Nephropathy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:8814163.
[3] KUSHWAHA K, KABRA U, DUBEY R, et al. Diabetic Nephropathy: Pathogenesis to Cure. Curr Drug Targets. 2022;23(15):1418-1429.
[4] ROCHETTE L, DOGON G, RIGAL E, et al. Lipid Peroxidation and Iron Metabolism: Two Corner Stones in the Homeostasis Control of Ferroptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;24(1):449.
[5] 陶倩, 刘念, 陈静,等. 铁死亡与肿瘤免疫[J]. 中南大学学报(医学版),2024,49(8):1309-1315.
[6] HENNING Y, BLIND US, LARAFA S, et al. Hypoxia aggravates ferroptosis in RPE cells by promoting the Fenton reaction. Cell Death Dis. 2022; 13(7):662.
[7] TANG D, CHEN X, KANG R, et al. Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res. 2021;31(2):107-125.
[8] HE J, LI Z, XIA P, et al. Ferroptosis and ferritinophagy in diabetes complications. Mol Metab. 2022;60:101470.
[9] URSINI F, MAIORINO M. Lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis: The role of GSH and GPx4. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;152:175-185.
[10] QIAO Y, SUN C, KAN S, et al. SRS 16-86 promotes diabetic nephropathy recovery by regulating ferroptosis. Exp Physiol. 2024;109(7):1199-1210.
[11] LIU Z, NAN P, GONG Y, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-triggered ferroptosis via the XBP1-Hrd1-Nrf2 pathway induces EMT progression in diabetic nephropathy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;164:114897.
[12] TAN H, CHEN J, LI Y, et al. Glabridin, a bioactive component of licorice, ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by regulating ferroptosis and the VEGF/Akt/ERK pathways. Mol Med. 2022;28(1):58.
[13] WU Q, HUANG F. Targeting ferroptosis as a prospective therapeutic approach for diabetic nephropathy. Ann Med. 2024;56(1):2346543.
[14] LI S, ZHENG L, ZHANG J, et al. Inhibition of ferroptosis by up-regulating Nrf2 delayed the progression of diabetic nephropathy. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;162:435-449.
[15] ZHANG Y, QU Y, CAI R, et al. Atorvastatin ameliorates diabetic nephropathy through inhibiting oxidative stress and ferroptosis signaling. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024;976:176699.
[16] XIONG D, HU W, HAN X, et al. Rhein Inhibited Ferroptosis and EMT to Attenuate Diabetic Nephropathy by Regulating the Rac1/NOX1/β-Catenin Axis. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023;28(5):100.
[17] WANG Y, BI R, QUAN F, et al. Ferroptosis involves in renal tubular cell death in diabetic nephropathy. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;888:173574.
[18] CHEN H, ZHANG Y, MIAO Y, et al. Vitamin D inhibits ferroptosis and mitigates the kidney injury of prediabetic mice by activating the Klotho/p53 signaling pathway. Apoptosis. 2024;29(9-10):1780-1792.
[19] LV S, LI H, ZHANG T, et al. San-Huang-Yi-Shen capsule ameliorates diabetic nephropathy in mice through inhibiting ferroptosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;165:115086.
[20] JIN T, CHEN C. Umbelliferone delays the progression of diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting ferroptosis through activation of the Nrf-2/HO-1 pathway. Food Chem Toxicol. 2022;163:112892.
[21] ZHANG S, LI Y, LIU X, et al. Carnosine alleviates kidney tubular epithelial injury by targeting NRF2 mediated ferroptosis in diabetic nephropathy. Amino Acids. 2023;55(9):1141-1155.
[22] LV S, FAN L, CHEN X, et al. Jian-Pi-Gu-Shen-Hua-Yu Decoction Alleviated Diabetic Nephropathy in Mice through Reducing Ferroptosis. J Diabetes Res. 2024;2024:9990304.
[23] FENG X, WANG S, SUN Z, et al. Ferroptosis Enhanced Diabetic Renal Tubular Injury via HIF-1α/HO-1 Pathway in db/db Mice. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:626390.
[24] FANG X, SONG J, CHEN Y, et al. LncRNA SNHG1 knockdown inhibits hyperglycemia induced ferroptosis via miR-16-5p/ACSL4 axis to alleviate diabetic nephropathy.J Diabetes Investig. 2023;14(9):1056-1069.
[25] XUE M, TIAN Y, ZHANG H, et al. Curcumin nanocrystals ameliorate ferroptosis of diabetic nephropathy through glutathione peroxidase 4. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15:1508312.
[26] ZHOU Y, HU T, ZENG H, et al. Naringenin Inhibits Ferroptosis in Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells of Diabetic Nephropathy Through SIRT1/FOXO3a Signaling Pathway. Drug Dev Res. 2025;86(1):e70044.
[27] ZHANG S, ZHANG S, WANG H, et al. Vitexin ameliorated diabetic nephropathy via suppressing GPX4-mediated ferroptosis. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023;951:175787.
[28] WU K, FEI L, WANG X, et al. ZIP14 is involved in iron deposition and triggers ferroptosis in diabetic nephropathy. Metallomics. 2022; 14(7):mfac034.
[29] 杨坤宝, 庞宗然. 藏药灰兜巴治疗糖尿病的研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2017,48(8):1682-1686.
[30] BAI YH, SHI DX, LU HY, et al.Hypoglycemic effects of Tibetan medicine Huidouba in STZ-induced diabetic mice and db/db mice. Chin Herb Med. 2021;13(2):202-209.
[31] YANG K, BAI Y, YU N, et al. Huidouba Improved Podocyte Injury by Down-Regulating Nox4 Expression in Rats With Diabetic Nephropathy. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:587995.
[32] 张圣英. 灰兜巴通过激活PPARγ介导TGF-β/Smad信号通路抑制高糖诱导的HK-2细胞纤维化机制研究[D].承德:承德医学院,2023.
[33] LU Q, CHEN Y B, YANG H, et al. Inactivation of TSC1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition of renal tubular epithelial cells in mouse diabetic nephropathy.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019;40(12):1555-1567.
[34] 刘东齐, 闫仕祺, 刘浩龙,等.芍药苷对糖尿病周围神经病变状态下线粒体输入途径蛋白TOM20的作用[J].中草药,2024,55(9): 2987-2995.
[35] 刁俊玲, 伍敏, 黄荣凤,等. 新型PPARγ激动剂CMHX008对高糖诱导人肾小管上皮HK-2细胞纤维化的影响及机制[J].中国药理学通报,2019,35(10):1363-1369.
[36] 谷李影, 杨胜富, 张启明,等. 香青兰总黄酮(TFDM)对高糖诱导的视网膜神经节细胞氧化损伤的影响及其机制[J]. 眼科新进展, 2024,44(12):937-942.
[37] 罗羽, 王仙园, 杨云青.糖尿病肾病肾纤维化病变的发病机制研究进展[J].护理研究,2013,27(4):292-295.
[38] LI J, SHU L, JIANG Q, et al. Oridonin ameliorates renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Ren Fail. 2024;46(1):2347462.
[39] WANG Y, YUE S, CAI F, et al. Treatment of berberine alleviates diabetic nephropathy by reducing iron overload and inhibiting oxidative stress. Histol Histopathol. 2023;38(9):1009-1016.
[40] CHEN J, ZHANG MH, ZHANG L, et al. [Protective effects and mechanism of glycosides/phenol component of Moutan Cortex on renal injury of diabetic nephropathy rats]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016; 41(11):1990-1998.
[41] MAO ZM, SHEN SM, WAN YG, et al. Huangkui capsule attenuates renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy rats through regulating oxidative stress and p38MAPK/Akt pathways, compared to α-lipoic acid. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015;173:256-265.
[42] WU X, LI H, WAN Z, et al. The combination of ursolic acid and empagliflozin relieves diabetic nephropathy by reducing inflammation, oxidative stress and renal fibrosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021; 144:112267.
[43] DU N, XU Z, GAO M, et al. Combination of Ginsenoside Rg1 and Astragaloside IV reduces oxidative stress and inhibits TGF-β1/Smads signaling cascade on renal fibrosis in rats with diabetic nephropathy. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018;12:3517-3524.
[44] ARZUK E, ARMAğAN G. Genistein and daidzein induce ferroptosis in MDA-MB-231 cells. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2024;8:rgae106.
[45] DODSON M, CASTRO-PORTUGUEZ R, ZHANG DD. NRF2 plays a critical role in mitigating lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 2019; 23:101107.
[46] NIELSEN SE, SCHJOEDT KJ, ASTRUP AS, et al. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL) and Kidney Injury Molecule 1 (KIM1) in patients with diabetic nephropathy: a cross-sectional study and the effects of lisinopril. Diabet Med. 2010;27(10):1144-1150.
[47] MORI Y, AJAY AK, CHANG JH, et al. KIM-1 mediates fatty acid uptake by renal tubular cells to promote progressive diabetic kidney disease. Cell Metab. 2021;33(5):1042-1061.
[48] WANG H, YU X, LIU D, et al. VDR Activation Attenuates Renal Tubular Epithelial Cell Ferroptosis by Regulating Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway in Diabetic Nephropathy.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(10):e2305563.
[49] JIA J, TAN R, XU L, et al. Hederagenin improves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy by regulating Smad3/NOX4/SLC7A11 signaling-mediated tubular cell ferroptosis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024;135:112303.
[50] KIM S, KANG S W, JOO J, et al. Characterization of ferroptosis in kidney tubular cell death under diabetic conditions. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(2):160.
[51] SHAN XM, CHEN CW, ZOU DW, et al. Suppression of ferroptosis through the SLC7A11/glutathione/glutathione peroxidase 4 axis contributes to the therapeutic action of the Tangshenning formula on diabetic renal tubular injury. Chin Med. 2024;19(1):151.
[52] HUANG J, CHEN G, WANG J, et al. Platycodin D regulates high glucose-induced ferroptosis of HK-2 cells through glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4). Bioengineered. 2022;13(3):6627-6637.
[53] CHEN J, OU Z, GAO T, et al. Ginkgolide B alleviates oxidative stress and ferroptosis by inhibiting GPX4 ubiquitination to improve diabetic nephropathy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;156:113953.
[54] 孟凡欣, 王立英, 宋静静,等.灰兜巴多糖对糖尿病降糖作用的研究[J].时珍国医国药,2012,23(6):1557-1558.
[55] 伍艳, 王小楠, 陈烽烽,等.灰兜巴活性成分治疗Ⅱ型糖尿病效果研究[J].中药材,2013,36(8):1313-1316. |