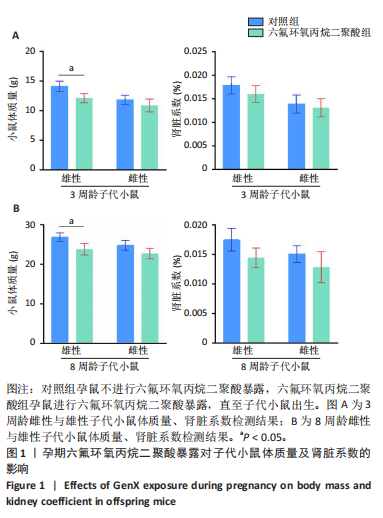
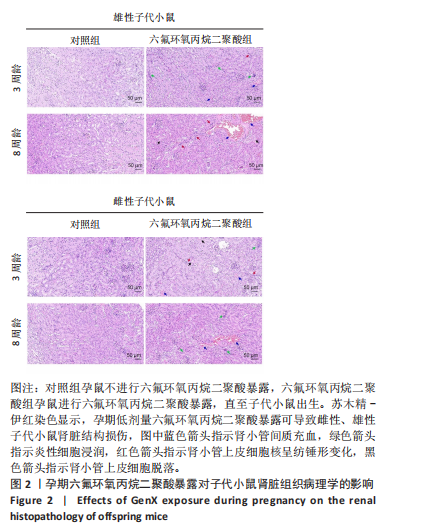
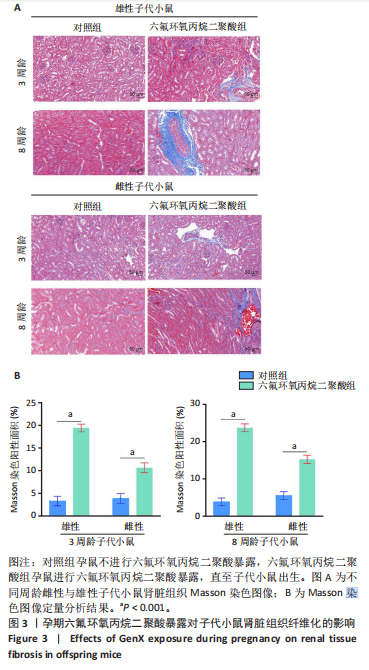
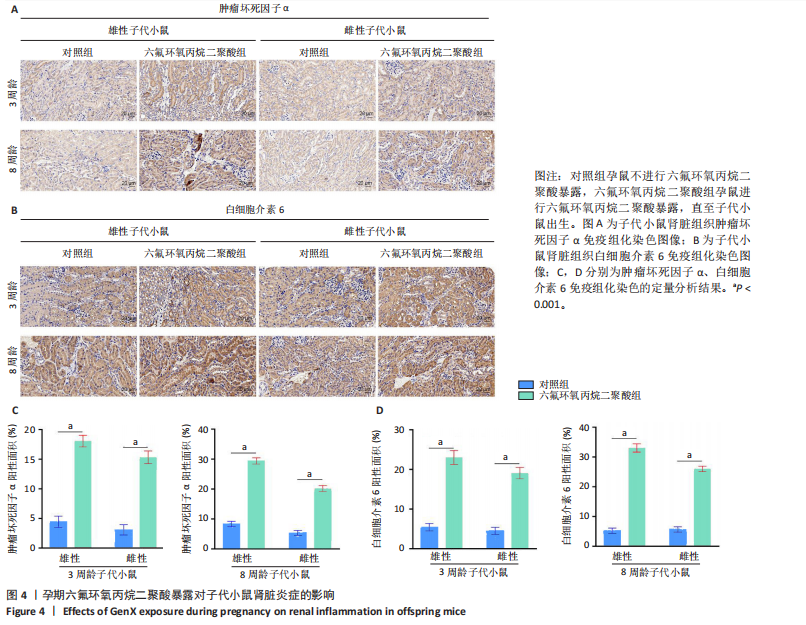
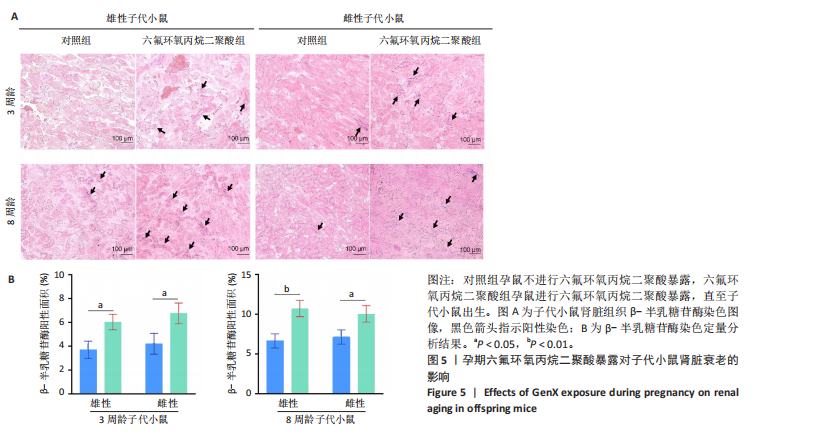
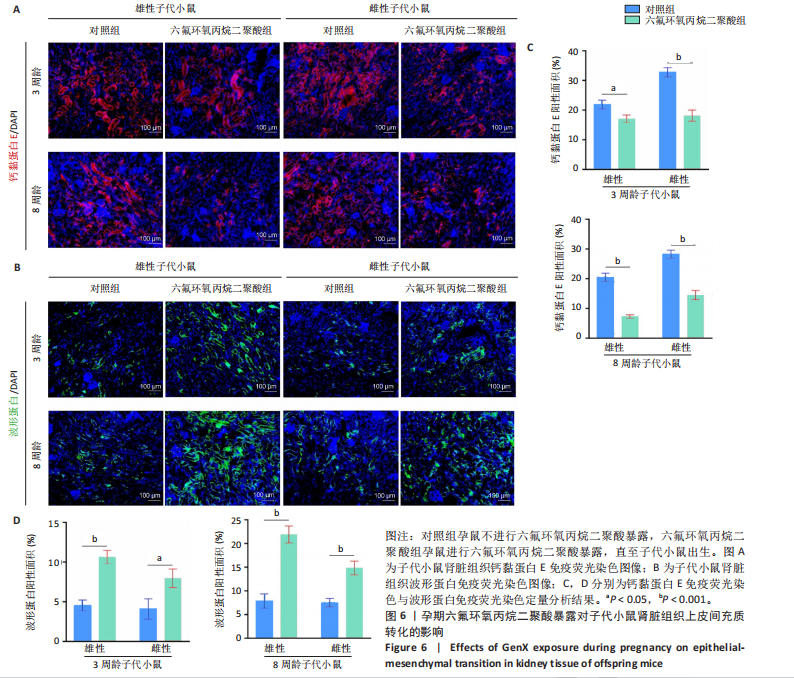
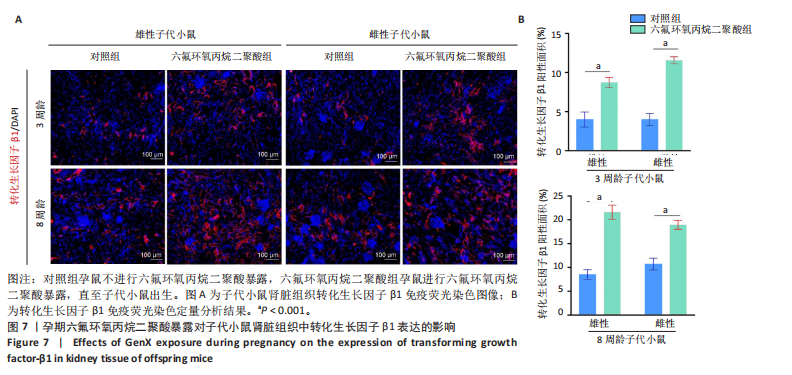
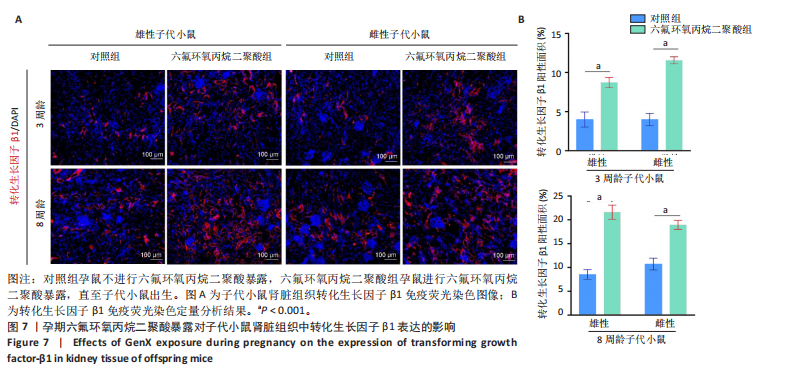
[1] COPERCHINI F, CROCE L, RICCI G, et al. Thyroid Disrupting Effects of Old and New Generation PFAS. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020; 11:612320.
[2] DIXIT F, DUTTA R, BARBEAU B, et al. PFAS removal by ion exchange resins: A review. Chemosphere. 2021;272:129777.
[3] PELCH KE, READE A, WOLFFE TAM, et al. PFAS health effects database: Protocol for a systematic evidence map. Environ Int. 2019;130:104851.
[4] KOSKELA A, FINNILÄ MA, KORKALAINEN M, et al. Effects of developmental exposure to perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) on long bone morphology and bone cell differentiation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016;301:14-21.
[5] SHRESTHA S, BLOOM MS, YUCEL R, et al. Perfluoroalkyl substances, thyroid hormones, and neuropsychological status in older adults. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2017;220(4):679-685.
[6] RUMSBY PC, MCLAUGHLIN CL, HALL T. Perfluorooctane sulphonate and perfluorooctanoic acid in drinking and environmental waters. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2009;367(1904):4119-4136.
[7] WANG Z, DEWITT JC, HIGGINS CP, et al. A Never-Ending Story of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs)? Environ Sci Technol. 2017;51(5):2508-2518.
[8] BLAKE BE, COPE HA, HALL SM, et al. Evaluation of Maternal, Embryo, and Placental Effects in CD-1 Mice following Gestational Exposure to Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) or Hexafluoropropylene Oxide Dimer Acid (HFPO-DA or GenX). Environ Health Perspect. 2020;128(2):27006.
[9] GALLOWAY JE, MORENO AVP, LINDSTROM AB, et al. Evidence of Air Dispersion: HFPO-DA and PFOA in Ohio and West Virginia Surface Water and Soil near a Fluoropolymer Production Facility. Environ Sci Technol. 2020;54(12):7175-7184.
[10] WU S, XIE J, ZHAO H, et al. Pre-differentiation GenX exposure induced neurotoxicity in human dopaminergic-like neurons. Chemosphere. 2023;332:138900.
[11] PAN Y, ZHANG H, CUI Q, et al. Worldwide Distribution of Novel Perfluoroether Carboxylic and Sulfonic Acids in Surface Water. Environ Sci Technol. 2018;52(14):7621-7629.
[12] HEIDARI H, ABBAS T, OK YS, et al. GenX is not always a better fluorinated organic compound than PFOA: A critical review on aqueous phase treatability by adsorption and its associated cost. Water Res. 2021;205:117683.
[13] REN W, WANG Z, GUO H, et al. GenX analogs exposure induced greater hepatotoxicity than GenX mainly via activation of PPARα pathway while caused hepatomegaly in the absence of PPARα in female mice. Environ Pollut. 2024;344:123314.
[14] PENG BX, LI F, MORTIMER M, et al. Perfluorooctanoic acid alternatives hexafluoropropylene oxides exert male reproductive toxicity by disrupting blood-testis barrier. Sci Total Environ. 2022;846:157313.
[15] LV D, LIU H, AN Q, et al. Association of adverse fetal outcomes with placental inflammation after oral gestational exposure to hexafluoropropylene oxide dimer acid (GenX) in Sprague-Dawley rats. J Hazard Mater. 2024;461:132536.
[16] XIE X, ZHOU J, HU L, et al. Exposure to hexafluoropropylene oxide dimer acid (HFPO-DA) disturbs the gut barrier function and gut microbiota in mice. Environ Pollut. 2021;290:117934.
[17] WANG X, WANG K, MAO W, et al. Emerging perfluoroalkyl substances retard skeletal growth by accelerating osteoblasts senescence via ferroptosis. Environ Res. 2024;258:119483.
[18] YAO D, SHAO J, JIA D, et al. Immunotoxicity of legacy and alternative per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances on zebrafish larvae. Environ Pollut. 2024;358:124511.
[19] PETRIELLO MC, MOTTALEB MA, SERIO TC, et al. Serum concentrations of legacy and emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the Anniston Community Health Surveys (ACHS I and ACHS II). Environ Int. 2022;158:106907.
[20] CALAFAT AM, KATO K, HUBBARD K, et al. Legacy and alternative per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the U.S. general population: Paired serum-urine data from the 2013-2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Environ Int. 2019;131:105048.
[21] LESLIE HA, VAN VELZEN MJM, BRANDSMA SH, et al. Discovery and quantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood. Environ Int. 2022;163:107199.
[22] DO NASCIMENTO LCP, NETO J, DE ANDRADE BV, et al. Maternal exposure to high-fat and high-cholesterol diet induces arterial hypertension and oxidative stress along the gut-kidney axis in rat offspring. Life Sci. 2020;261:118367.
[23] NIELSEN F, FISCHER FC, LETH PM, et al. Occurrence of Major Perfluorinated Alkylate Substances in Human Blood and Target Organs. Environ Sci Technol. 2024;58(1):143-149.
[24] RHEE J, CHANG VC, CHENG I, et al. Serum concentrations of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and risk of renal cell carcinoma in the Multiethnic Cohort Study. Environ Int. 2023;180:108197.
[25] GUO WQ, HAO WD, XIAO WS. Emerging Perfluorinated Chemical GenX: Environmental and Biological Fates and Risks. Environment & Health. 2024; doi: 10.1021/envhealth.4c00164.
[26] HUANG W, HICKSON LJ, EIRIN A, et al. Cellular senescence: the good, the bad and the unknown. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2022;18(10):611-627.
[27] SHENG L, ZHUANG S. New Insights Into the Role and Mechanism of Partial Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Kidney Fibrosis. Front Physiol. 2020;11:569322.
[28] SELVARANI R, MOHAMMED S, RICHARDSON A. Effect of rapamycin on aging and age-related diseases-past and future. Geroscience. 2021;43(3):1135-1158.
[29] MANNICK JB, LAMMING DW. Targeting the biology of aging with mTOR inhibitors. Nat Aging. 2023;3(6):642-660.
[30] LAU C, THIBODEAUX JR, HANSON RG, et al. Effects of perfluorooctanoic acid exposure during pregnancy in the mouse. Toxicol Sci. 2006;90(2): 510-518.
[31] PAN C, WANG X, FAN Z, et al. Polystyrene microplastics facilitate renal fibrosis through accelerating tubular epithelial cell senescence. Food Chem Toxicol. 2024;191:114888.
[32] CONLEY JM, LAMBRIGHT CS, EVANS N, et al. Dose additive maternal and offspring effects of oral maternal exposure to a mixture of three PFAS (HFPO-DA, NBP2, PFOS) during pregnancy in the Sprague-Dawley rat. Sci Total Environ. 2023;892:164609.
[33] KATO K, KALATHIL AA, PATEL AM, et al. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and fluorinated alternatives in urine and serum by on-line solid phase extraction-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Chemosphere. 2018;209:338-345.
[34] FENG L, LANG Y, FENG Y, et al. Maternal F-53B exposure during pregnancy and lactation affects bone growth and development in male offspring. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024;279:116501.
[35] IMAM MU, ISMAIL M, OOI DJ, et al. Increased risk of insulin resistance in rat offsprings exposed prenatally to white rice. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2015;59(1):180-184.
[36] MA T, ZHOU Y, XIA Y, et al. Maternal Exposure to Di-n-butyl Phthalate Promotes the Formation of Testicular Tight Junctions through Downregulation of NF-κB/COX-2/PGE(2)/MMP-2 in Mouse Offspring. Environ Sci Technol. 2020;54(13):8245-8258.
[37] LUO C, ZHOU S, ZHOU Z, et al. Wnt9a Promotes Renal Fibrosis by Accelerating Cellular Senescence in Tubular Epithelial Cells. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;29(4):1238-1256.
[38] BAKER DJ, CHILDS BG, DURIK M, et al. Naturally occurring p16(Ink4a)-positive cells shorten healthy lifespan. Nature. 2016;530(7589):184-189.
[39] CHOU X, LI X, MIN Z, et al. Sirtuin-1 attenuates cadmium-induced renal cell senescence through p53 deacetylation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022;245:114098.
[40] KALLURI R, NEILSON EG. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 2003;112(12):1776-1784.
[41] BURNS WC, KANTHARIDIS P, THOMAS MC. The role of tubular epithelial-mesenchymal transition in progressive kidney disease. Cells Tissues Organs. 2007;185(1-3):222-231.
[42] PAN C, WU Y, HU S, et al. Polystyrene microplastics arrest skeletal growth in puberty through accelerating osteoblast senescence. Environ Pollut. 2023;322:121217.
[43] WANG S, CHEN L, SHI X, et al. Polystyrene microplastics-induced macrophage extracellular traps contributes to liver fibrotic injury by activating ROS/TGF-β/Smad2/3 signaling axis. Environ Pollut. 2023; 324:121388.
[44] ISHII T, WARABI E. Mechanism of Rapid Nuclear Factor-E2-Related Factor 2 (Nrf2) Activation via Membrane-Associated Estrogen Receptors: Roles of NADPH Oxidase 1, Neutral Sphingomyelinase 2 and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR). Antioxidants (Basel). 2019;8(3):69.
[45] CHU C, GAO X, LI X, et al. Involvement of Estrogen Receptor-α in the Activation of Nrf2-Antioxidative Signaling Pathways by Silibinin in Pancreatic β-Cells. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2020;28(2):163-171.
[46] TAWARAYAMA H, UCHIDA K, HASEGAWA H, et al. Estrogen, via ESR2 receptor, prevents oxidative stress-induced Müller cell death and stimulates FGF2 production independently of NRF2, attenuating retinal degeneration. Exp Eye Res. 2024;248:110103.
[47] VILLA A, RIZZI N, VEGETO E, et al. Estrogen accelerates the resolution of inflammation in macrophagic cells. Sci Rep. 2015;5:15224.
[48] SVEDLUND EE, LANTERO RM, HALVORSEN B, et al. Testosterone exacerbates neutrophilia and cardiac injury in myocardial infarction via actions in bone marrow. Nat Commun. 2025;16(1):1142.
[49] KANG DH, YU ES, YOON KI, et al. The impact of gender on progression of renal disease: potential role of estrogen-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor regulation and vascular protection. Am J Pathol. 2004;164(2):679-688.
[50] DISTECHE CM. Dosage compensation of the sex chromosomes and autosomes. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016;56:9-18.
[51] LI X, HOU M, ZHANG F, et al. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Female Health Concern: Gender-based Accumulation Differences, Adverse Outcomes, and Mechanisms. Environ Sci Technol. 2025;59(3): 1469-1486.
|