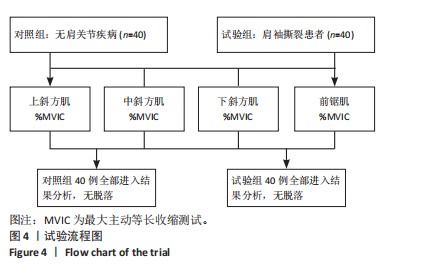
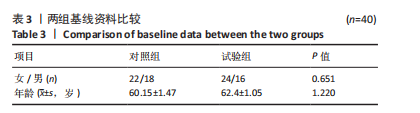
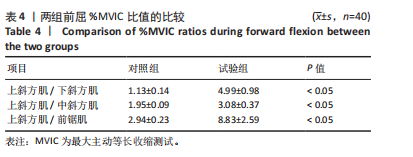
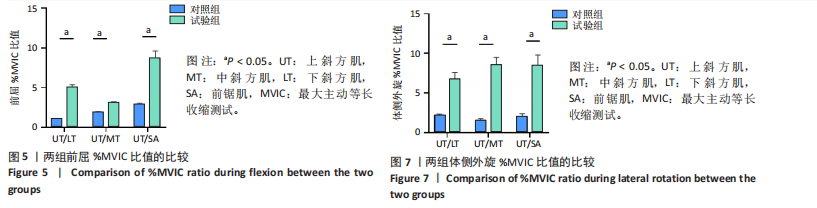
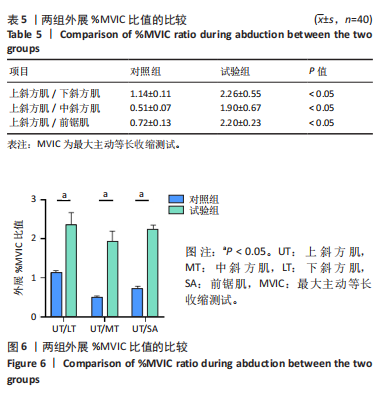
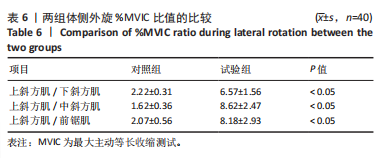
[1] 张磊, 马佳, 刘劲松, 等. 老年人肩袖损伤特点及关节镜手术中期疗效[J]. 中国微创外科杂志,2016,16(6):525-528.
[2] 周天心, 朱慧芳, 熊道海, 等. 肩袖损伤的发病机制、诊断及保守治疗进展[J]. 按摩与康复医学,2023,14(5):35-40.
[3] BEDI A, BISHOP J, KEENER J, et al. Rotator cuff tears. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2024;10(1):8.
[4] COULET B, TEISSIER J, FATTAL C, et al. Weight-bearing shoulder and rotator cuff tear. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2022;108(1S):103170.
[5] 谢露, 罗丁元, 王玮宁, 等. 肩袖撕裂与肩胛骨动力障碍相关性研究进展[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(11):1002-1006.
[6] 陈长安. 肩袖损伤致肩关节不同运动模式的机制探讨[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学,2020.
[7] LONGO UG, RISI AL, CANDELA V, et al. Scapular Kinematics and Patterns of Scapular Dyskinesis in Rotator Cuff Tears: A Prospective Cohort Study. J Clin Med. 2023;12(11):3841.
[8] GUTMAN MJ, JOYCE CD, PATEL MS, et al. Early repair of traumatic rotator cuff tears improves functional outcomes. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2021;30(11):2475-2483.
[9] 陈康, 邓思敏, 何岚娟, 等. 肩胛骨动力学评估的研究进展[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2015,30(11):1188-1191.
[10] 宁健. 基于动力链理论的肩外旋运动对肩胛带肌肉肌电活动的影响[D].北京:北京体育大学,2022.
[11] MALAHIAS MA, CHYTAS D, KOSTRETZIS L, et al. Arthroscopic anatomic complete versus non-anatomic repair of massive rotator cuff tears: a systematic review of comparative trials. Musculoskelet Surg. 2020; 104(2):145-154.
[12] 秦路峰, 焦丰叶, 彭玲, 等. 表面肌电技术在临床康复中的应用进展[J]. 青岛医药卫生,2023,55(5):350-352.
[13] CHEN KS, CHEN R. Principles of Electrophysiological Assessments for Movement Disorders. J Mov Disord. 2020;13(1):27-38.
[14] 上官毅, 龙健锋. 羽毛球运动员肩袖疲劳后肩胛骨的表面肌电特征[C]//.第十三届全国体育科学大会, 天津,2023.
[15] 中华中医药学会.肩袖损伤中西医结合诊疗指南(2023年版)[J].中医正骨,2024,36(1):1-9.
[16] 王健, 李建华, 主编. 表面肌电图诊断技术临床应用[M]. 杭州:浙江大学出版社,2015.
[17] SCHWARTZ C, TUBEZ F, WANG FC, et al. Normalizing shoulder EMG: An optimal set of maximum isometric voluntary contraction tests considering reproducibility. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2017;37:1-8.
[18] EDWARDS PK, EBERT JR, LITTLEWOOD C, et al. A Systematic Review of Electromyography Studies in Normal Shoulders to Inform Postoperative Rehabilitation Following Rotator Cuff Repair. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2017;47(12):931-944.
[19] MCCANN PD, WOOTTEN ME, KADABA MP, et al. A kinematic and electromyographic study of shoulder rehabilitation exercises. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993(288):179-188.
[20] 杨雨昕. 微生物介导的肩袖损伤炎症机制研究[J]. 工业微生物, 2024,54(3):28-30.
[21] DYRNA F, KUMAR NS, OBOPILWE E, et al. Relationship Between Deltoid and Rotator Cuff Muscles During Dynamic Shoulder Abduction: A Biomechanical Study of Rotator Cuff Tear Progression. Am J Sports Med. 2018;46(8):1919-1926.
[22] 皮尚伯. 肩胛部肌肉力量的平衡对肩关节功能康复的影响[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2013,28(8):782-784.
[23] SHIRAI T, IJIRI T, SUZUKI T. Scapular motion during shoulder joint extension movement. J Biomech. 2024;166:112019.
[24] 李磊, 高奉, 付一峰, 等. 伴Ⅲ型肩胛动力障碍肩袖撕裂患者的肩胛骨运动及肩部功能表现[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2024,43(3):167-174.
[25] KEENER JD, PATTERSON BM, ORVETS N, et al. Degenerative Rotator Cuff Tears: Refining Surgical Indications Based on Natural History Data. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019;27(5):156-165.
[26] KOLK A, DE WITTE PB, HENSELER JF, et al. Three-dimensional shoulder kinematics normalize after rotator cuff repair. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016;25(6):881-889.
[27] MIURA Y, KAI Y, MORIHARA T, et al. Three-dimensional Scapular Kinematics During Arm Elevation in Massive Rotator Cuff Tear Patients. Prog Rehabil Med. 2017;2:20170005.
[28] HUANG LL, HUANG TS, LIN YH, et al. Effects of Upper Trapezius Myofascial Trigger Points on Scapular Kinematics and Muscle Activation in Overhead Athletes. J Hum Kinet. 2022;84:32-42.
[29] CASTELEIN B, COOLS A, PARLEVLIET T, et al. The influence of induced shoulder muscle pain on rotator cuff and scapulothoracic muscle activity during elevation of the arm. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26(3): 497-505.
[30] 方镇洙, 李中正, 杨荣, 等. 肩胛骨运动障碍[C]//. 2013中国工程院科技论坛暨浙江省骨科学学术年会, 浙江萧山,2013.
[31] LUDEWIG PM, COOK TM. Alterations in shoulder kinematics and associated muscle activity in people with symptoms of shoulder impingement. Phys Ther. 2000;80(3):276-291.
[32] SAHRMANN S, AZEVEDO DC, DILLEN LV. Diagnosis and treatment of movement system impairment syndromes. Braz J Phys Ther. 2017; 21(6):391-399.
[33] COOLS AM, DEWITTE V, LANSZWEERT F, et al. Rehabilitation of scapular muscle balance: which exercises to prescribe? Am J Sports Med. 2007; 35(10):1744-1751.
[34] ISHIKAWA H, MURAKI T, MORISE S, et al. Differences in scapular motion and parascapular muscle activities among patients with symptomatic and asymptomatic rotator cuff tears, and healthy individuals. JSES Int. 2021;5(2):238-246.
[35] 李军君. 筋膜加压带训练对肩袖损伤患者肩关节功能影响的研究[D]. 西安:西安体育学院,2022.
[36] 贾品茹, 张静, 陆博, 等. 肩周肌群训练联合肌内效贴治疗肩袖损伤的疗效观察[J]. 中国康复,2022,37(5):289-292.
[37] 陈斌. 肌肉加固训练对乒乓球运动员肩关节损伤肌肉群影响研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2017.
[38] OSTERNIG LR, ROBERTSON R, TROXEL R, et al. Muscle activation during proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) stretching techniques. Am J Phys Med. 1987;66(5):298-307.
[39] MERTENS MG, MEEUS M, LLUCH GE, et al. Differences in biomechanical and metabolic factors between patients with frozen shoulder and asymptomatic individuals. A cross-sectional study. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2024;72:102980.
[40] SINGH H, THIND A, MOHAMED NS. Subacromial Impingement Syndrome: A Systematic Review of Existing Treatment Modalities to Newer Proprioceptive-Based Strategies. Cureus. 2022;14(8):e28405.
|