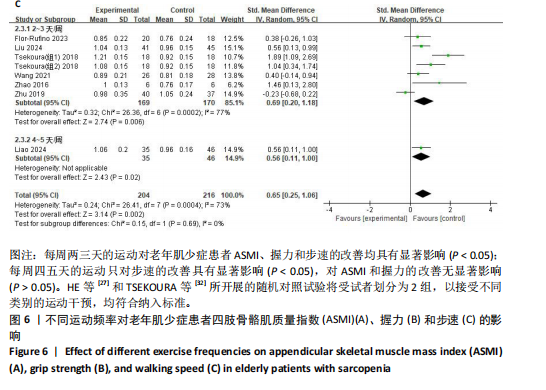
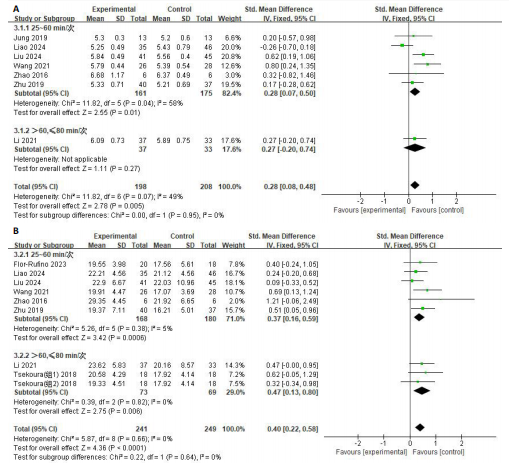
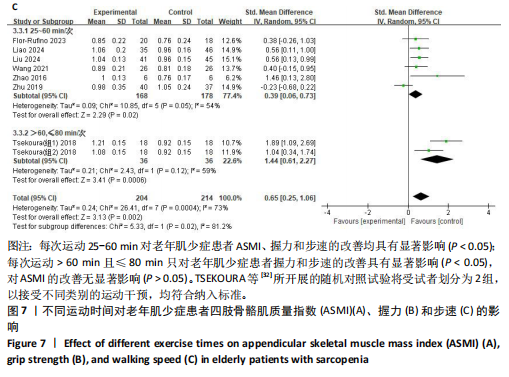
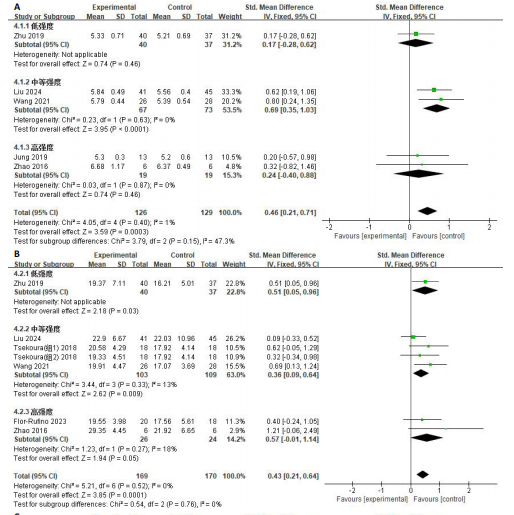
[1] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, SAYER AA. Sarcopenia. Lancet. 2019;393(10191):2636-2646.
[2] YE C, ZHENG X, AIHEMAITIJIANG S, et al. Sarcopenia and catastrophic health expenditure by socio‐economic groups in China: an analysis of household‐based panel data. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022; 13(3):1938-1947.
[3] YUAN S, LARSSON SC. Epidemiology of sarcopenia: Prevalence, risk factors, and consequences. Metabolism. 2023;144: 155533.
[4] 沈睿, 王茜茜, 徐霓影, 等. 老年肌少症患者运动干预的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志,2021,56(10):1560-1566.
[5] IZQUIERDO M, MERCHANT RA, MORLEY JE, et al. International Exercise Recommendations in Older Adults (ICFSR): Expert Consensus Guidelines. J Nutr Health Aging. 2021;25(7):824-853.
[6] OLIVEIRA JS, PINHEIRO MB, FAIRHALL N, et al. Evidence on Physical Activity and the Prevention of Frailty and Sarcopenia Among Older People: A Systematic Review to Inform the World Health Organization Physical Activity Guidelines. J Phys Act Health. 2020; 17(12):1247-1258.
[7] HURST C, ROBINSON SM, WITHAM MD, et al. Resistance exercise as a treatment for sarcopenia: prescription and delivery. Age Ageing. 2022;51(2):afac003.
[8] YANG CL, HUANG JP, WANG TT, et al. Effects and parameters of community-based exercise on motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis. BMC Neurol. 2022; 22(1):505.
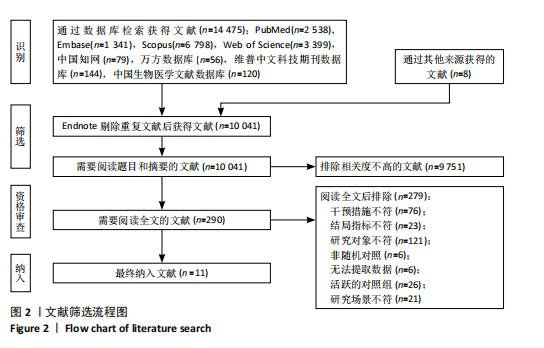
[9] PAGE MJ, MCKENZIE JE, BOSSUYT PM, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n71.
[10] CHEN LK. Sarcopenia in Asia: Consensus Report of the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2014; 15(2):95-101.
[11] CHEN LK, LEE WJ, PENG LN, et al. Recent Advances in Sarcopenia Research in Asia: 2016 Update From the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2016;17(8):767.e1-7.
[12] CHEN LK, WOO J, ASSANTACHAI P, et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2020; 21(3):300-307.e2.
[13] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, BAEYENS JP, BAUER JM, et al. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2010; 39(4):412-423.
[14] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, BAHAT G, BAUER J, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2019; 48(1):16-31.
[15] DRAHOTA A, UDELL JE, MACKENZIE H, et al. Psychological and educational interventions for preventing falls in older people living in the community. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024;10(10):CD013480.
[16] GALLARDO-GÓMEZ D, SALAZAR-MARTÍNEZ E, ALFONSO-ROSA RM, et al. Optimal Dose and Type of Physical Activity to Improve Glycemic Control in People Diagnosed With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Diabetes Care. 2024;47(2): 295-303.
[17] 刘海宁, 吴昊, 姚灿, 等. Meta分析中连续性数据的深度提取方法[J]. 中国循证医学杂志,2017,17(1):117-121.
[18] JAYEDI A, EMADI A, SHAB-BIDAR S. Dose-Dependent Effect of Supervised Aerobic Exercise on HbA1c in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Sports Med. 2022;52(8): 1919-1938.
[19] ASHOR AW, LARA J, SIERVO M, et al. Exercise Modalities and Endothelial Function: A Systematic Review and Dose–Response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Sports Med. 2015;45(2):279-296.
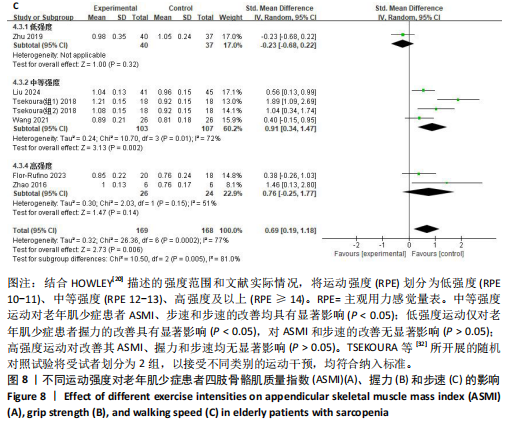
[20] HOWLEY ET. Type of activity: resistance, aerobic and leisure versus occupational physical activity. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2001; 33(6 Suppl):S364-369;discussion S419-420.
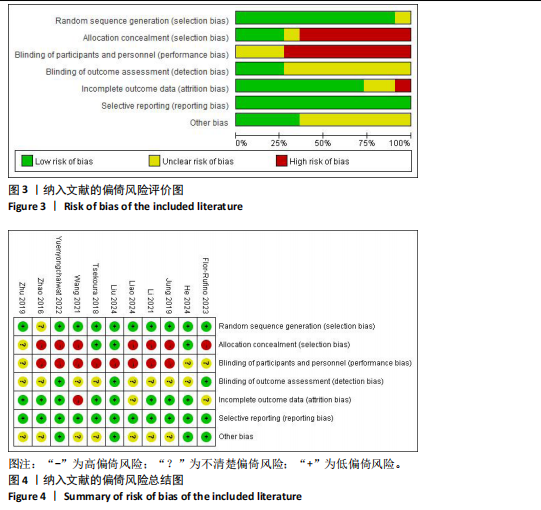
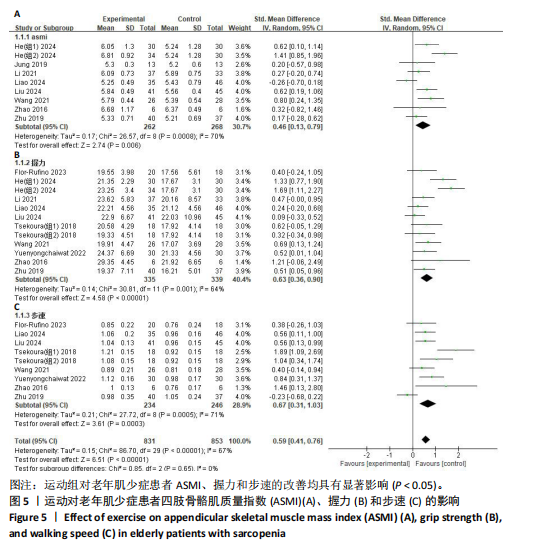
[21] HIGGINS JPT, ALTMAN DG, GØTZSCHE PC, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011;343:d5928.
[22] MOSELEY AM, RAHMAN P, WELLS GA, et al. Agreement between the Cochrane risk of bias tool and Physiotherapy Evidence Database (PEDro) scale: A meta-epidemiological study of randomized controlled trials of physical therapy interventions. PloS One. 2019;14(9): e0222770.
[23] DE ALMEIDA FO, SANTANA V, CORCOS DM, et al. Effects of Endurance Training on Motor Signs of Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2022;52(8):1789-1815.
[24] 王光辉, 蔡文玮, 沈晓君, 等. 弹力带抗阻运动训练12周对社区老年肌少症患者肌力的影响[J]. 中国临床保健杂志,2021, 24(6):800-804.
[25] 赵永军, 张育民, 郭艳花, 等. 推拿结合抗阻运动对骨骼肌衰减症患者日常生活活动能力的影响[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2016,31(9):989-994.
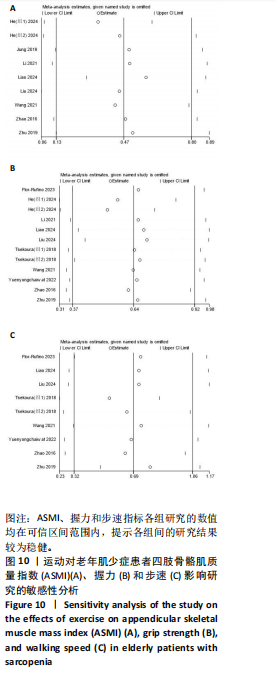
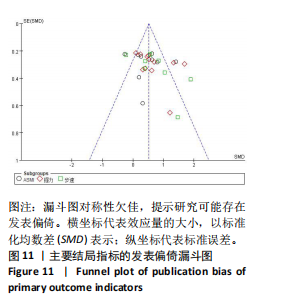
[26] FLOR-RUFINO C, BARRACHINA-IGUAL J, PÉREZ-ROS P, et al. Fat infiltration and muscle hydration improve after high-intensity resistance training in women with sarcopenia. A randomized clinical trial. Maturitas. 2023;168:29-36.
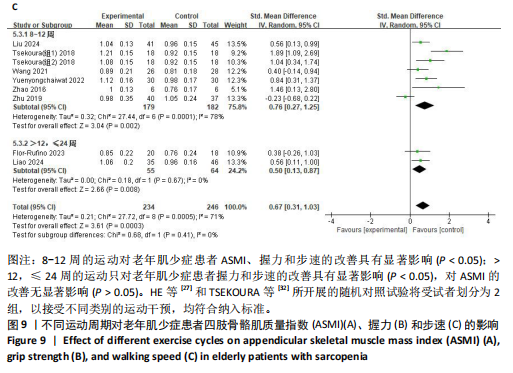
[27] HE S, WEI M, MENG D, et al. Self-determined sequence exercise program for elderly with sarcopenia: A Randomized controlled trial with clinical assistance from explainable artificial intelligence. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2024;119:105317.
[28] JUNG WS, KIM YY, PARK HY. Circuit Training Improvements in Korean Women with Sarcopenia. Percept Mot Skills. 2019; 126(5):828-842.
[29] LI Z, CUI M, YU K, et al. Effects of nutrition supplementation and physical exercise on muscle mass, muscle strength and fat mass among sarcopenic elderly: a randomized controlled trial. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2021;46(5):494-500.
[30] LIAO X, CHENG D, LI J, et al. Effects of oral oligopeptide preparation and exercise intervention in older people with sarcopenia: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Geriatr. 2024;24(1):260.
[31] LIU M, LI J, XU J, et al. Graded Progressive Home-Based Resistance Combined with Aerobic Exercise in Community-Dwelling Older Adults with Sarcopenia: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin Interv Aging. 2024;19: 1581-1595.
[32] TSEKOURA M, BILLIS E, TSEPIS E, et al. The Effects of Group and Home-Based Exercise Programs in Elderly with Sarcopenia: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Clin Med. 2018;7(12):480.
[33] YUENYONGCHAIWAT K, AKEKAWATCHAI C. Beneficial effects of walking-based home program for improving cardio-respiratory performance and physical activity in sarcopenic older people: a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2022;58(6):838-844.
[34] ZHU LY, CHAN R, KWOK T, et al. Effects of exercise and nutrition supplementation in community-dwelling older Chinese people with sarcopenia: a randomized controlled trial. Age Ageing. 2019;48(2):220-228.
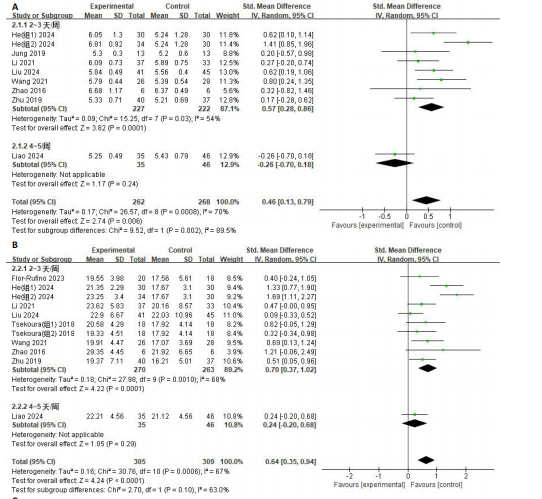
[35] ZHANG Y, ZOU L, CHEN ST, et al. Effects and Moderators of Exercise on Sarcopenic Components in Sarcopenic Elderly: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Med. 2021;8:649748.
[36] BAO W, SUN Y, ZHANG T, et al. Exercise Programs for Muscle Mass, Muscle Strength and Physical Performance in Older Adults with Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Aging Dis. 2020;11(4):863-873.
[37] HASSAN BH, HEWITT J, KEOGH JWL, et al. Impact of resistance training on sarcopenia in nursing care facilities: A pilot study. Geriatr Nurs. 2016;37(2):116-121.
[38] DOS SANTOS VR, ANTUNES M, DOS SANTOS L, et al. Effects of Different Resistance Training Frequencies on Body Composition, Muscular Strength, Muscle Quality, and Metabolic Biomarkers in Sarcopenic Older Women. J Strength Cond Res. 2024;38(9): e521.
[39] LIU M, MEI DH, ZHANG YL, et al. Meta-analysis of exercise intervention on health behaviors in middle-aged and older adults. Front Psychol. 2024;14:1308602.
[40] APPELL HJ, SOARES JMC, DUARTE JAR. Exercise, Muscle Damage and Fatigue. Sports Med. 1992;13(2):108-115.
[41] 赵婉越, 张伯煜, 孙婷, 等. 运动改善老年人衰弱状况的剂量效应Meta分析[J]. 中国慢性病预防与控制,2023,31(11): 860-866.
[42] TAN TW, TAN HL, HSU MF, et al. Effect of non-pharmacological interventions on the prevention of sarcopenia in menopausal women: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Women’s Health. 2023;23(1):606.
[43] 郝莹, 陈卓. 抗阻运动提升老年人下肢肌肉力量及功能状态的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国循证医学杂志,2024,24(2):175-182.
[44] HUANG LY, LIM AY, HSU CC, et al. Sustainability of exercise-induced benefits on circulating MicroRNAs and physical fitness in community-dwelling older adults: a randomized controlled trial with follow up. BMC Geriatr. 2024;24(1):473.
[45] NAMBI G, ABDELBASSET WK, ALRAWAILI SM, et al. Comparative effectiveness study of low versus high-intensity aerobic training with resistance training in community-dwelling older men with post-COVID 19 sarcopenia: A randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2022;36(1):59-68.
[46] TAN KHL, SIAH CJR. Effects of low-to-moderate physical activities on older adults with chronic diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Nurs. 2022;31(15-16):2072-2086.
[47] CHEN N, HE X, FENG Y, et al. Effects of resistance training in healthy older people with sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur Rev Aging Phys Act. 2021;18(1): 23.
[48] ZHUANG M, JIN M, LU T, et al. Effects of three modes of physical activity on physical fitness and hematological parameters in older people with sarcopenic obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Physiol. 2022;13:917525.
[49] CHANG MC, LEE AY, KWAK S, et al. Effect of Resistance Exercise on Depression in Mild Alzheimer Disease Patients With Sarcopenia. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2020;28(5):587-589.
[50] SEN EI, EYIGOR S, YAGLI MD, et al. Effect of Home-Based Exercise Program on Physical Function and Balance in Older Adults With Sarcopenia: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Study. J Aging Phys Activ. 2021; 29(6):1010-1017.
[51] 王丽丽, 田丽雅, 牛琪, 等. 11种运动对老年肌少症患者身体功能改善效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中华护理杂志,2022, 57(21):2652-2660. |