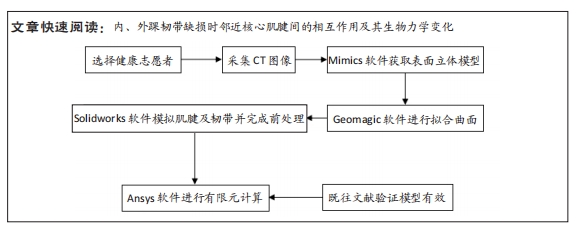
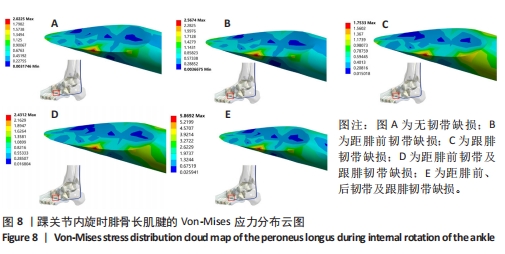
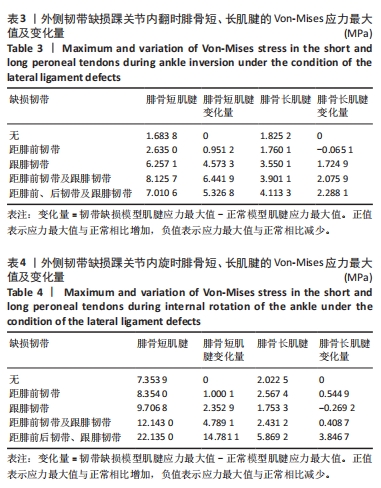
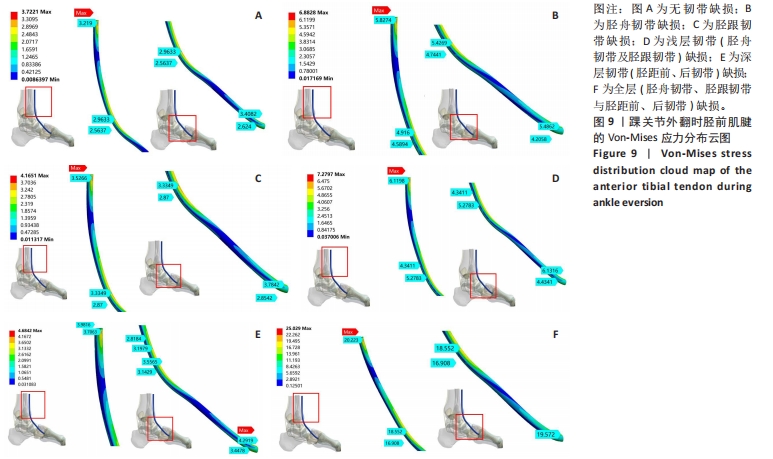
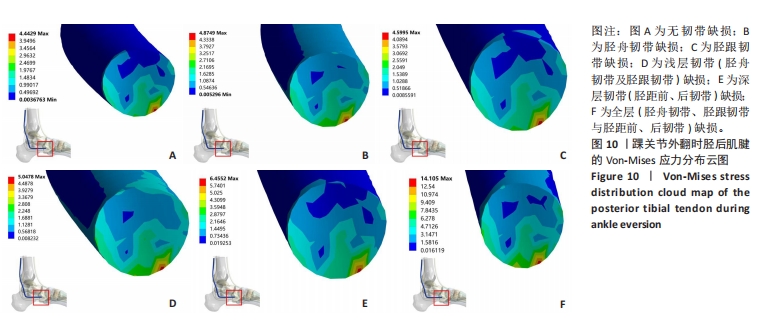
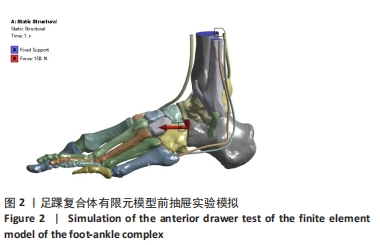
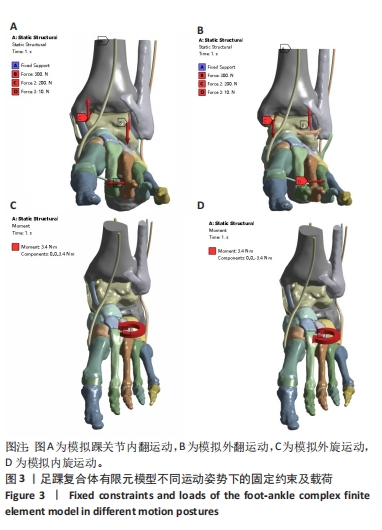
[1] 杨海洲,杨秋翔,陈雨灵,等.踝关节外侧副韧带的解剖研究及对重建手术的意义[J].解剖学研究,2021,43(3):264-267.
[2] VEGA J, GUELFI M. Arthroscopic assessment and treatment of medial collateral ligament complex. Foot Ankle Clin. 2021;26(2):305-313.
[3] CRUZ-DÍAZ D, HITA-CONTRERAS F, LOMAS-VEGA R, et al. Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Spanish version of the Cumberland Ankle Instability Tool (CAIT): an instrument to assess unilateral chronic ankle instability. Clin Rheumatol. 2013;32(1):91-98.
[4] 刘松波,李兴华,刘化文,等.自体腓骨短肌腱重建距腓前韧带和跟腓韧带治疗慢性踝关节外侧不稳定[J].中国骨伤,2022,35(2):172-177.
[5] 鞠峰.部分腓骨短肌腱解剖重建陈旧性距腓前韧带损伤的临床疗效观察[D].青岛:青岛大学,2018.
[6] YANG Z, LIU F, CUI L, et al. Comparison of the effects of reconstruction of the lateral ankle ligaments using peroneus longus and peroneus brevis tendon graft. Medicine. 2020;99(46):e22912.
[7] KRIPS R, VAN DIJK CN, HALASI T, et al. Anatomical reconstruction versus tenodesis for the treatment of chronic anterolateral instability of the ankle joint: a 2-to 10-year follow-up, multicenter study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2000;8(3):173-179.
[8] 张银龙,崔玉凤,张之智.切取腓骨长肌肌腱移植对踝关节外翻力度和角度的影响[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2017,32(8):878-879.
[9] HADDAD SL, DEDHIA S, REN Y, et al. Deltoid ligament reconstruction: a novel technique with biomechanical analysis. Foot Ankle Int. 2010; 31(7):639-651.
[10] ISMAIL EE SR, AL SAFFAR RA, MOTAWEI K, et al. Defining the Components of the Deltoid Ligament (DL): a cadaveric study. Cureus. 2022;14(3):e23051.
[11] DO AMARAL E CASTRO A, GODOY-SANTOS AL, TANEJA AK. Advanced imaging in the chronic lateral ankle instability: an algorithmic approach. Foot Ankle Clin. 2023;28(2):265-282.
[12] BIANCHI S, BORTOLOTTO C, DRAGHI F. Os peroneum imaging: normal appearance and pathological findings. Insights imaging. 2017;8(1):59-68.
[13] LI J, WEI Y, WEI M. Finite element analysis of the effect of talar osteochondral defects of different depths on ankle joint stability. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e921823.
[14] 国婷婷,谢红,徐光华.弹性护踝防护性能的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(7):1031-1037.
[15] 戴海飞,余斌,张凯瑞,等.踝关节周围韧带损伤对距骨稳定性影响的有限元分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(2):121-124.
[16] ZHANG Y, GUO Y, LONG X, et al. Analysis of the main soft tissue stress associated with flexible flatfoot deformity: a finite element study. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2021;20:2169-2177.
[17] 边蔷,胡海威,温建民,等.足部相关肌肉-肌腱组织材料弹性模量的测定[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(12):1919-1923.
[18] 许灿,张明彦,雷光华,等.踝关节内侧韧带损伤肌腱重建的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(35):6478-6483.
[19] WANG CW, MUHEREMU A, BAI JP. Use of three-dimensional finite element models of the lateral ankle ligaments to evaluate three surgical techniques. J Int Med Res. 2018;46(2):699-709.
[20] LEE KT, LEE JI, SUNG KS, et al. Biomechanical evaluation against calcaneofibular ligament repair in the Brostrom procedure: a cadaveric study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2008;16(8):781-786.
[21] WILLIAMS J, DAVIES M, GUDURI V, et al. The multi-ligament ankle fracture: Epidemiology, key anatomical findings and fixation strategies in unstable open injuries. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2023;36:102086.
[22] LI Y, TONG J, WANG H, et al. Investigation into the effect of deltoid ligament injury on rotational ankle instability using a three-dimensional ankle finite element model. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12:1386401.
[23] CIFUENTES-DE LA PORTILLA C, PASAPULA C, GUTIÉRREZ-NARVARTE B, et al. Peroneus Longus overload caused by soft tissue deficiencies associated with early adult acquired flatfoot: A finite element analysis. Clin Biomech. 2021;86:105383.
[24] KIM JS, YOUNG KW, CHO HK, et al. Concomitant syndesmotic instability and medial ankle instability are risk factors for unsatisfactory outcomes in patients with chronic ankle instability. Arthroscopy. 2015;31(8): 1548-1556.
[25] CASADO-HERNÁNDEZ I, BECERRO-DE-BENGOA-VALLEJO R, LOSA-IGLESIAS ME, et al. Association between anterior talofibular ligament injury and ankle tendon, ligament, and joint conditions revealed by magnetic resonance imaging. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2021;11(1):84.
[26] SAKI F, YALFANI A, FOUSEKIS K, et al. Anatomical risk factors of lateral ankle sprain in adolescent athletes: A prospective cohort study. Phys Ther Sport. 2021;48:26-34.
[27] YOSHIZUKA H, KURAOKA A. Calcaneofibular ligament may act as a tensioner of peroneal tendons as revealed by a contactless three-dimensional scan system on cadavers. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):16650.
[28] MIRANDA FC, KIHARA FILHO EN, PRADO MP, et al. Acute ankle injuries: association between sprain severity and ancillary findings. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2023;21:eAO0162.
[29] WILLIAMS III DS, MCCLAY IS, HAMILL J. Arch structure and injury patterns in runners. Clin Biomech. 2001;16(4):341-347.
[30] ZWIRNER J, KOUTP A, VIDAKOVIC H, et al. Assessment of plantaris and peroneus tertius tendons as graft materials for ankle ligament reconstructions–A cadaveric biomechanical study. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021;115:104244.
[31] WIERER G, GWINNER C, SCHEFFLER S. Peroneus Longus Split Versus Semitendinosus Tendon Autograft Size: A Cross-sectional Study. Am J Sports Med. 2023;51(7):1743-1751.
[32] PUNNOOSE DJ, VARGHESE J, THERUVIL B, et al. Peroneus Longus Tendon Autografts have Better Graft Diameter, Less Morbidity, and Enhanced Muscle Recuperation than Hamstring Tendon in ACL Reconstruction. Indian J Orthop. 2024;58(7):979-986.
[33] GOYAL T, PAUL S, CHOUDHURY AK, et al. Full-thickness peroneus longus tendon autograft for anterior cruciate reconstruction in multi-ligament injury and revision cases: outcomes and donor site morbidity. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2023;33(1):21-27.
[34] 董伊隆,钱约男,李一民,等.跟腓韧带解剖重建的解剖学研究[J].中国骨伤,2021,34(9):847-850.
|