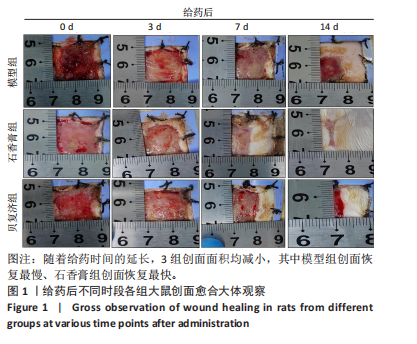
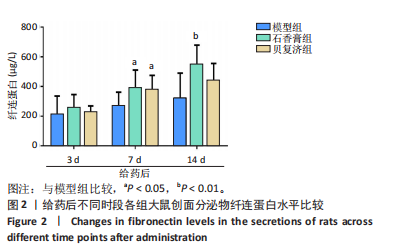
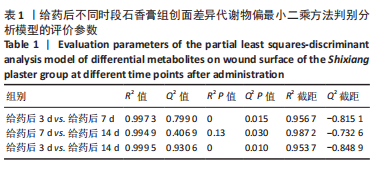
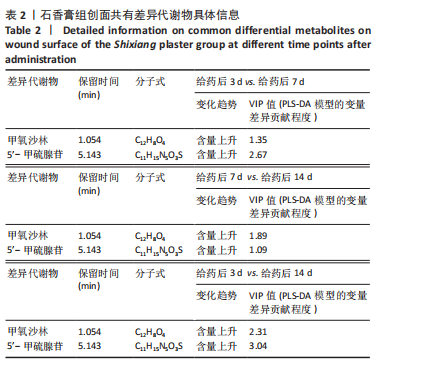
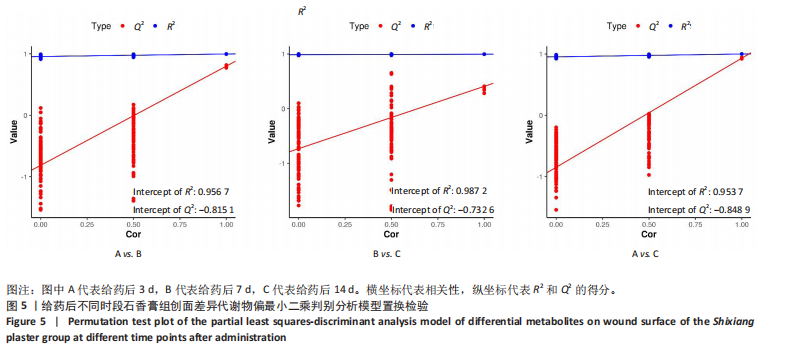
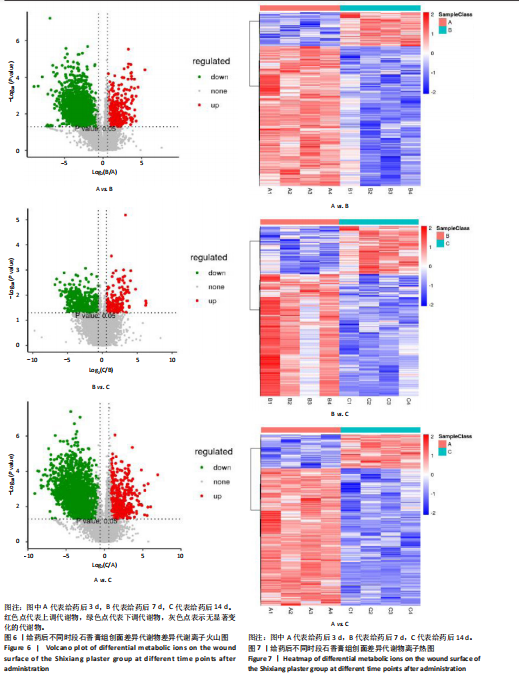
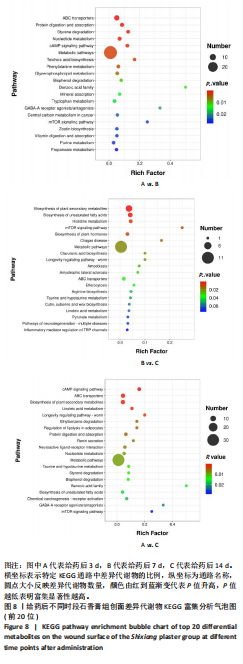
[1] 谭谦,徐晔.慢性创面治疗的理论和策略[J].中华烧伤杂志,2020, 36(9):798-802.
[2] HAALBOOM M. Chronic Wounds: Innovations in Diagnostics and Therapeutics. Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(41):5772-5781.
[3] 陈鏖宇,王一兵.慢性创面的病因及发病机制的研究进展[J].临床医学进展,2023,13(3):2958-2966.
[4] ZHAO R, LIANG H, CLARKE E, et al. Inflammation in Chronic Wounds. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(12):2085.
[5] 吕阳.慢性难愈性创面的临床与基础研究[D].合肥:安徽医科大学, 2022.
[6] LENSELINK EA. Role of fibronectin in normal wound healing. Int Wound J. 2015;12(3):313-316.
[7] JOHNSON MB, PANG B, GARDNER DJ, et al. Topical Fibronectin Improves Wound Healing of Irradiated Skin. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):3876.
[8] 董云青.重组类人胶原蛋白及重组类人纤连蛋白促进小鼠急性创面愈合的研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2022.
[9] VAHIDINIA Z, AZAMI TAMEH A, BARATI S, et al. Nrf2 activation: a key mechanism in stem cell exosomes-mediated therapies. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024;29(1):30.
[10] JERE SW, HOURELD NN, ABRAHAMSE H. Role of the PI3K/AKT (mTOR and GSK3β) signalling pathway and photobiomodulation in diabetic wound healing. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019; 50:52-59.
[11] ZHANG H, KONG Q, WANG J, et al. Complex roles of cAMP-PKA-CREB signaling in cancer. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2020;9(1):32.
[12] YAN L, WANG Y, FENG J, et al. Mechanism and application of fibrous proteins in diabetic wound healing: a literature review. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024;15:1430543.
[13] PATTEN J, WANG K. Fibronectin in development and wound healing. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;170:353-368.
[14] ZHANG X, LI H, CHEN L, et al. NRF2 in age-related musculoskeletal diseases: Role and treatment prospects. Genes Dis. 2023;11(6): 101180.
[15] JUNG KA, KWAK MK. The Nrf2 system as a potential target for the development of indirect antioxidants. Molecules. 2010;15(10):7266-7291.
[16] 王鹏飞,陈奕.甲硫氨酸腺苷转移酶2A在肿瘤发生中的作用及其抑制剂研发现状[J].药学进展,2022,46(12):884-897.
[17] LI Y, WANG Y, WU P. 5’-Methylthioadenosine and Cancer: old molecules, new understanding. J Cancer. 2019;10(4):927-936.
[18] 费冀,张开伟,周一夫,等.石香膏干预糖尿病溃疡创面模型大鼠创面组织晚期糖基化终产物及其受体与内皮型一氧化氮合成酶表达的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(20):3196-3201.
[19] 刘志伦,关智宇,蒋太平,等. 石香膏干预大鼠感染难愈创面的愈合机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(26):4126-4131.
[20] FEI J, WANG LL, LIU M, et al. Study on the effect of Shixiang plaster on the expression of CD31, serum FN, and VEGF in a rat model with chronic wounds. Tradit Med Res. 2024;9(12):70.
[21] 李文华.慢性难愈合创面动物模型制备方法的评价与选择[A].中国中西医结合学会烧伤专业委员会.第15届全国烧伤创疡学术会议论文汇编[C].中国中西医结合学会烧伤专业委员会,2018:6.
[22] VAN DE VYVER M, IDENSOHN PJ, NIESLER CU. A regenerative approach to the pharmacological management of hard-to-heal wounds. Biochimie. 2022;194:67-78.
[23] FEI J, LING YM, ZENG MJ, et al. Shixiang Plaster, a Traditional Chinese Medicine, Promotes Healing in a Rat Model of Diabetic Ulcer Through the receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products (RAGE)/Nuclear Factor kappa B (NF-κB) and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)/Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (VCAM-1)/Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase (eNOS) Signaling Pathways. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:9446-9457.
[24] MUSIIME M, CHANG J, HANSEN U, et al. Collagen Assembly at the Cell Surface: Dogmas Revisited. Cells. 2021;10(3):662.
[25] DUBEY S, DUBEY PK, UMESHAPPA CS, et al. Inhibition of RUNX1 blocks the differentiation of lung fibroblasts to myofibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 2022;237(4):2169-2182.
[26] KURACH Ł, KULCZYCKA-MAMONA S, KOWALCZYK J, et al. Mechanisms of the Procognitive Effects of Xanthotoxin and Umbelliferone on LPS-Induced Amnesia in Mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1779.
[27] SAHA S, BUTTARI B, PANIERI E, et al. An Overview of Nrf2 Signaling Pathway and Its Role in Inflammation. Molecules. 2020;25(22):5474.
[28] HU B, WEI H, SONG Y, et al. NF-κB and Keap1 Interaction Represses Nrf2-Mediated Antioxidant Response in Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus Infection. J Virol. 2020;94(10):e00016-e00020.
[29] CHU CT, URUNO A, KATSUOKA F, et al. Role of NRF2 in Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024;13(12):1529.
[30] KIM JH, CHOI YK, LEE KS, et al. Functional dissection of Nrf2-dependent phase II genes in vascular inflammation and endotoxic injury using Keap1 siRNA. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012;53(3):629-40.
[31] 岑丽君,左远娟,唐乾利.NRF2信号通路对慢性难愈合创面修复影响的研究进展[J].右江民族医学院学报,2022,44(5):749-753.
[32] KONDRATENKO ND, ZINOVKINA LA, ZINOVKIN RA. [Transcription Factor NRF2 in Endothelial Functions]. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2023;57(6):1058-1076.
[33] JOMOVA K, ALOMAR SY, ALWASEL SH, et al. Several lines of antioxidant defense against oxidative stress: antioxidant enzymes, nanomaterials with multiple enzyme-mimicking activities, and low-molecular-weight antioxidants. Arch Toxicol. 2024;98(5):
1323-1367.
[34] MA Q. Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2013;53:401-426.
[35] NGUYEN VN, ZHAO Z, TANG BZ, et al. Organic photosensitizers for antimicrobial phototherapy. Chem Soc Rev. 2022;51(9):3324-3340.
[36] AVILA MA, GARCIA-TREVIJANO ER, LU SC, et al. Methylthioadenosine. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004;36:2125-2130.
[37] DUCATI RG, HARIJAN RK, CAMERON SA, et al. Transition-State Analogues of Campylobacter jejuni 5’-Methylthioadenosine Nucleosidase. ACS Chem Biol. 2018;13(11):3173-3183.
[38] ZHANG H, LIU Y, LIU J, et al. cAMP-PKA/EPAC signaling and cancer: the interplay in tumor microenvironment. J Hematol Oncol. 2024; 17(1):5.
[39] 张瑜,解文浩,翟笑妍.PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路在EMT发生发展过程中的研究进展[J].临床医学进展,2024,14(4):3005-3011.
[40] FAN J, TO KKW, CHEN ZS, et al. ABC transporters affects tumor immune microenvironment to regulate cancer immunotherapy and multidrug resistance. Drug Resist Updat. 2023;66:100905.
[41] 陈福暖,黄瑜,蔡佳,等.ABC转运蛋白结构及其在细菌致病性中的研究进展[J].生物技术通报,2022,38(6):43-52.
[42] SIMCOX J, LAMMING DW. The central moTOR of metabolism. Dev Cell. 2022;57(6):691-706. |