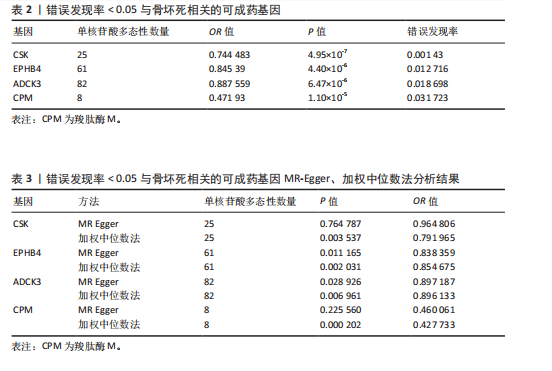
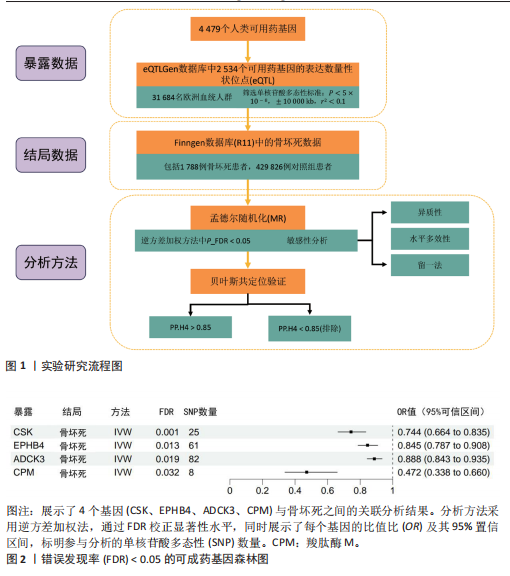
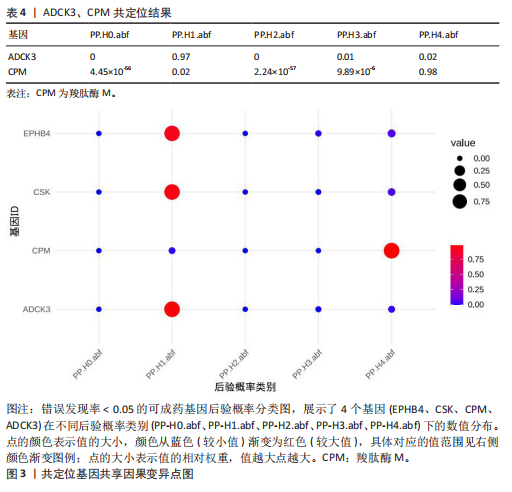
[1] MANKIN HJ. Nontraumatic necrosis of bone (osteonecrosis). N Engl J Med. 1992;326(22): 1473-1479.
[2] JONES LC, HUNGERFORD DS. Osteonecrosis: etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2004;16(4):443-449.
[3] RIPAMONTI CI, NAPOLI N. Are We Ready to Use Teriparatide to Treat Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw in Clinical Practice? J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(26):2949-2951.
[4] SUN X, CHEN B, QI Y, et al. Multi-omics Mendelian randomization integrating GWAS, eQTL and pQTL data revealed GSTM4 as a potential drug target for migraine. J Headache Pain. 2024;25(1):117.
[5] SEKULA P, DEL GRECO MF, PATTARO C, et al. Mendelian Randomization as an Approach to Assess Causality Using Observational Data. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;27(11):3253-3265.
[6] MAIMAITI A, TURHON M, ABULAITI A, et al. DNA methylation regulator-mediated modification patterns and risk of intracranial aneurysm: a multi-omics and epigenome-wide association study integrating machine learning, Mendelian randomization, eQTL and mQTL data. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):660.
[7] LIU Y, LI B, MA Y, et al. Mendelian Randomization Integrating GWAS, eQTL, and mQTL Data Identified Genes Pleiotropically Associated With Atrial Fibrillation. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:745757.
[8] SKRIVANKOVA VW, RICHMOND RC, WOOLF BAR, et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology Using Mendelian Randomization: The STROBE-MR Statement. JAMA. 2021;326(16):1614-1621.
[9] FINAN C, GAULTON A, KRUGER FA, et al. The druggable genome and support for target identification and validation in drug development. Sci Transl Med. 2017; 9(383):eaag1166.
[10] VÕSA U, CLARINGBOULD A, WESTRA HJ, et al. Large-scale cis- and trans-eQTL analyses identify thousands of genetic loci and polygenic scores that regulate blood gene expression. Nat Genet. 2021;53(9):1300-1310.
[11] BIRNEY E. Mendelian Randomization. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2022;12(4): a041302.
[12] ZHANG Y, WANG M, LI Z, et al. An overview of detecting gene-trait associations by integrating GWAS summary statistics and eQTLs. Sci China Life Sci. 2024;67(6):1133-1154.
[13] GKATZIONIS A, BURGESS S, NEWCOMBE PJ. Statistical methods for cis-Mendelian randomization with two-sample summary-level data. Genet Epidemiol. 2023;47(1):
3-25.
[14] PIERCE BL, AHSAN H, VANDERWEELE TJ. Power and instrument strength requirements for Mendelian randomization studies using multiple genetic variants. Int J Epidemiol. 2011;40(3):740-752.
[15] KURKI MI, KARJALAINEN J, PALTA P, et al. FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population. Nature. 2023;613(7944):508-518.
[16] MINTON K. The FinnGen study: disease insights from a ‘bottlenecked’ population. Nat Rev Genet. 2023;24(4):207.
[17] YAVORSKA OO, BURGESS S. Mendelian Randomization: an R package for performing Mendelian randomization analyses using summarized data. Int J Epidemiol. 2017;46(6): 1734-1739.
[18] BURGESS S, THOMPSON SG. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur J Epidemiol. 2017;32(5):377-389.
[19] BURGESS S, DUDBRIDGE F, THOMPSON SG. Combining information on multiple instrumental variables in Mendelian randomization: comparison of allele score and summarized data methods. Stat Med. 2016;35(11):1880-1906.
[20] COHEN JF, CHALUMEAU M, COHEN R, et al. Cochran’s Q test was useful to assess heterogeneity in likelihood ratios in studies of diagnostic accuracy. J Clin Epidemiol. 2015; 68(3):299-306.
[21] BOWDEN J, DEL GRECO MF, MINELLI C, et al. Assessing the suitability of summary data for two-sample Mendelian randomization analyses using MR-Egger regression: the role of the I2 statistic. Int J Epidemiol. 2016;45(6):1961-1974.
[22] GEORGE NI, BOWYER JF, CRABTREE NM, et al. An Iterative Leave-One-Out Approach to Outlier Detection in RNA-Seq Data. PLoS One. 2015;10(6):e0125224.
[23] SIMOVSKI B, KANDURI C, GUNDERSEN S, et al. Coloc-stats: a unified web interface to perform colocalization analysis of genomic features. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(W1):W186-W193.
[24] RASOOLY D, PELOSO GM, GIAMBARTOLOMEI C. Bayesian Genetic Colocalization Test of Two Traits Using coloc. Curr Protoc. 2022; 2(12):e627.
[25] KANDURI C, SANDVE GK, HOVIG E, et al. Editorial: Genomic Colocalization and Enrichment Analyses. Front Genet. 2021;11: 617876.
[26] LIN J, ZHOU J, XU Y. Potential drug targets for multiple sclerosis identified through Mendelian randomization analysis. Brain. 2023;146(8):3364-3372.
[27] YUAN N, ZHANG W, YANG W, et al. Exosomes derived from M2 macrophages prevent steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by modulating inflammation, promoting bone formation and inhibiting bone resorption. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024;19(1):243.
[28] WISNIEWSKI P, GANGNUS T, BURCKHARDT BB. Recent advances in the discovery and development of drugs targeting the kallikrein-kinin system. J Transl Med. 2024;22(1):388.
[29] BUELLI S, IMBERTI B, MORIGI M. The Complement C3a and C5a Signaling in Renal Diseases: A Bridge between Acute and Chronic Inflammation. Nephron. 2024;148(10):712-723.
[30] DEITEREN K, HENDRIKS D, SCHARPÉ S, et al. Carboxypeptidase M: Multiple alliances and unknown partners. Clin Chim Acta. 2009; 399(1-2):24-39.
[31] TSAKIRIS I, TOROCSIK D, GYONGYOSI A, et al. Carboxypeptidase-M is regulated by lipids and CSFs in macrophages and dendritic cells and expressed selectively in tissue granulomas and foam cells. Lab Invest. 2012;92(3):345-361.
[32] HERNIGOU P, HERNIGOU J, SCARLAT M. Shoulder Osteonecrosis: Pathogenesis, Causes, Clinical Evaluation, Imaging, and Classification. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(5):1340-1349.
[33] TAMARI T, KAWAR-JARAISY R, DOPPELT O, et al. The Paracrine Role of Endothelial Cells in Bone Formation via CXCR4/SDF-1 Pathway. Cells. 2020;9(6):1325.
[34] MARQUEZ-CURTIS L, JALILI A, DEITEREN K, et al. Carboxypeptidase M expressed by human bone marrow cells cleaves the C-terminal lysine of stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha: another player in hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell mobilization? Stem Cells. 2008;26(5):1211-1220.
[35] JALILI A, SHIRVAIKAR N, MARQUEZ-CURTIS L, et al. Fifth complement cascade protein (C5) cleavage fragments disrupt the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis: further evidence that innate immunity orchestrates the mobilization of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Exp Hematol. 2010; 38(4):321-332.
[36] KOBAYASHI M, WAKABAYASHI I, SUZUKI Y, et al. Tubulin carboxypeptidase activity of vasohibin-1 inhibits angiogenesis by interfering with endocytosis and trafficking of pro-angiogenic factor receptors. Angiogenesis. 2021;24(1):159-176.
[37] ZHANG X, TAN F, BROVKOVYCH V, et al. Carboxypeptidase M augments kinin B1 receptor signaling by conformational crosstalk and enhances endothelial nitric oxide output. Biol Chem. 2013;394(3):335-345.
[38] ZHANG X, YANG Z, XU Q, et al. Dexamethasone Induced Osteocyte Apoptosis in Steroid-Induced Femoral Head Osteonecrosis through ROS-Mediated Oxidative Stress. Orthop Surg. 2024;16(3):733-744.
[39] CAWLEY NX, YANIK T, WORONOWICZ A, et al. Obese carboxypeptidase E knockout mice exhibit multiple defects in peptide hormone processing contributing to low bone mineral density. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010;299(2):E189-E197.
[40] XI L, SONG Y, WU W, et al. Investigation of bone matrix composition, architecture and mechanical properties reflect structure-function relationship of cortical bone in glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis. Bone. 2020;136:115334.
[41] HARDY E, FERNANDEZ-PATRON C. Destroy to Rebuild: The Connection Between Bone Tissue Remodeling and Matrix Metalloproteinases. Front Physiol. 2020;11:47.
[42] LIAO Z, ZHENG X, LI H, et al. Carboxypeptidase M modulates BMSCs osteogenesis-adipogenesis via the MAPK/ERK pathway: An integrated single-cell and bulk transcriptomic study. FASEB J. 2024;38(9):e23657. |