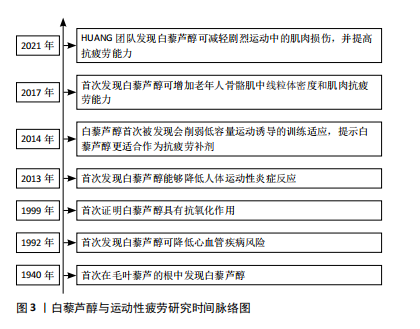
2.1 白藜芦醇与运动性疲劳的研究历程 1940年,日本科学家Takaoka首次在毛叶藜芦的根中发现白藜芦醇[4]。1992年,Renaud和De Lorgeril首次发现葡萄酒相关的多酚摄入与不良心血管结局风险降低有关,因此葡萄酒内含量较高的白藜芦醇被认为是“法国悖论”的可能解释[11]。随后大量的研究致力于探索白藜芦醇的各种生物学特性的表征,特别是它的抗炎和抗氧化作用。1999年,JANG等[12]首次证实了白藜芦醇能够抑制酵母多糖刺激的小鼠巨噬细胞Raw264.7、人单核细胞和中性粒细胞中活性氧的产生。随着时间的推移,学者们开始探索白藜芦醇对运动性疲劳的延缓作用及其潜在机制。2013年,ZAHEDI等[13]首次在篮球职业运动员中发现定期补充白藜芦醇能够显著降低长时间运动后炎症反应。在最近的研究中,HUANG研究团队[14]发现白藜芦醇可有效减轻年轻男性进行增强式训练导致的肌肉损伤,并提高机体的抗疲劳能力。白藜芦醇与运动性疲劳的研究历程时间脉络图,见图3。
2.2 白藜芦醇概述
2.2.1 白藜芦醇的来源 白藜芦醇是植物在响应不同的应激条件和病原体感染时所产生的一种抗菌素,最初于1940年由日本科学家Takaoka从毛叶藜芦的根中分离得到,而后又在葡萄、浆果、可可、蓝莓和中草药等70多种植物中被发现[4]。白藜芦醇在不同植物中含量不尽相同,其中新鲜葡萄果皮中白藜芦醇含量最高,可达50-100 mg/kg[15]。
2.2.2 白藜芦醇的理化特性 白藜芦醇(3,5,4’-三羟基二苯乙烯)属于一种非黄酮类多酚二苯乙烯,其化学式为C14H12O3,难溶于水,但易溶于乙醚、甲醇和乙酸乙酯等有机溶剂,具有顺式和反式两种结构异构形式,见图4,其中反式白藜芦醇因稳定性更高而应用范围更广。反式白藜芦醇可由对香豆酰辅酶A和丙二酰辅酶A合成,并可在高温和紫外线照射后转化为其他顺式异构体[16]。由于白藜芦醇的分子质量小(228.25 Da)且具有较高的亲脂性,因此它可以很轻松地透过血脑屏障并渗透到脑组织中,从而发挥相应作用[17]。此外,因白藜芦醇难溶于水,经肝脏快速代谢进入血浆后,必须通过与血清中白蛋白和低密度脂蛋白等浓度较高的蛋白质结合,才能促进自身被细胞摄取[18]。
2.3 运动性疲劳的产生机制 运动性疲劳是机体在剧烈运动后发出的保护性信号。在人体试验中,主要通过测量运动表现(如无法维持既定强度的运动)、生理指标(如心率达到最大心率的90%以上)和主观感受(如受试者主
述停止运动或主观疲劳程度量表评分超过17分)等来作为判断疲劳产生的依据[19]。在动物实验中,运动性疲劳的判断标准通常为大/小鼠在被刺激后,仍无法继续运动,且翻身反射明显迟缓[20]。运动性疲劳的产生机制较为复杂,涉及外周机制和中枢机制两方面,见图5。
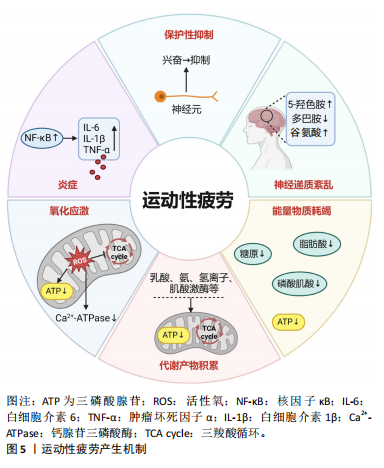
2.3.1 运动性疲劳的外周机制 运动性疲劳的外周机制是多种因素共同作用的结果,主要涉及能量物质耗竭、代谢产物积累、氧化应激和炎症反应等方面。这些机制通过影响肌肉的正常收缩能力,从而导致疲劳的产生。
(1)能量物质衰竭理论:能量供应对肌肉收缩至关重要。肌肉纤维的主要能量来源,包括身体系统内的ATP、糖原和脂肪。不同运动条件对能量物质的消耗有所不同:短时间高强度运动时,骨骼肌中ATP和磷酸肌酸含量迅速减少,直接导致运动性疲劳;碳水化合物是中等强度运动的主要消耗底物;而脂肪则是长时间耐力运动中消耗的关键能量物质。当这些能量物质在运动过程中被大量消耗时,骨骼肌因能量匮乏而无法维持有效的收缩或完成既定的工作量,进而导致疲劳的产生[21]。
(2)代谢物积累理论:代谢物积累理论认为,剧烈运动产生的过量代谢物(如乳酸和氨等)在骨骼肌和血液中积累,从而导致疲劳[22]。乳酸蓄积被认为是骨骼肌疲劳的最重要原因之一。长时间高强度的运动可能导致ATP生成和利用率下降,引起ATP消耗增加和氢离子和无机磷酸盐等代谢副产物积累,进而导致肌肉疲劳。此外,在剧烈运动时,骨骼肌中氨浓度升高,升高的氨激活磷酸果糖激酶,抑制丙酮酸氧化为乙酰辅酶A,然后促进血乳酸、血尿素氮和肌酸激酶等代谢产物产生,从而影响内环境稳态,引起疲劳[23]。
(3)氧化应激:研究表明,过度的肌肉运动会增加身体组织和器官(包括心肌组织、肝脏、骨骼肌和血液)中活性氧的产生,从而导致细胞内氧化-抗氧化稳态失衡[24]。
低至中等水平的活性氧被认为对人的体能有益,而高水平的活性氧通过攻击生物大分子(脂质、蛋白质和核酸)破坏细胞或细胞器的膜结构[24]。另外,过度运动诱导的活性氧降低了骨骼肌浆网钙腺苷三磷酸酶的活性,导致钙离子在细胞质内蓄积,影响肌纤维的兴奋-收缩耦合[25]。
因此,肌肉收缩的能力降低,从而导致疲劳。此外,升高的内源性和外源性活性氧还会破坏线粒体功能,抑制有氧代谢,导致运动性疲劳[26]。
(4)炎症:炎症也被认为在运动性疲劳的发生中扮演了重要角色。研究表明,高强度或长时间的运动不仅可诱导活性氧的过度产生导致氧化应激,也会引起急性炎症,导致白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α等促炎细胞因子的过度释放[27]。升高的促炎细胞因子可通过激活核因子κB,进一步引起炎症反应和线粒体功能障碍,以此形成恶性循环[28]。同时,受损的线粒体可产生更多的活性氧,从而导致肌肉力量下降和疲劳产生[24]。
2.3.2 运动性疲劳的中枢机制 运动性疲劳的中枢机制指的是大脑和中枢神经系统在运动过程中对疲劳的调控,特别是大脑对运动强度和持续时间的调节。中枢性疲劳主要与中枢保护性抑制和神经递质紊乱有关:
(1)保护性抑制理论:中枢抑制在运动诱导的疲劳中发挥重要作用,被认为是一种机体运动到一定程度时产生的防御作用。骨骼肌收缩产生的神经兴奋不断刺激大脑皮质中相应的神经元,并在运动过程中保持兴奋,从而导致ATP、脂肪酸、磷酸肌酸和葡萄糖的持续消耗[29]。随后,大脑皮质和中枢神经系统通过负反馈调节机制从兴奋转换到抑制,防止能量物质的过度消耗,从而引起疲劳[30]。
(2)神经递质紊乱:研究表明,大脑神经递质(如5-羟色胺、多巴胺和谷氨酸等)在剧烈运动中加速疲劳起主导作用[21]。中枢神经系统对运动的调控主要依赖于这些神经递质的平衡,而运动过程中神经递质水平的失衡会影响大脑中枢神经系统对运动控制、肌肉收缩及疲劳感知的调节,进而加速疲劳的发生。因此,神经递质分泌紊乱被认为是运动性中枢疲劳产生的主要原因。
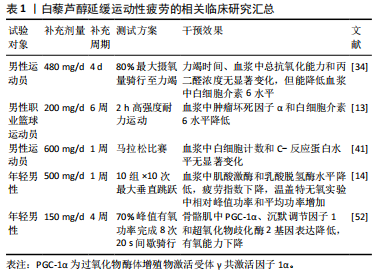
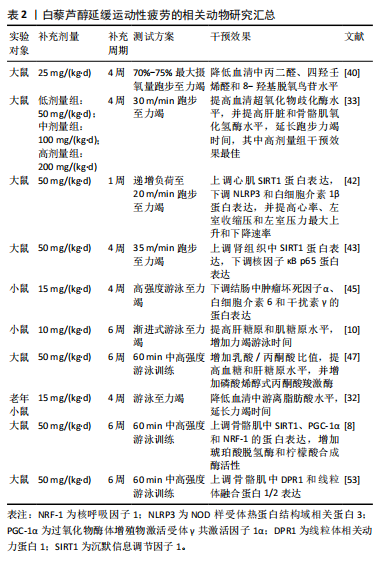
2.4 补充白藜芦醇延缓运动性疲劳的作用效果 白藜芦醇作为一种潜在的抗疲劳补充剂,在延缓运动性疲劳方面展现出积极作用。动物实验表明,每日补充10 mg/kg(以体质量计)的白藜芦醇并联合8周有氧运动干预,能够明显延长小鼠的跑步力竭时间和运动距离[31]。MUHAMMAD等[32]的研究也显示,为期4周、每日15 mg/kg剂量的白藜芦醇灌胃处理,老年小鼠的游泳力竭时间相较于安慰剂组有了明显延长。此外,赵昆等[33]分别对SD大鼠进行4周低剂量(50 mg/kg)、中等剂量(100 mg/kg)和高剂量(200 mg/kg)白藜芦醇灌胃,并完成跑步力竭测试后发现,与安慰剂组相比,各白藜芦醇补充组跑步力竭时间均得到显著提高,且高剂量组提高效果优于中、低剂量组,表明白藜芦醇可能以剂量依赖性方式提高机体的抗疲劳能力。然而,尽管大量动物实验结果支持这一效果,但在人体试验中,有研究发现白藜芦醇的抗疲劳效果并不那么显著。例如,TASO等[34]的研究发现,与安慰剂相比,连续4 d白藜芦醇补充(480 mg/d,总共1 920 mg)并未明显延长男性运动员在80%最大摄氧量强度骑行力竭测试时的力竭时间,其原因可能是由于补充时间过短和补充总剂量较低导致白藜芦醇未能在体内形成足够的累积效应,因此不足以有效延缓疲劳发生。POLLEY等[35]发现,为期4周、每日500 mg的白藜芦醇补充能够显著提高年轻男性骨骼肌线粒体容量。鉴于骨骼肌线粒体容量与机体抗疲劳能力呈高度正相关[36],因此在未来的人体试验中可通过适当延长补充周期(≥4周),以进一步验证白藜芦醇对运动性疲劳的延缓效果。
值得注意的是,白藜芦醇补充剂量并不是越高越好。VODUC等[37]报道,在健康成人中进行为期4周的白藜芦醇补充试验(第1周每日500 mg,后3周每日1 000 mg)后,白藜芦醇组的胃肠道不良反应发生率显著高于安慰剂组(77% vs. 15%),提示高剂量白藜芦醇补充可能引起胃肠不适。此外,KHATTAR等[38]的研究指出,尽管人体对白藜芦醇的耐受性良好,但长期每日大剂量(≥ 1 000 mg)口服白藜芦醇可能会对生殖系统产生不良影响,认为对体质量70 kg成人而言,每日补充500 mg是安全剂量。
综上所述,规律性补充白藜芦醇具有提高机体抗疲劳能力进而提升运动表现的潜力。虽然现有人体研究尚未明确剂量标准,但根据现有临床数据,建议每日补充白藜芦醇500 mg,持续4周以上,以确保在实现抗疲劳效果的同时减少不良反应的风险。未来研究需进一步探索白藜芦醇的剂量-效应关系,以建立科学的补充剂量和使用周期,为运动性疲劳的干预提供更精确的指导。
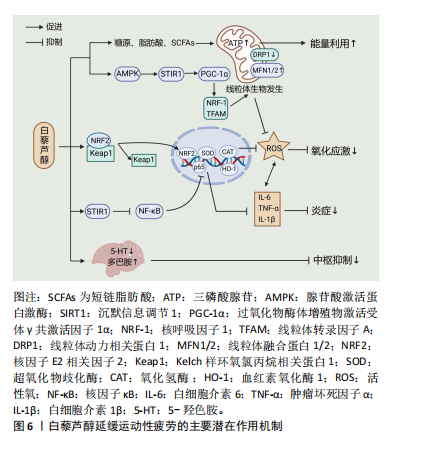
2.5 补充白藜芦醇延缓运动性疲劳的作用机制 补充白藜芦醇对运动性疲劳的延缓作用可能通过减轻运动引起的氧化应激和炎症反应、提高能量物质的利用、改善线粒体质量以及减轻肌肉损伤等方面发挥作用。
2.5.1 提高抗氧化能力 调节机体氧化应激水平是白藜芦醇最显著的特征之一。研究证实,白藜芦醇可通过激活Kelch样环氧氯丙烷相关蛋白1 /核因子E2相关因子2通路来上调抗氧化相关基因的表达,如超氧化物歧化酶、血红素加氧酶1和过氧化氢酶等,从而发挥抗氧化作用[39]。动物研究表明,4周白藜芦醇50 mg/(kg·d)灌胃可显著降低大鼠剧烈跑台运动后血清和肌肉中丙二醛、4-羟基壬烯酸和8-羟基脱氧鸟苷的水平,对剧烈运动引起的氧化损伤和脂质过氧化起到保护作用[40]。同样,NASIRI等[5]研究发现,12周白藜芦醇的补充可显著提高小鼠力竭运动后谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶和过氧化氢酶活性,并增加总抗氧化能力,提示白藜芦醇可能通过防止脂质过氧化来预防力竭运动诱导的氧化应激。赵昆等[33]对雄性大鼠进行4周白藜芦醇灌胃并完成跑步力竭测试后发现,与对照组相比,补充白藜芦醇组大鼠跑步力竭时间均明显延长,同时肝脏和肌肉中过氧化氢酶和超氧化物歧化酶活性显著提高,而氧化氢酶活性显著降低,说明白藜芦醇可能通过提高机体抗氧化能力来延缓疲劳发生。
上述研究表明,白藜芦醇可作为一种有效的外源性抗氧化剂,能够通过降低丙二醛、4-羟基壬烯酸和8-羟基脱氧鸟苷的水平,并提高机体谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶和过氧化氢酶等抗氧化酶活性,从而发挥积极的抗疲劳作用。
2.5.2 提高抗炎能力 补充白藜芦醇可降低运动性炎症反应已被证实。ZAHEDI等[13]对男性职业篮球运动员补充(200 mg/d)白藜芦醇6周后,通过检测2 h高强度耐力运动后血清中白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α的水平发现,白藜芦醇的补充显著降低了血清中白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α水平。不过,LAUPHEIMER等[41]将7名男性运动员随机分配补充白藜芦醇(600 mg/d)或安慰剂7 d后发现,与安慰剂组相比,白藜芦醇组并未显著降低马拉松赛后受试者血浆中白细胞计数和C-反应蛋白水平,其原因可能与白藜芦醇补充时间较短以及受试者数量过少造成统计结果出现较大误差有关。
除了可降低运动后血液中炎症标志物水平外,白藜芦醇亦可在多种组织中发挥抗炎作用。研究发现,连续7 d白藜芦醇腹腔注射可显著上调急性力竭运动后大鼠心肌沉默信息调节因子1(silent information regulator 1,SIRT1)的蛋白表达,下调心肌中NOD 样受体热蛋白结构域相关蛋白3(nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3,NLRP3)炎症小体以及白细胞介素1β的蛋白表达,并改善血流动力学[42],提示白藜芦醇可通过调节SIRT1/NLRP3炎症小体/白细胞介素1β信号通路来减轻力竭运动诱导的心肌炎症损伤,改善心功能。李方等[43]的研究显示,白藜芦醇可通过上调大鼠力竭运动后肾组织中SIRT1表达来抑制核因子κB p65的表达,从而降低力竭运动诱导的肾脏炎症反应。运动过程中肾脏炎症的降低有利于防止代谢产物(如乳酸、尿素和肌酸酐)清除功能障碍和电解质失衡,提高机体的抗疲劳能力[44]。因此,白藜芦醇可能通过降低肾脏炎症反应来延缓疲劳的发生。此外,4周白藜芦醇补充可显著抑制高强度运动诱导的小鼠结肠中肿瘤坏死因子α、干扰素γ和白细胞介素6的表达,同时减轻结肠损伤,改善肠屏障功能[45]。而肠道屏障功能的改善不仅有助于维持正常的营养物质吸收,提加运动中能量供应,还可阻碍脂多糖等毒性物质肠道移位进入循环中诱发全身性炎症反应[46]。这提示白藜芦醇也可能通过降低剧烈运动引发的肠道炎症,改善肠道屏障功能,从而延缓疲劳的发生。
综上,白藜芦醇可能通过减轻机体在长时间或高强度运动时的炎症反应,从而延缓运动性疲劳。然而,迄今为止,关于补充白藜芦醇对运动后炎症反应与疲劳改善的相关性评估的研究仍较少,故未来需通过进一步开展相关人体试验来给予证实。
2.5.3 提高能量物质的利用 提高机体能量物质的利用是白黎芦醇发挥抗疲劳作用的另一重要机制。研究发现,补充白藜芦醇可显著提高耐力训练后小鼠的肝糖原和肌糖原水平,并明显延长小鼠负重力竭游泳时间[10],说明白藜芦醇可能通过提高机体糖原储备来延缓疲劳的发生。阮蓉等[47]研究表明,为期6周的白藜芦醇补充可增加中高强度运动后大鼠肝脏中乳酸/丙酮酸比值,同时提高磷酸烯醇式丙酮酸羧激酶(一种肝脏糖异生限速酶)活性,从而促进肝脏糖异生、提高血糖和肝糖原水平。另外,白藜芦醇可通过积极调控肠道菌群来促进短链脂肪酸的产生[48]。短链脂肪酸是由肠道菌群发酵纤维素和膳食中的其他可溶性纤维产生的脂肪酸,在调节宿主能量代谢方面扮演着重要角色。短链脂肪酸主要包括乙酸盐、丙酸盐和丁酸盐。丁酸盐可直接被肠道上皮细胞吸收,为其提供70%以上的能量;而乙酸盐和丙酸盐则主要通过进入血液循环作为糖异生的底物被肌肉和肝脏吸收,参与维持血糖稳定[49]。基于这一特性,白藜芦醇可能通过促进短链脂肪酸产生来维持血糖水平,进而增加能量供应。由此可见,补充白藜芦醇能够延缓运动性疲劳的原因可能与其积极调控糖异生有关。
此外,作为腺苷酸激活蛋白激酶(AMP-activated protein kinase,AMPK)的有效激活剂,白藜芦醇一方面能够通过激活AMPK促进脂肪酸氧化,并通过调控下游的酶类和代谢途径,加速脂肪酸向线粒体的转运和氧化;另一方面,AMPK的激活还会促进过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ共激活因子1α(peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α,PGC-1α)的表达,进而促进线粒体的生成和功能改善,从而增加细胞对脂肪酸的利用率。相关研究也指出,为期4周的白藜芦醇补充可显著延长老年大鼠跑步力竭时间,并降低血清中游离脂肪酸的水平,表明白藜芦醇可能通过提高脂肪酸的氧化能力来增加能量供应,从而延缓疲劳的发生[32]。
综上所述,补充白藜芦醇可能通过促进机体糖异生,并促使脂肪酸氧化增加,以优化耐力运动中脂肪酸氧化供能,减少糖原消耗,延缓运动性低血糖的过早产生,从而提高机体的抗疲劳能力。
2.5.4 改善线粒体质量 补充白藜芦醇对线粒体质量相关指标的积极改善作用已被证实。研究发现,12周白藜芦醇(500 mg/d)补充联合运动干预可显著增加老年受试者的股外侧肌线粒体密度,并提高膝关节伸展平均功率和重复7次的平均峰值力矩[50],提示白藜芦醇可能通过改善线粒体质量来提高肌肉抗疲劳能力。白藜芦醇能够改善线粒体质量,这与其可调节线粒体生物发生、融合和分裂和激活线粒体自噬有关。线粒体生物发生是细胞为了响应能量需求而增加线粒体数量和提高线粒体功能的过程,主要受PGC-1α/AMPK/NRF-1/TFAM通路调节[51]。研究发现,补充白藜芦醇可通过激活SIRT1/PGC-1α/NRF-1通路促进运动性疲劳模型大鼠骨骼肌线粒体生物发生,增加线粒体能量代谢相关酶的活性(如琥珀酸脱氢酶和柠檬酸合成酶),提高骨骼肌总超氧化物歧化酶活性,从而延缓运动性疲劳[8]。然而,SCRIBBANS等[52]对年轻男性进行为期4周的低容量高强度间歇训练(以170%峰值有氧功率完成8次20 s间歇骑行,3次/周)并联合白藜芦醇(150 mg/d)或安慰剂补充后发现,与安慰剂组相比,白藜芦醇组骨骼肌中PGC-1α、SIRT1和超氧化物歧化酶2基因表达显著降低,且有氧和无氧能力也下降,提示补充白藜芦醇可能会削弱运动诱导的正常训练反应。出现上述结果的原因可能是由于白藜芦醇钝化了低容量运动诱导的适度活性氧产生,而活性氧水平的降低导致其对PGC-1α、SIRT1和超氧化物歧化酶2基因表达激活程度减少[24],进而导致训练效果下降。因此,白藜芦醇似乎更适用于那些长期从事高强度运动的人群,用来作为一种抗疲劳营养补剂,而不太适合那些进行较低运动强度或运动量的人群。
线粒体融合和分裂也是调控线粒体质量控制的重要机制,可防止线粒体中氧化和功能障碍蛋白的积累。研究显示,补充白藜芦醇可上调运动性疲劳模型大鼠骨骼肌线粒体融合蛋白1/2和视神经萎缩蛋白1的基因表达,同时下调线粒体动力相关蛋白1和线粒体分裂蛋白1的基因表达,提示补充白藜芦醇可促进线粒体融合,抑制线粒体过度分裂,进而改善运动性疲劳大鼠的线粒体质量[53]。此外,线粒体自噬同样有利于改善线粒体质量和维持细胞稳态,可减轻受损线粒体导致的细胞损伤。SEBORI等[54]研究发现,白藜芦醇可通过诱导线粒体自噬减轻杜氏肌营养不良引起的肌肉萎缩,表现为同源性磷酸酶张力蛋白诱导激酶1和帕金森蛋白等线粒体自噬相关基因表达水平升高。体外实验表明,白藜芦醇不仅能够激活线粒体自噬保护人髓核细胞免受过氧化氢诱导的细胞毒性[55],也可在鱼藤酮诱导的氧化应激SH-SY5Y细胞模型中通过上调线粒体自噬来发挥神经保护作用[56]。不过,由于目前有关白藜芦醇调节线粒体自噬的研究均在病理模型中进行,而非在运动性疲劳模型中,故白藜芦醇是否能够通过激活线粒体自噬来延缓运动性疲劳仍有待进一步研究证实。
2.5.5 减轻肌肉损伤 长时间或剧烈运动会导致骨骼肌纤维出现微损伤,引起局部炎症并降低肌肉功能[57]。此外,肌肉损伤还会破坏肌细胞膜,导致细胞内外钙离子浓度平衡失调。过量的钙离子进入肌细胞通过激活钙依赖性酶(如钙蛋白酶),加剧肌细胞结构的损伤,同时影响肌肉的正常收缩功能,进而导致疲劳产生[58]。因此,减轻运动过程中肌肉损伤有利于延缓疲劳的发生。HUANG等[14]研究发现,白藜芦醇(500 mg/d)补充7 d可降低年轻男性增强式训练后血浆中肌酸激酶和乳酸脱氢酶等肌肉损伤指标水平,并改善其在温盖特无氧试验中的相对峰值功率、相对平均功率和疲劳指数,说明补充白藜芦醇可能通过减轻剧烈运动导致的肌肉损伤来延缓疲劳。进一步研究表明,白藜芦醇减轻肌肉损伤的机制可能与其降低运动诱导的炎症反应、清除自由基、抑制脂质过氧化反应,从而维持肌细胞膜的结构与功能稳定有关[6,59]。此外,白藜芦醇可能通过与膜脂质相互作用,在维持肌细胞膜的流动性和弹性方面起到关键作用。例如,NEVES等[60]利用X射线散射技术探究了白藜芦醇对双层脂质域结构组织的影响,发现白藜芦醇能够诱导相分离,促进L-α-磷脂酰胆碱、L-α-磷脂酰胆碱:胆固醇(4∶1)和L-α-磷脂酰胆碱∶胆固醇∶鞘磷脂(1∶1∶1)双层中脂质结构域的形成,从而为膜带来一些结构组织,这有利于增加细胞膜的流动性,使其在受到外部应力时能够保持一定的弹性和柔韧性,降低膜裂的风险。因此,白藜芦醇可能通过增加肌细胞膜的流动性,减少运动诱导的肌细胞损伤,进而延缓疲劳的发生。
白藜芦醇也被证明能够调节肌细胞膜上钙离子相关通道,减少钙离子的过度流入。兰尼碱受体是位于肌浆网膜上的细胞内钙离子释放通道,在剧烈运动时易发生异常剪切,导致细胞内钙离子超载,从而引起肌细胞损伤[61]。SANTORO等[62]通过对白藜芦醇处理强直性肌营养不良1型肌管的研究发现,白藜芦醇能够纠正兰尼碱受体1异常剪切,并改善去极化诱导的钙离子从兰尼碱受体1的释放。钠钙交换体是肌细胞膜上的另一种离子交换蛋白,其主要功能是通过逆向或正向交换,将细胞内多余的钙离子排出,同时允许钠离子进入细胞。在高强度或长时间运动过程中,钠钙交换体的功能可能受到影响,进而导致钙离子过度流入肌细胞内[63]。YAN等[64]研究表明,白藜芦醇可刺激质膜上的钠钙交换体,对腺苷5’-三磷酸诱导的钙离子从肌浆网释放起到调节作用,进而减少平滑肌细胞胞浆中钙离子过度蓄积。由此可见,白藜芦醇可能通过调节兰尼碱受体1和钠钙交换体,防止因钙离子过度内流而引发的肌细胞损伤,从而延缓疲劳的发生。
遗憾的是,尽管上述研究证实了白藜芦醇对细胞膜流动性和钙离子通道的调节作用,但这些研究的对象并非骨骼肌细胞。因此,白藜芦醇是否在高强度或长时间运动条件下对骨骼肌细胞表现出类似的调节效应仍有待商榷,需在未来的研究中进行更多的实验加以验证。
2.5.6 其他作用 除了上述作用机制外,补充白藜芦醇还可能通过以下几个方面来延缓运动性疲劳的产生:①调节神经递质分泌。如前所述,神经递质的紊乱在运动性疲劳的发生中起关键作用。5-羟色胺是由色氨酸合成的神经递质,可以在特定载体的帮助下通过血脑屏障。在长时间的运动中,血浆和脑中的色氨酸浓度升高,进而导致脑内5-羟色胺水平升高[65]。据报道,高浓度的5-羟色胺促进嗜睡和自觉劳累,从而导致运动表现受限和中枢疲劳[66]。GUALDONI等[67]在人体试验中发现白藜芦醇的补充可显著降低健康受试者血浆中色氨酸水平。基于这一特性,白藜芦醇可能在运动过程中对脑内5-羟色胺浓度升高起到有效的缓冲作用,从而降低机体的疲劳感。高温是影响耐力运动的一个关键因素,而多巴胺作为体温调节中枢中的重要神经递质,其在脑室内释放减少已被证明会影响运动过程中的核心体温调节,进而导致中枢疲劳产生[68]。GU等[69]报道,白藜芦醇腹腔注射可以剂量依赖方式提高小鼠前额叶皮质中多巴胺水平,这提示补充白藜芦醇可能通过增加脑内多巴胺释放来缓解运动过程中由高温所引起的中枢疲劳。此外,谷氨酸是主要的兴奋性神经递质,参与神经信号的传递和神经元的活化。在剧烈运动后,谷氨酸释放过量可能导致神经元过度兴奋,进而引发兴奋毒性作用,损伤神经元功能,导致神经系统失衡,出现中枢性疲劳[30]。NASR等[9]研究发现,通过服用含有白藜芦醇的纳米乳剂能够显著降低高氨血症大鼠脑中谷氨酸含量,减少其毒性累积。因此,白藜芦醇也可能通过减少运动中脑内谷氨酸过度释放,从而延缓中枢性疲劳的产生。②减少代谢产物积累。乳酸是无氧代谢的重要副产物,过度积累会引起肌肉酸化,影响肌肉收缩能力和神经信号传递。KAN等[70]发现白藜芦醇补充4周可显著降低老年小鼠急性游泳运动后血浆中乳酸水平,并明显延长力竭游泳时间,提示白藜芦醇可能通过减少乳酸堆积而延缓疲劳的发生。进一步研究表明,白藜芦醇能够促进乳酸清除可能与其增强乳酸脱氢酶的活性,进而加速乳酸向丙酮酸的转化有关[71]。此外,HAN等[72]的研究表明,白藜芦醇联合定期有氧运动能够改善血管反应性与血管功能相关的生物标志物,如上调抗氧化酶和内皮型一氧化氮合酶的表达,增强主动脉中非选择性磷酸二酯酶1/2/3及环磷酸腺苷选择性磷酸二酯酶4的基因表达。这提示白藜芦醇可能通过改善血管内皮功能和促进血管扩张,增加血液循环,从而加速代谢产物的清除。
补充白藜芦醇延缓运动性疲劳的作用机制总结见图6。表1,2汇总了白藜芦醇延缓运动性疲劳的相关研究。