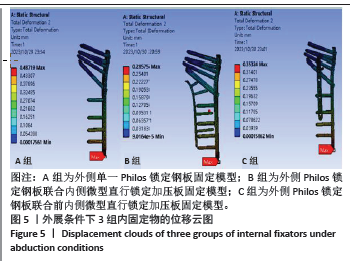
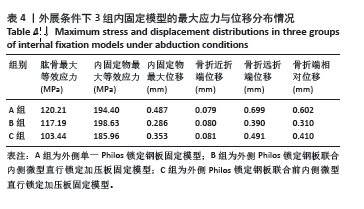
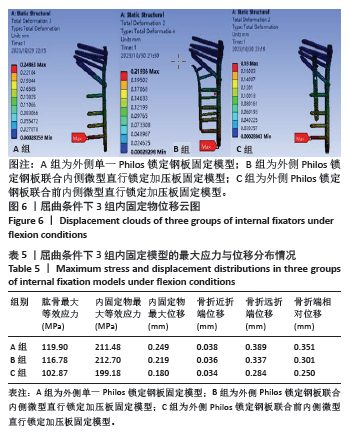
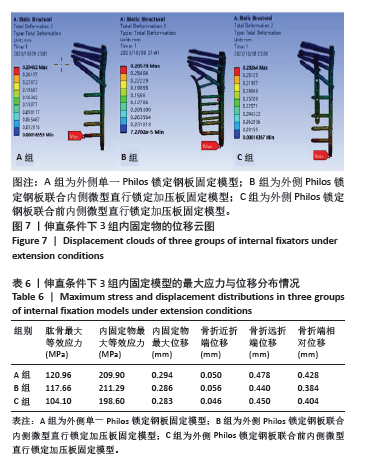
[1] 张玉富,蒋协远.肱骨近端骨折手术治疗的进展与思考[J].中国骨伤,2023,36(2):99-102.
[2] ZHU Z, CHANG Z, ZHANG W, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of novel intra- and extramedullary assembly fixation for proximal humerus fractures in the elderly. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1182422.
[3] MICHEL P, RASCHKE M, KATTHAGEN J, et al. Double Plating for Complex Proximal Humeral Fractures: Clinical and Radiological Outcomes. J Clin Med. 2023;12(2):696.
[4] BAKER HP, GUTBROD J, CAHILL M, et al. Optimal Treatment of Proximal Humeral Fractures in the Elderly: Risks and Management Challenges.Orthop Res Rev. 2023;15:129-137.
[5] WANG Y, LI J, MEN Y, et al. Intrinsic Cortical Property Analysis of the Medial Column of Proximal Humerus. Orthop Surg. 2023;15(3): 793-800.
[6] DANG KH, ORNELL SS, REYES G, et al. A new risk to the axillary nerve during percutaneous proximal humeral plate fixation using the Synthes PHILOS aiming system. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2019;28(9): 1795-1800.
[7] BAKER HP, GUTBROD J, STRELZOW JA, et al. Management of Proximal Humerus Fractures in Adults—A Scoping Review. J Clin Med. 2022; 11(20):6140.
[8] DOSHI C. Treatment of Proximal Humerus Fractures using PHILOS Plate. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017;11(7):10-13.
[9] MCLEAN AS, PRICE N, GRAVES S, et al. Nationwide trends in management of proximal humeral fractures: an analysis of 77,966 cases from 2008 to 2017. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2019;28(11):2072-2078.
[10] 李波,张世民,胡孙君,等.肱骨头下皮质外距螺钉重建内侧柱稳定性的三维有限元分析[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2022,36(8): 995-1002.
[11] 常祖豪,张伟,唐佩福,等.内侧支撑重建增强固定技术在肱骨近端骨折治疗中的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(3): 375-380.
[12] JHAMNANI R, DHANDA MS, SURANA A. Study of Functional Outcome and Postoperative Complications Among Proximal Humerus Fracture Patients Treated With Proximal Humerus Internal Locking System (PHILOS) Plating. Cureus. 2023;15(7):42411.
[13] JUNG WB, MOON ES, KIM SK, et al. Does medial support decrease major complications of unstable proximal humerus fractures treated with locking plate? BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013;14:102.
[14] RAITHATHA H, PATIL VS, PAI M, et al. Clinical and Radiological Outcome of Dual Plating for Proximal Humerus Fractures. Cureus. 2023;15(1): e33570.
[15] 姚灿,杨光永,娄菊红,等.双钢板与单钢板内固定治疗肱骨近端骨折的临床研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2023,31(6):24-28.
[16] 瞿杭波,杨自荣,闫应朝,等.双钢板固定治疗老年复杂肱骨近端骨折[J].中国骨伤,2023,36(2):103-109.
[17] YE Y, YOU W, ZHU W, et al. The Applications of Finite Element Analysis in Proximal Humeral Fractures. Comput Math Methods Med. 2017; 2017:1-9.
[18] SANDERS BS, BULLINGTON AB, MCGILLIVARY GR, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of locked plating in proximal humeral fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16(2):229-234.
[19] 刘炎,葛鸿庆,陈文治,等.肱骨近端骨折中不同腓骨支撑方式重建内侧柱的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(18): 2804-2808.
[20] LI D, LV W, CHEN W, et al. Application of a lateral intertubercular sulcus plate in the treatment of proximal humeral fractures: a finite element analysis. BMC Surg. 2022;22(1):98.
[21] HE Y, HE J, WANG F, et al. Application of Additional Medial Plate in Treatment of Proximal Humeral Fractures With Unstable Medial Column. Medicine. 2015;94(41):e1775.
[22] VAJGEL A, CAMARGO IB, WILLMERSDORF RB, et al. Comparative Finite Element Analysis of the Biomechanical Stability of 2.0 Fixation Plates in Atrophic Mandibular Fractures. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;71(2): 335-342.
[23] LAUX CJ, GRUBHOFER F, WERNER CML, et al. Current concepts in locking plate fixation of proximal humerus fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):137.
[24] ADIYEKE L. Comparison of effective factors in loss of reduction after locking plate-screw treatment in humerus proximal fractures. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2022;28(7):1008-1015.
[25] SEETHARAM CT, JAYARAM M, BACHHAPPA SH, et al. Study of surgical management of fracture of proximal humerus by PHILOS plate and screws. Int J Res Orthop. 2020;6(3):462-466.
[26] LEE J, KIM J, KIM K, et al. Effect of Calcar Screw in Locking Compression Plate System for Osteoporotic Proximal Humerus Fracture: A Finite Element Analysis Study. Biomed Res Int. 2022; 2022:1268774.
[27] ZENG LQ, ZENG LL, JIANG YW, et al. Influence of Medial Support Screws on the Maintenance of Fracture Reduction after Locked Plating of Proximal Humerus Fractures. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018;131(15): 1827-1833.
[28] XU J, ZHAN S, LING M, et al. How can medial support for proximal humeral fractures be achieved when positioning of regular calcar screws is challenging? Slotting and off-axis fixation strategies. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2022;31(4):782-791.
[29] HE Y, ZHANG Y, WANG Y, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of a novel dualplate fixation method for proximal humeral fractures without medial support. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):72.
[30] YANG P. Biomechanical effect of medial cortical support and medial screw support on the locking plate fixation of the proximal humeral fractures with a medial gap: a finite element analysis. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2015;49(2):203-209.
[31] DI TULLIO P, GIORDANO V, SOUTO E, et al. Biomechanical behavior of three types of fixation in the two-part proximal humerus fracture without medial cortical support. PLoS One. 2019;14(7):e0220523.
[32] 贾进,陆晓涛,蒙顺,等.双钢板与锁定钢板在复杂肱骨近端骨折治疗中的疗效比较[J].昆明医科大学学报,2022,43(2):82-88.
[33] XIANG H, WANG Y, YANG Y, et al. Anatomical study for the treatment of proximal humeral fracture through the medial approach. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):17-35.
[34] WANG F, WANG Y, DONG J, et al. A novel surgical approach and technique and short-term clinical efficacy for the treatment of proximal humerus fractures with the combined use of medial anatomical locking plate fixation and minimally invasive lateral locking plate fixation. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):16-29.
[35] WARNHOFF M, JENSEN G, DEY HAZRA RO, et al. Double plating - surgical technique and good clinical results in complex and highly unstable proximal humeral fractures. Injury. 2021;52(8):2285-2291.
[36] 欧阳敏.改良肱骨近端锁定钢板治疗肱骨近端骨折的三维有限元分析[D].南昌: 南昌大学,2023.
[37] BREKELMANS WA, POORT HW, SLOOFF TJ. A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts. Acta Orthop Scand. 1972; 43(5):301-317.
[38] LEWIS GS, MISCHLER D, WEE H, et al. Finite Element Analysis of Fracture Fixation. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2021;19(4):403-416. |