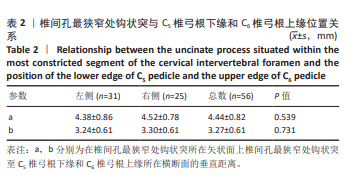
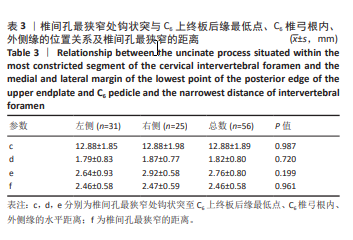
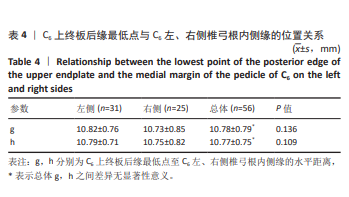
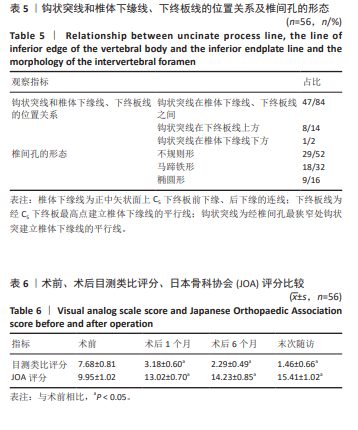
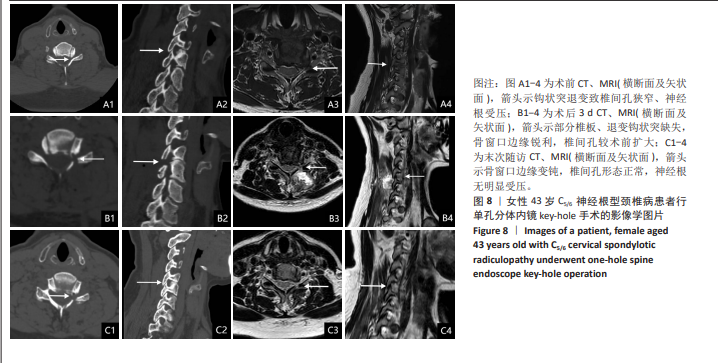
[1] YANG R, HU YX, HUANG J, et al. Minimally Invasive Posterior Cervical Foraminotomy Vs. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion in the Treatment of Patients with Single-Level Unilateral Cervical Radiculopathy. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2024;14:3982-3992.
[2] LILES C, CHANBOUR H, LYONS AT, et al. Revisiting the Posterior Approach for Cervical Radiculopathy Utilizing Endoscopic Techniques: A Favorable Short-Term Outcome and Cost Comparison with Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion. Int J Spine Surg. 2024;4:431-440.
[3] SUN B, XU C, ZHANG Y, et al. Intervertebral Foramen Width is an Important Factor in Deciding Additional Uncinate Process Resection in Acdf-a Retrospective Study. Front Surg. 2021;8:626344.
[4] WANG S, YUAN S, LIU P, et al. Comparative Study of Preoperative Sagittal Spinal Pelvic Alignment in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Radiculopathy, Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament, and Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. Orthop Surg. 2024;11:2688-2698.
[5] SUN B, XU C, QI M, et al. Predictive Effect of Intervertebral Foramen Width On Pain Relief After Acdf for the Treatment of Cervical Radiculopathy. Glob Spine J. 2023;1:133-139.
[6] STOYCHEV V, SIMONOVICH A, ALPEROVITCH-NAJENSON D, et al. Developing a Grading Scale for the Evaluation of Degenerative Changes in Uncovertebral (Luschka) Joints. Clin Anat. 2022;2:186-193.
[7] 王星, 阿格茹, 吉热格乐根, 等. 颈椎钩突的增龄形态学特征及临床意义[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(22):3580-3586.
[8] PROTAS M, CARDONA JJ, CHAIYAMOON A, et al. The Echancrure of the Uncovertebral Joint: A Forgotten Structure of the C3-C7 Cervical Vertebral Bodies. Cureus J Med Science. 2022;12:e32471.
[9] 张德洲, 王超群, 史君, 等. 颈椎钩突相关夹角增龄变化的特征与意义[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024,28(36):5766-5772.
[10] DEMONDION X, LEFEBVRE G, FISCH O, et al. Radiographic Anatomy of the Intervertebral Cervical and Lumbar Foramina (Vessels and Variants). Diagn Interv Imag. 2012;9:690-697.
[11] MAUGERI R, BRUNASSO L, SCIORTINO A, et al. The Impact of Single-Level Acdf On Neural Foramen and Disc Height of Surgical and Adjacent Cervical Segments: A Case-Series Radiological Analysis. Brain Sci. 2023; 13(1):101.
[12] HUANG T, QIN J, ZHONG W, et al. The Ct Assessment of Uncovertebral Joints Degeneration in a Healthy Population. Eur J Med Res. 2021;1: 145.
[13] HOU GL, CHEN CM, CHEN KT, et al. Circumferential Decompression Technique of Posterior Endoscopic Cervical Foraminotomy. Biomed Res Int. 2022:2022:5873333.
[14] YIN M, DING X, ZHU Y, et al. Safety and Efficacy of Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion with Uncinate Process Resection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Glob Spine J. 2022;8:1956-1967.
[15] BAI LL, WANG WT, WANG JF, et al. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Combined with Foraminotomy Assisted by High-Definition 3-Dimensional Exoscope in the Treatment of Cervical Spondylotic Radiculopathy Secondary to Bony Foraminal Stenosis. Orthop Surg. 2021;8:2318-2326.
[16] HIRAI S, KATO S, NAKAJIMA K, et al. Anatomical Study of Cervical Intervertebral Foramen in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Radiculopathy. J Orthop Sci. 2021;1:86-91.
[17] MARCO B, EVANS D, SYMONDS N, et al. Determining the Level of Cervical Radiculopathy: Agreement Between Visual Inspection of Pain Drawings and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Pain Pract. 2023;1:32-40.
[18] SHAH H, PHALAK M. Minimally Invasive Microscopic C5-6 Foraminotomy and Discectomy: Operative Nuances. Neurol India. 2024;5:976-978.
[19] KOTHEERANURAK V, JITPAKDEE K, LEWANDROWSKI KU, et al. Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes of Cervical Disc Replacement Versus Posterior Endoscopic Cervical Decompression: A Matched-Pair Comparison Analysis. Neurospine. 2024;3:1040-1050.
[20] OSHINA M, KAWAMURA N, TACHIBANA N, et al. Comparison of Surgical Outcomes for Cervical Radiculopathy by Nerve Root Level. Sci Rep-Uk. 2024;1:18891.
[21] KIM HS, WU PH, CHIN B, et al. Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of a Comparative Study of Anterior Cervical Decompression and Fusion with Partial Pediculotomy, Partial Vertebrotomy (Pppv) Posterior Endoscopic Cervical Decompression (Pecd) for Cervical Foraminal Pathology. Medicina-Lithuania. 2023;59(7):1222.
[22] GIDEON B, TAKEBAYASHI K, INUI T, et al. Comparison of the Outcomes of Microendoscopic Cervical Foraminotomy Versus Full-Endoscopic Cervical Foraminotomy for the Treatment of Cervical Radiculopathy. Neurol Med-Chir. 2023;9:426-431.
[23] KIM JY, HEO DH, LEE DC, et al. Comparative Analysis with Modified Inclined Technique for Posterior Endoscopic Cervical Foraminotomy in Treating Cervical Osseous Foraminal Stenosis: Radiological and Midterm Clinical Outcomes. Neurospine. 2022;3:603-615.
[24] JUNG SB, KIM N. Biportal Endoscopic Spine Surgery for Cervical Disk Herniation: A Technical Notes and Preliminary Report. Medicine. 2022;27:e29751.
[25] ABUDOUAINI H, WU T, LIU H, et al. Partial Uncinatectomy Combined with Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion for the Treatment of One-Level Cervical Radiculopathy: Analysis of Clinical Efficacy and Sagittal Alignment. Bmc Musculoskel Dis. 2021;1:777.
[26] KEOROCHANA G, TANTRAKANSAKUN C, SURIYONPLENGSAENG C, et al. The Anatomical Relationship Between the Cervical Nerve Roots, Intervertebral Discs and Bony Cervical Landmark for Posterior Endoscopic Cervical Foraminotomy and Discectomy: A Cadaveric Study. Glob Spine J. 2024;7:2116-2123.
[27] WANG S, ZHANG YN, YANG X, et al. Anatomic Research of the Safe Space Between the Cervical Uncinate Process and the V2 Vertebral Artery. World Neurosurg. 2024:191:e713-e722.
[28] FENG Y, ZHANG W, LI K, et al. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Cervical One-Hole Split Endoscopic Keyhole Surgery for Cervical Radiculopathy. J Pain Res. 2024:3093-3099.
[29] WANG D, XU J, ZHU C, et al. Comparison of Outcomes Between Unilateral Biportal Endoscopic and Percutaneous Posterior Endoscopic Cervical Keyhole Surgeries. Medicina-Lithuania. 2023;59(3):437.
[30] LI J, ZHANG T. Comparison of Clinical Outcomes and Complications of Biportal and Uniportal Endoscopic Decompression for the Treatment of Cervical Spondylotic Radiculopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Joint Dis Relat Surg. 2024;3:583-593.
[31] GUO L, WANG J, ZHAO Z, et al. Microscopic Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Versus Posterior Percutaneous Endoscopic Cervical Keyhole Foraminotomy for Single-Level Unilateral Cervical Radiculopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin Spine Surg. 2023;2:59-69.
[32] LIU Y, WU T, YUAN J, et al. Evaluation of Safety and Efficacy of Preoperative Coronal Mri-Guided Minimally Invasive Surgery for Cervical Spondylotic Radiculopathy. Med Sci Monitor. 2023:29:e942137.
[33] 陈应东, 侯国黎, 许三恩, 等. 后路全内镜下椎间孔环形减压治疗伴骨性椎间孔狭窄的神经根型颈椎病[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2020,30(5):473-476.
[34] LIN T, SHANGGUAN Z, XIAO Z, et al. Whether the Potential Degree of Cervical Instability and Cervical Muscle Degeneration in Patients with Cervical Spondylosis Radicular Affect the Efficacy of Cervical Traction. Sci Rep-Uk. 2024;1:20467.
[35] PENG Y, WU J, WU Y, et al. Abdominal Acupuncture Therapy for Cervical Spondylotic Radiculopathy: A Systematic Review and Metaanalysis. Asian J Surg. 2023;12:5776-5778.
[36] GAO QY, WEI FL, ZHU KL, et al. Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Surgical Treatments in Patients with Pure Cervical Radiculopathy. Front Public Health. 2022;10:892042.
[37] SHI M, WANG C, WANG H, et al. Posterior Cervical Full-Endoscopic Technique for the Treatment of Cervical Spondylotic Radiculopathy with Foraminal Bony Stenosis: A Retrospective Study. Front Surg. 2022:1035758.
[38] AKBARI KK, LEE TT, KANADE U, et al. Clinical Outcomes Following Treatment of Cervical Spondylotic Radiculopathy with Cervical Posterior Decompression Using Unilateral Biportal Endoscopic Technique: A Single Center Retrospective Series of 20 Patients. Int J Spine Surg. 2025;19(1):19-26.
[39] APAYDIN AS, GUNES M. Relationships Between Stenosis Severity, Functional Limitation, Pain, and Quality of Life in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Radiculopathy. Turk J Med Sci. 2024;4:727-734.
[40] KANG X, QIAN M, LIU M, et al. Predictive Factors Associated with Chronic Neck Pain in Patients with Cervical Degenerative Disease: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J Pain Res. 2023:4229-4239.
[41] LAMBRECHTS MJ, ISSA TZ, LEE Y, et al. How Does the Severity of Neuroforaminal Compression in Cervical Radiculopathy Affect Outcomes of Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion. Asian Spine J. 2023;6:1051-1058.
[42] WANG Q, LI H, KONG J, et al. Diagnostic Agreement Between 3.0-T Mri Sequences of Nerve Root and Surgery in Patients with Cervical Radiculopathy: A Retrospective Study. Medicine. 2021;4:e24207.
[43] SHIMAUCHI-OHTAKI H, TAKAHASHI T, MINAMI M, et al. Morphological Changes in Nerve Rootlets in Patients with Cervical Radiculopathy Assessed Using Computed Tomography Myelogram. Surg Neurol Int. 2022;13:391. |