中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (33): 7231-7240.doi: 10.12307/2025.837
• 骨与关节综述 bone and joint review • 上一篇 下一篇
人工智能与颈椎图像识别:应用前景与挑战
王思敏1,张德洲1,赵 静1,王超群2,李 琨3,4,陈 杰3,白 雪4,赵海龙4,张少杰3,4,马 渊4,郝韵腾4,杨 洋3,李志军3,4,史 君5,王 星3,4
- 内蒙古医科大学,1研究生院,3基础医学院解剖学教研室,5基础医学院生理学教研室,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010110;2内蒙古医科大学附属医院影像科,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010050; 4内蒙古医科大学基础医学院数字医学中心/内蒙古自治区数字转化医学工程技术研究中心,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010059
-
收稿日期:2024-07-17接受日期:2024-09-05出版日期:2025-11-28发布日期:2025-04-15 -
通讯作者:王星,博士,副教授,内蒙古医科大学基础医学院解剖学教研室,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010110;内蒙古医科大学基础医学院数字医学中心/内蒙古自治区数字转化医学工程技术研究中心,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010059 史君,副教授,内蒙古医科大学基础医学院生理学教研室,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010110 -
作者简介:王思敏,女,1996年生,山西省吕梁市人,内蒙古医科大学在读硕士,主要从事脊柱与脊髓的数字化研究。 张德洲,男,1998年生,贵州省铜仁市人,土家族,内蒙古医科大学在读硕士,主要从事脊柱与脊髓的数字化研究。 -
基金资助:内蒙古自治区高等学校青年科技英才支持计划资助(NJYT22009),项目负责人:王星;内蒙古医科大学科研重点项目(YKD2021ZD011),项目负责人:王星;内蒙古自治区卫生健康委医疗卫生科技计划项目(202201217),项目负责人:王星;内蒙古医科大学博士启动基金项目(YKD2023BSQD014),项目负责人:王星;内蒙古自治区硕士研究生科研创新计划(S20231186Z),项目负责人:王思敏;内蒙古自治区硕士研究生科研创新计划(S20231182Z),项目负责人:郝韵腾
Artificial intelligence and cervical spine image recognition: application prospects and challenges
Wang Simin1, Zhang Dezhou1, Zhao Jing1, Wang Chaoqun2, Li Kun3, 4, Chen Jie3, Bai Xue4, Zhao Hailong4, Zhang Shaojie3, 4, Ma Yuan4, Hao Yunteng4, Yang Yang3, Li Zhijun3, 4, Shi Jun5, Wang Xing3, 4
- 1Graduate School of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010110, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Imaging, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010050, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 3Anatomy Teaching and Research Section, School of Basic Medicine, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010110, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 4Digital Medicine Center/Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Digital Translational Medicine Engineering Technology Research Center, School of Basic Medicine, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010059, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 5Physiology Teaching and Research Section, School of Basic Medicine, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010110, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-07-17Accepted:2024-09-05Online:2025-11-28Published:2025-04-15 -
Contact:Wang Xing, MD, Associate professor, Anatomy Teaching and Research Section, School of Basic Medicine, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010110, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; Digital Medicine Center/Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Digital Translational Medicine Engineering Technology Research Center, School of Basic Medicine, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010059, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China Shi Jun, Associate professor, Physiology Teaching and Research Section, School of Basic Medicine, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010110, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wang Simin, Master candidate, Graduate School of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010110, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China Zhang Dezhou, Master candidfate, Graduate School of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010110, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region College Young Science and Technology Talent Support Program, No. NJYT22009 (to WX); Key Research Project of Inner Mongolia Medical University, No. YKD2021ZD011 (to WX); Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Health Commission Medical and Health Science and Technology Plan Project, No. 202201217 (to WX); Inner Mongolia Medical University Doctoral Start-up Fund Project, No. YKD2023BSQD014 (to WX); Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Master's Research Innovation Program, No. S20231186Z (to WSM); Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Master's Research Innovation Program, No. S20231182Z (to HYT)
摘要:
文题释义:
人工智能:是一门新兴的技术科学,致力于研究开发用于模拟、延伸和扩展人类智能理论、方法、技术及应用系统。作为智能学科的重要组成部分,人工智能旨在理解智能的本质,并开发类似于人类并能够做出反应的智能机器。深度学习:是机器学习领域中一个新的研究方向,它的最终目标是让机器能够像人一样具有分析学习能力,能够识别文字、图像和声音等数据。
背景:颈椎病是一种慢性退行性疾病,已经成为威胁人类健康的常见病和多发病之一。目前对颈椎及其周围结构病变的初步诊断主要倚赖于放射科医师对医学影像的解读,这不仅对操作人员技术要求较高,而且存在主观性较强、劳动强度高、效率低等缺点。随着人工智能技术的快速发展,其强大的数据处理和图像识别能力使其在医疗领域展现出广阔的应用前景,深度学习也在脊柱疾病的研究中取得了一定的进展。
目的:综述近年来人工智能技术在颈椎影像图像中的应用现状和研究进展,评估人工智能模型的表现以及未来的发展趋势及需要克服的挑战。方法:由第一作者在 2024 年 6 月以“人工智能,深度学习,颈椎” 为 中 文 检 索 词,以“Artificial Intelligence,AI,Cervical Vertebrae,Cervical”为英文检索词分别在万方数据库、中国知网和PubMed数据库进行检索,最终纳入101篇文章进行综述分析。
结果与结论:①人工智能技术可通过对医学图像部位进行分割、分类、关键点识别等技术实现对颈椎椎体的自动分割及曲度改变的测量,检测颈椎骨折、神经根和脊髓型颈椎病,识别颈椎后纵韧带骨化,预测手术后相关危险因素以及颈椎成熟度分类等;②尽管人工智能技术在颈椎研究领域已展现出巨大潜力,但其仍处于初期探索与快速发展阶段,有无限的发展与创新空间。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0059-4921 (王星)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
王思敏, 张德洲, 赵 静, 王超群, 李 琨, 陈 杰, 白 雪, 赵海龙, 张少杰, 马 渊, 郝韵腾, 杨 洋, 李志军, 史 君, 王 星. 人工智能与颈椎图像识别:应用前景与挑战[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(33): 7231-7240.
Wang Simin, Zhang Dezhou, Zhao Jing, Wang Chaoqun, Li Kun, Chen Jie, Bai Xue, Zhao Hailong, Zhang Shaojie, Ma Yuan, Hao Yunteng, Yang Yang, Li Zhijun, Shi Jun, Wang Xing. Artificial intelligence and cervical spine image recognition: application prospects and challenges[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7231-7240.
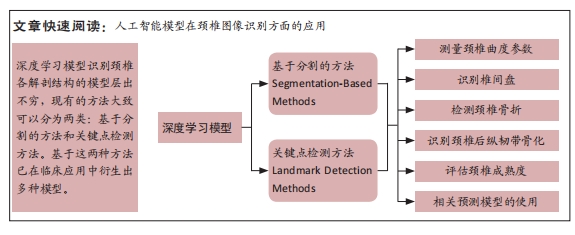
2.2 深度学习在颈椎图像分割中的应用 颈椎病是一种常见的临床表现,可能是先天性畸形、全身炎症、肿瘤和脊柱创伤的结果[22]。临床针对颈椎病治疗的术式众多,而术前图像规划方案可实现术前生物力学稳定性分析,从而提高患者的治疗和恢复时间[23-24]。对颈椎图像的识别分割是开展术前辅助诊断和规划治疗的关键,随着计算机技术的飞速发展,通过深度学习实现对颈椎各解剖结构精准关键点的识别和分割的模型层出不穷,现有的方法大致可以分为两类:基于分割的方法和关键点检测方法。
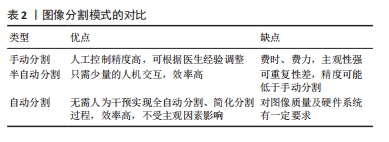
医学图像分割的发展过程经历了手工分割、半自动分割和自动分割3个阶段[25]。然而,颈椎区域的解剖结构(如骨骼、韧带、血管、神经等)的复杂性以及图像上密度和信号强度的接近性、正常椎体与病理椎体之间的解剖变异性以及图像采集相关参数的差异,对单个椎体以及颈椎相关结构进行自动分割是非常困难的[26-27]。相比于手动分割和半自动分割需要人为的参与,自动分割技术则完全不需要人为干预,仅依靠计算机计算就能够完成图像的分割(表2)。端到端自动分割系统的建立可以自行完成后续的分割工作,用户只需提供输入即可,自动分割技术的出现极大地简化了分割过程,减少了人工干预的需求[25]。人工智能是一门新兴技术,在医学影像领域得到了广泛的研究和应用。通过深度学习进行的自动图像分割已经在肾脏、前列腺和乳房中实现,这些研究利用深度学习或放射组学方法提取相应人体组织器官的特征,实现对这些组织或器官的自动分割,从而实现后续的临床任务或目标[27]。
ALARIF等[28]提出了一种基于深度学习的全自动颈椎X射线影像分割框架用于颈椎椎体分割,该框架首先定位脊柱区域,继而锁定椎体中心,最后实现椎体分割,其Dice系数为0.84。U-Net作为卷积神经网络的一个变体,其在生物医学图像分割任务中展现出了优秀的性能[29],张磊磊[25]在 U-Net++基础上进行改进,提出一种适合小尺寸输入、小数据集任务的分割网络对颈椎CT图像进行分割,该模型在测试集上的Dice系数为0.925 9。BAE等[30]针对颈椎3D CT图像,运用U-Net成功实现了对CT上的每个扫描层面的分割,不仅能够在单层CT横断面影像上准确识别上、下椎体,而且在内部验证和外部验证中分别获得了94.37%和88.67%的Dice系数,该模型可用于区分复杂结构的边界,但分割精度可能会受到不规则形状、伪影和层间较厚变异性的影响。ZHANG等[26]提出了一种基于PointNet++和收敛分割的颈椎图像分割新方法,这一方法不仅实现了颈椎椎体的高效分割,准确率高达96.15%,而且在分类性能上表现出色,能够直接且有效地分割出三维椎体结构。段硕等[31]以Mask R-卷积神经网络为基础建立了颈椎MRI自动分割测量模型,对颈椎的深层伸肌面积、肌肉功能面积、椎间盘面积进行了自动分割与测量,模型组与手动分割的同类相关系数为 0.852-0.914,模型的识别、分割与测量结果与人工测量一致性良好。ZHANG等[32]在经典U-Net架构的基础上,开发了一种新的改进模型——SeUneter,可用于颈椎MRI图像的自动分割。郭春麟[8]提出了一种基于U-Net和VGG16模型相结合的算法来实现对颈椎图像的精确分割,该模型可提高图像的细节信息,获得更准确的分割结果,Dice系数达到了95.18%。DAENZER等[33]提出了一种用于MRI图像中三维颈椎检测的全自动算法,该研究模型不仅在C3-C7每块颈椎上的表现出色,在存在严重人工噪声的图像上,所提出的算法仍然取得了良好的效果。
脊髓型颈椎病是颈椎病中最常见的类型,主要是由颈椎椎骨间连接结构退变导致,除对颈椎骨性结构的分割外,深度学习图像分割技术可以对MRI进行分析和处理。脊髓分割是基于图谱的脊髓图像分析的第一步,但对退行性脊髓型颈椎病患者的受压脊髓进行分割是具有挑战性的[34]。侯立宪[35]提出了基于SER18-UNet和M-UNet的两种分割方法,两种模型对病灶都具有较高的分割精度。ZHU等[27]设计了一种基于3D U-Net的模型,不仅可以自动分割成人颈椎MRI图像上的颈段脊髓,同时能够自动测量健康成人蛛网膜下腔和脊髓的直径。朱逸峰等[36]利用3D U-Net模型在颈椎矢状面T1加权像和T2加权像上进行了创新性的尝试,成功实现了对颈椎椎体、椎间盘、硬膜囊、脊髓以及椎间孔的自动分割,总体Dice系数达到了0.80,可准确分割颈椎各结构。LEE等[37]开发了一种使用颈椎X射线侧位片检测脊髓型颈椎病的卷积神经网络模型,模型检测脊髓型颈椎病的准确率为87.1%。
通过上述概述,可以看出上述基于深度学习的研究模型,在自动分割颈椎椎体及其相邻组织的影像图像上均具有较高的准确性,深度学习技术在颈椎影像分割领域的广泛应用为临床诊断与治疗提供了强有力的技术支持。
2.3 深度学习在识别颈椎图像关键点中的应用 关键点检测是计算机视觉领域的一种重要任务,它旨在识别图像或视频中的关键位置或特征点。在医学影像处理研究领域,基于关键点检测方法的医学图像自动检测是一个备受瞩目且快速发展的研究方向,它构成了多种医学影像识别与分析应用的基石,其应用范畴广泛涵盖了医学图像配准、组织分割、参数测量、病理诊断以及治疗规划、手术引导或其他医学图像处理的初始化等[38]。
医学X射线颈椎图像富含大量的容易误匹配的点特征信息,深度学习可用于关键点自动检测和对齐分析。宋璐杰[39]在基于点特征描述的医学颈椎X射线图像上进行了配准研究,使图像拥有更好的视觉效果,为医生诊断提供了更多信息。YEH等[15]针对脊柱开发的深度学习模型能够自动定位 45个解剖关键点。WANG等[40]采用改进的U-Net结构作为主干网开发的深度学习模型MultiIA-
UNet,能够更好地提取变化的全局特征,该方法在识别关键点最小平均点对点误差为12.988像素。YAN等[41]开发的基于深度学习的模型,可用于基于屈曲-中立-伸展颈椎X射线侧位片的矢状面椎间旋转运动分析全自动测量,模型标记结果显示,观察者内标记距离在2 mm阈值内的百分比为98%-99%。
2.4 人工智能在识别颈椎图像上的临床应用
2.4.1 人工智能技术自动化测量颈椎曲度参数 颈椎位于脊柱的颈段,是整个脊柱在矢状位上活动度最大的部位[42]。正常的颈椎生理曲度是脊柱耦合运动的必要条件,异常颈曲会导致椎体、椎间盘、脊髓、小关节、颈部肌肉等结构的应力再分布,加速颈椎病变的发展,因此颈椎矢状面 X 射线测量不仅可作为诊断依据,还可为治疗计划的制定及疗效评价提供重要参考[43-45]。
目前针对颈椎矢状面的测量,常见的测量方法有Borden氏测量法、颈曲指数、颈椎椎体重心测量法、Cobb角等测量方法[46-47]。但在临床上,并非所有出现生理曲度异常的患者都会发展成颈椎病,AKBAR等[48-49]认为正常的颈椎生理曲度可以是前凸、直立或者后凸的,因此临床常常使用2种或2种以上的方法联合评估。同时传统的诊断方法还存在主观性强、效率低等缺点[50]。
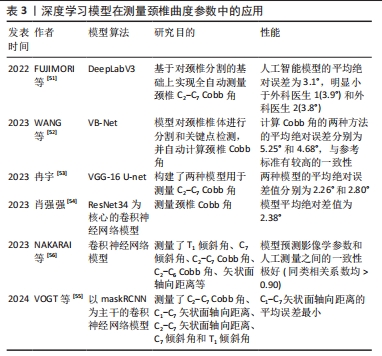
近年来,基于深度学习模型的自动测量颈椎曲度改变的研究越来越多,表3汇总了部分关于人工智能技术在自动测量颈椎曲度参数的模型[51-56]。FUJIMORI等[51]提出了一种DeepLabV3的分割架构并构建了一种自动测量颈椎C2-C7 Cobb角的模型,人工智能模型平均绝对误差为3.1°,明显小于外科医生1(3.9°)和外科医生2(3.8°)。冉宇[53]使用VGG-16 U-net 神经网络构建了两种模型用于测量C2-C7 Cobb角,两种模型的平均绝对误差值分别为2.26°和2.80°。肖强强[54]构建了一种轻量化的卷积神经网络模型,用于测量颈椎Cobb角,该模型识别精度与MVE-Net和RU-Net模型对比误差更小。除了Cobb角的自动测量外,VOGT等[55]开发模型并测量了C2-C7 Cobb角、C1-C7矢状面轴向距离、C2-C7矢状面轴向距离、C7倾斜角和T1倾斜角。NAKARAI等[56]开发的模型可以测量颈椎矢状面参数,包括T1倾斜角、C7倾斜角、C2-C7 Cobb角、C2-C6 Cobb角、矢状面轴向距离、枕颈角、Redlund-Johnell距离、颅骨倾斜角和颅颈角,结果显示以上影像学参数模型预测和人工测量之间的一致性极好。
2.4.2 人工智能技术识别椎间盘 颈椎间盘突出从而压迫脊髓是造成颈椎病的主要原因。目前,颈椎间盘突出体积仍需通过手工测量来获取,而人工勾勒常误将椎体后结构一同纳入突出区域,观察者间可靠性较差。FU等[57]开发了一种基于矢状面MRI的颈椎间盘突出体积自动测量算法,能够帮助医生评估颈椎间盘突出的进展。延亚洁等[58]开发了一种改进的迁移学习模型,用于对颈椎间盘突出类型进行分类(膨出型、突出型、未患病)。马少龙[59]的Faster R-CNN算法可以对颈段脊髓损伤以及颈椎间盘突出的损伤区域进行识别预测。
MRI可清晰显示纤维环破裂、髓核突出的部位,是评估肌肉骨骼疾病的常用成像方式。但MRI获取高分辨率的图像耗时长,较长的扫描时间可能诱发患者焦虑,出现伪影;当缩短扫描时间则面临信噪比降低的问题。迄今为止,深度学习加速成像技术已经应用于各种肌肉骨骼领域,如脊柱、肩部和膝盖等[60]。基于深度学习的重建技术可以显著减少噪声和伪影,辅助重建磁共振图像,缩短扫描时间,同时通过增强真实性来提高图像质量,使医师能够更专注于解剖细节和病理改变。在饶显锋等[61]的研究中,2名医师基于超快速和常规图像诊断椎间盘退行性病变的Kappa值分别为0.94,1.00,诊断椎间盘突出时分别为0.96,0.98。与传统扫描方案相比,深度学习技术在颈椎MRI扫描中能够显著缩短扫描时间。
2.4.3 人工智能技术检测颈椎骨折 颈椎骨折可能导致脊髓损伤和神经功能障碍,颈椎骨折的快速准确诊断对于指导治疗决策和确保患者的最佳预后至关重要。多层螺旋CT已经成为评价颈椎损伤的标准影像技术,能够准确评估骨折类型和相关损伤。颈椎由于其复杂的解剖结构和对创伤(如撞击和跌倒)的易感性,特别容易发生骨折[62]。人工评估不仅耗时,而且细微的骨折有可能被漏诊或误诊。人工智能技术越来越多地被用于帮助放射科医生检测骨折和确定病例的优先顺序。
SMALL等[63]研发了一种名为C-spine的卷积神经网络用于在CT上检测颈椎骨折,卷积神经网络在颈椎骨折检测中的准确率为92%。VOTER等[64]的深度学习模型正确识别了122个骨折中的67个(54.9%),该模型在慢性骨折的检测识别中表现虽然较差,但诊断准确性不会因研究适应证或患者特征而改变。传统多层螺旋CT诊断的骨折检出率为61.4%,朱小龙等[65]的研究中多层螺旋CT结合人工智能模式的骨折检出率为77.1%,多层螺旋CT结合人工智能可有效提高上颈椎隐匿性骨折的检出率,为颈椎损伤患者提供更佳的治疗时机,并改善患者预后。GOLLA等[66]基于U-Net的算法能够对脊柱骨折进行分割,检测出87.2%的颈椎骨折。VAN DEN WITTENBOER等[67]所开发的人工智能模型与主诊放射科医生相比,人工智能对需要保守治疗的骨折具有较低的敏感性和较高的漏诊率,但它能够发现大多数放射科医生未发现的骨折。RUITENBEEK等[68]评估其开发的人工智能应用程序在CT上诊断颈椎骨折的总体敏感性为89.8%。
2.4.4 人工智能技术识别颈椎后纵韧带骨化 后纵韧带骨化会导致脊髓病变和急性脊髓损伤等严重问题。为了减少创伤的发生率,早期准确诊断后纵韧带骨化与预防至关重要。
基于残差神经网络的图像识别在辅助骨科疾病诊断方面显示出潜力。侧位X射线平片是评估后纵韧带骨化的重要方法,MURATA等[69]使用了2 318 张颈椎侧位X射线平片图像对残差神经网络进行了训练,模型的平均准确率、灵敏度、特异性、假阳性率和假阴性率分别为 98.9%,97.0%,99.4%,2.2%和1.0%,结果研究显示:残差神经网络算法可以对颈椎侧位 X射线图像上的后纵韧带骨化进行二元分类,并作为一种筛查工具,帮助医生识别后纵韧带骨化患者。MIURA 等[70]评估了卷积神经网络鉴别诊断颈椎病和颈椎后纵韧带骨化的能力,并与脊柱外科医生的诊断准确性进行了比较,卷积神经网络的准确率高于脊柱外科医生。TAMAI等[71]的算法不仅可以诊断颈椎X射线片上是否存在后纵韧带骨化,还可以在阳性病例中突出显示骨化区域,该算法的诊断准确率为0.88,与医生相比准确性更高。OGAWA等[72]开发的卷积神经网络模型的准确率为90%,敏感性为80%,特异性为100%。相比之下,骨科医生的平均准确率为70%,敏感性和特异性分别为73%和67%,卷积神经网络模型诊断后纵韧带骨化具有成功的诊断准确性和足够的特异性。
QU等[73]基于MRI图像开发了卷积神经网络模型来区分后纵韧带骨化和多节段退行性椎管狭窄。除识别后纵韧带骨化外,MAKI等[74]使用机器学习模型为后纵韧带骨化患者的手术结果创建了一个预后模型,该模型有助于外科医生向患者提供预后信息并系统地管理患者。
2.4.5 人工智能技术评估颈椎成熟度 颈椎椎体的形态会随着年龄增长而变化,颈椎成熟度是根据在不同生长发育阶段颈椎形状、大小等有规律性的改变来预测骨龄。MATHEW等[75]最早提出颈椎成熟度这一概念,临床上颈椎成熟度的评定可用来判断正畸的时机,目前神经网络在基于头颅侧位片的颈椎成熟阶段自动分类中显示出潜力[76-78]。
RADWAN等[79]使用了U-Net网络结构,并将其应用于颈椎成熟阶段的分类,实验结果显示,该网络在测试集上取得的Dice系数为0.931,该模型能够自动识别颈椎生长阶段。AKAY等[80]的实验结果表明,其卷积神经网络模型在颈椎成熟度阶段分类中达到了58.66%的分类准确率。KHAZAEI等[81]提出了一种基于ConvNeXtBase-296的卷积神经网络模型,能够通过颈椎成熟度分期来自动确定青春期的生长突增。ATICI等[82]提出了一种新的卷积神经网络模型,它内置了新的定向滤波器,可以突出显示颈椎边缘,与常用的预训练网络模型相比,该模型有更高的精度。Ⅲ类错牙合是一种罕见的牙科疾病,由于牙槽结构的复杂性和多样性、不同的治疗途径可能导致不可逆转的后果,医生在选择治疗方案时面临着巨大的挑战。TARAJI等[83]的研究目的是确定青春期后Ⅲ类错牙合治疗的形态学特征,并评估算法预测治疗计划的能力,结果显示算法对治疗方案的预测正确率为91%。AMASYA等[84]通过训练X射线片上标记的26个点,开发了基于人工神经网络的新软件用于颈椎成熟度的分类,算法与人类观察者之间的一致性为58.3%,开发的人工神经网络模型在颈椎成熟度分析中表现接近甚至优于人类观察者。随着人工智能领域的持续创新,新兴的算法迭代更新,展现出了在图像自动分类与识别方面的卓越能力,人工智能算法有望在未来逐步取代传统颈椎成熟度评估方法。
2.4.6 人工智能预测模型的使用 颈椎前路椎间盘切除术和融合术是治疗颈椎退行性疾病的常用手术方法。目前还没有标准化的风险分层工具来评估哪些患者适合颈椎前路椎间盘切除和融合术,因此预测术后不良结果具有必要性。WANG等[85]通过机器学习算法开发新的预测模型,用于识别适合颈椎前路椎间盘切除和融合术患者,并将其与传统指标进行比较,模型预测的受试者工作特征曲线的曲线下面积为0.757。颈椎前路椎间盘切除术和融合术后产生的力学改变可能导致早发性邻近节段退变,RUDISILL等[86]开发的机器学习模型用来预测颈椎前路椎间盘切除和融合术后的退变,模型预测的受试者工作特征曲线的曲线下面积为0.794,说明该模型识别了术后退变的风险因素并预测了其发展,具有良好的区分度和整体性能。GOEDMAKERS等[87]开发的深度学习算法仅通过术前颈椎MRI图像就能预测颈椎前路椎间盘切除术和融合术患者的节段退变。术后医疗服务的减少是提高手术护理质量的重要目标和评估指标,KHAZANCHI等[88]构建了一系列机器学习模型,以预测接受颈椎前路椎间盘切除和融合术患者的术后医疗资源利用结果,结果显示所有模型都能预测感兴趣的结果。KARABACAK等[89]开发的一套机器学习模型,不仅能够预测颈椎前路椎间盘切除和融合手术后的不良术后结果,还可以将这些模型嵌入到应用程序中,使操作更加简便。
椎板成形术是用于治疗颈椎病的一种外科手术方法,通过预测患者短期术后结果,医生可以制定更准确的患者护理策略,从而降低不良后果的可能性。KARABACAK等[90]的研究共纳入了1 740例接受椎板成形术治疗的患者,开发了一系列用于预测术后短期结果的机器学习模型,性能评估表明,TabPFN模型在预测家庭长期护理、再次手术和主要并发症受试者工作特征曲线的曲线下面积分别为0.830,0.847和0.858。
手术减压是治疗退行性脊髓型颈椎病的主要方法之一,总体上效果良好,然而,部分术后患者仍表现出功能下降。术前脊柱外科医生必须考虑与疾病表现、影像学特征和患者特征相关信息,以确定患者是否会从术中受益。KHAN等[91]使用机器学习算法来确定患者手术干预后功能状态恶化的预测因子,该算法的工作特征曲线下面积为 0.834,成功使用机器学习算法预测术后较差的功能状态并确定了相关的预测因子。MERALI等[92]应用机器学习方法开发了一个分类模型来预测退行性脊髓型颈椎病患者术后的个体结局,该模型在独立测试集中显示在个体患者水平上具有良好的准确性,证明了机器学习在脊柱手术预测中的适用性。SONG等[93]采用回顾性分析研究,建立了一个基于机器学习算法的预后预测模型,并能够预测与退行性脊髓型颈椎病患者手术效果不佳的相关因素。
MOUSTAFA等[94]探讨了机器学习在预测慢性颈痛患者接受颈椎伸展牵引多模式治疗后的结果中的应用。研究人员利用治疗前的人口统计学和临床变量建立了预测模型,该模型能够预测2014-2020年间接受治疗的570例患者颈椎前凸角、疼痛和残疾程度的变化。这项研究将机器学习技术与脊柱康复相结合,可用于定制干预措施、设定切合实际的期望值,以及根据患者的个体特征优化治疗策略。
手术部位感染是颈椎后路手术最常见的并发症之一,早期诊断困难,可能导致伤口裂开、中枢神经系统感染等严重后果。LU等[95]的随机森林模型获得了最高的受试者工作特征曲线的曲线下面积,机器学习技术的应用促进了预测后路颈椎手术部位感染模型的发展,为临床医生评估感染风险并在临床实践中预防感染提供了有效工具。
临床上超过40%的肿瘤患者可出现脊柱转移疾病,实施脊柱转移性疾病手术后的死亡率是患者能否从这一重大干预中获益的一个评估标准,术前对死亡率的预测至关重要。KARHADE等[17]纳入了白蛋白、白细胞计数、血细胞比容、碱性磷酸酶、转移位置以及基础疾病的严重程度等术前因素预测接受手术后30 d的死亡率,结果显示机器学习算法在预测脊柱肿瘤术后结局方面具有很好的前景,这些算法可以作为临床的决策工具,同时随着肿瘤学数据量的持续增长,未来创建相关的大数据系统并作为可供医生和患者访问的工具可能有助于预测和管理术后结局。
脊髓损伤是脊柱损伤最严重的并发症,往往会导致损伤节段以下的肢体功能障碍。由于脊髓休克和损伤异质性等问题,预测急性脊髓损伤的神经系统结局具有挑战性。OKIMATSU等[96]基于MRI图像开发了可以自动提取影像学特征的卷积神经网络模型用于预测颈椎急性脊髓损伤患者的功能预后,并评估了预测神经系统结果的能力。研究表明,模型预测急性颈椎脊髓损伤的短期神经系统结果是可行的。人工智能模型利用多维临床数据和影像学数据,越来越多地被用于开发患者风险评估和功能预后模型,帮助制定治疗指南和个性化护理计划,有助于医疗保健决策的制定。
2.4.7 人工智能技术在其他方面的应用 通过视频荧光镜诊断吞咽运动障碍是评估吞咽障碍的黄金标准。然而,受其训练和经验的主观影响,该方法在不同的观察者间存在很大差异。ZHANG等[97]通过吞咽视频荧光镜图像训练了一种新型的卷积神经网络模型,可以高精度地自动检测常规吞咽的关键点,模型预测点与标记点之间的平均距离误差为4.20像素。
类风湿性关节炎是一种以滑膜炎和多关节破坏为特征的慢性自身免疫性疾病。类风湿性关节炎患者除了四肢关节外,脊柱也会受到影响,颈椎病变是类风湿性关节炎最常见的脊柱病变,占患者的25%-80%。OKITA等[98]用深度学习模型通过测量寰齿间距和脊髓可用空间自动评估类风湿性关节炎寰枢椎半脱位,并与临床医生的测量值进行比较,显示模型性能良好。
CHMELIK等[18]描述了一种基于卷积神经网络的新方法,可对全脊柱CT中溶骨性和硬化性骨组织进行分割和分类,该算法能够对大于1.4 mm3的小病灶进行检测、分割和分类。JARDON等[99]基于深度学习算法重建的三维MRI不易出现运动伪影,医生在诊断椎管和中央狭窄时的一致性更佳,从而节省了整体扫描时间。MARA?等[100]将深度学习算法应用在了诊断颈椎骨关节病变、前凸消失及椎间盘狭窄方面。过去的25年里,颈部疼痛的发病率明显上升,HWANG等[101]开发了使用颅颈姿势和运动对非特异性颈部疼痛进行分类的机器学习模型。

| [1] 柯尊华,王静怡.颈椎病流行病学及发病机理研究进展[J].颈腰痛杂志,2014,35(1):62-64. [2] 郝东昶,蒋宜伟,宋重东,等.国内外采用手法治疗神经根型颈椎病的研究进展[J].湖南中医杂志,2023,39(8):207-211. [3] 张靖慧,孙大炜,黄晓琳.颈椎曲度测量方法进展与及临床意义[J].中国康复,2009,24(5):347-349. [4] 付玏,李克,王梦龙.医学影像互联网产品发展现状及前景展望[J].中国医学计算机成像杂志,2016,22(3):283-285. [5] 李小雷.人工智能在医学影像图像处理中的研究进展[J].中国医学计算机成像杂志,2023,29(4):454-457. [6] HINTON GE, OSINDERO S, TEH YW. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Comput. 2006;18(7):1527-1554. [7] 邬超,李佳伟,高明杰,等.深度学习在青少年特发性脊柱侧凸诊疗中应用的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2023,33(4):358-362. [8] 郭春麟.基于深度学习的颈椎X射线图像分割算法研究[D].太原:中北大学,2023. [9] LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, HINTON G. Deep learning. Nature. 2015;521(7553): 436-444. [10] LITJENS G, KOOI T, BEJNORDI BE, et al. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med Image Anal. 2017;42:60-88. [11] YıLMAZ H, ZATERI C, KUSVURAN OZKAN A, et al. Prevalence of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in Turkey: an epidemiological study. Spine J. 2020;20(6):947-955. [12] AZIMI P, YAZDANIAN T, BENZEL EC, et al. A Review on the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Spinal Diseases. Asian Spine J. 2020;14(4):543-571. [13] LANDRIEL F, FRANCHI BC, MOSQUERA C, et al. Artificial Intelligence Assistance for the Measurement of Full Alignment Parameters in Whole-Spine Lateral Radiographs. World Neurosurg. 2024;187:e363-e382. [14] NGUYEN TP, JUNG JW, YOO YJ, et al. Intelligent Evaluation of Global Spinal Alignment by a Decentralized Convolutional Neural Network. J Digit Imaging. 2022;35(2):213-225. [15] YEH YC, WENG CH, HUANG YJ, et al. Deep learning approach for automatic landmark detection and alignment analysis in whole-spine lateral radiographs. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):7618. [16] SONG SY, SEO MS, KIM CW, et al. AI-Driven Segmentation and Automated Analysis of the Whole Sagittal Spine from X-ray Images for Spinopelvic Parameter Evaluation. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023; 10(10):1229. [17] KARHADE AV, THIO QCBS, OGINK PT, et al. Development of Machine Learning Algorithms for Prediction of 30-Day Mortality After Surgery for Spinal Metastasis. Neurosurgery. 2019;85(1):E83-E91. [18] CHMELIK J, JAKUBICEK R, WALEK P, et al. Deep convolutional neural network-based segmentation and classification of difficult to define metastatic spinal lesions in 3D CT data. Med Image Anal. 2018;49:76-88. [19] 欧阳汉强,姜亮,刘晓光,等.人工智能在脊柱外科诊断与治疗中的应用现状和发展趋势[J].中华骨科杂志,2019,39(24):1543-1548. [20] BERLIN C, ADOMEIT S, GROVER P, et al. Novel AI-Based Algorithm for the Automated Computation of Coronal Parameters in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Patients: A Validation Study on 100 Preoperative Full Spine X-Rays. Global Spine J. 2024;14(6):1728-1737. [21] HUSSEIN YY, KHAN MM. Using Artificial Intelligence to Predict the Development of Kyphosis Disease: A Systematic Review. Cureus. 2023; 15(11):e48341. [22] STINO AM, LORUSSO SJ. Myelopathies Due to Structural Cervical and Thoracic Disease. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2018;24(2, Spinal Cord Disorders):567-583. [23] WANG H, LIU Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Feasibility and accuracy of computer-assisted individual drill guide template for minimally invasive lumbar pedicle screw placement trajectory. Injury. 2018;49(3):644-648. [24] YU Z, ZHANG G, CHEN X, et al. Application of a novel 3D drill template for cervical pedicle screw tunnel design: a cadaveric study. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(9):2348-2356. [25] 张磊磊. 基于深度学习的颈椎CT图像分割和定位[D].武汉: 华中科技大学,2020. [26] ZHANG L, WANG H. A novel segmentation method for cervical vertebrae based on PointNet++ and converge segmentation. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021;200:105798. [27] ZHU Y, LI Y, WANG K, et al. A quantitative evaluation of the deep learning model of segmentation and measurement of cervical spine MRI in healthy adults. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024;25(3):e14282. [28] AL ARIF SMMR, KNAPP K, SLABAUGH G. Fully automatic cervical vertebrae segmentation framework for X-ray images. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2018;157:95-111. [29] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2015, 2015. [30] BAE HJ, HYUN H, BYEON Y, et al. Fully automated 3D segmentation and separation of multiple cervical vertebrae in CT images using a 2D convolutional neural network. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020;184:105119. [31] 段硕,崔维,张舵,等.神经网络模型自动分割测量颈椎MRI椎间盘及深层伸肌面积的可行性研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2021, 31(9):833-840. [32] ZHANG X, YANG Y, SHEN YW, et al. SeUneter: Channel attentive U-Net for instance segmentation of the cervical spine MRI medical image. Front Physiol. 2022;13:1081441. [33] DAENZER S, FREITAG S, VON SACHSEN S, et al. VolHOG: a volumetric object recognition approach based on bivariate histograms of oriented gradients for vertebra detection in cervical spine MRI. Med Phys. 2014;41(8):082305. [34] NOZAWA K, MAKI S, FURUYA T, et al. Magnetic resonance image segmentation of the compressed spinal cord in patients with degenerative cervical myelopathy using convolutional neural networks. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2023;18(1):45-54. [35] 侯立宪.基于U型网络的脊髓型颈椎病MRI分割方法的研究[D].桂林:桂林理工大学,2023. [36] 朱逸峰,赵凯,郭丽,等.基于深度学习模型实现颈椎MR图像上各结构的自动分割[J].放射学实践,2021,36(12):1558-1562. [37] LEE GW, SHIN H, CHANG MC. Deep learning algorithm to evaluate cervical spondylotic myelopathy using lateral cervical spine radiograph. BMC Neurol. 2022;22(1):147. [38] 李居朋,王颖慧,李刚.医学图像关键点检测深度学习方法研究与挑战[J].电子学报,2022,50(1):226-237. [39] 宋璐杰.基于点特征描述的医学颈椎X光图像配准研究[D].北京:北京化工大学,2021. [40] WANG Y, HUANG L, WU M, et al. Multi-input adaptive neural network for automatic detection of cervical vertebral landmarks on X-rays. Comput Biol Med. 2022;146:105576. [41] YAN Y, ZHANG X, MENG Y, et al. Sagittal intervertebral rotational motion: a deep learning-based measurement on flexion-neutral-extension cervical lateral radiographs. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):967. [42] 杨胜,唐超,钟德君.150例健康成人下颈椎矢状位曲度相关影像学参数测量及临床意义[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2020,38(5):549-553+558. [43] 蒋芳华,林建平,王诗忠. 不同颈椎矢状位参数测量颈椎前凸曲度的比较分析[J].颈腰痛杂志,2022,43(5):707-710. [44] SCHEER JK, TANG JA, SMITH JS, et al. Cervical spine alignment, sagittal deformity, and clinical implications: a review. J Neurosurg Spine. 2013; 19(2):141-159. [45] MIYAZAKI M, HYMANSON HJ, MORISHITA Y, et al. Kinematic analysis of the relationship between sagittal alignment and disc degeneration in the cervical spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008; 33(23):E870-E876. [46] LING FP, CHEVILLOTTE T, LEGLISE A, et al. Which parameters are relevant in sagittal balance analysis of the cervical spine? A literature review. Eur Spine J. 2018;27(Suppl 1):8-15. [47] 杨云霄,黄承兰,侯俞彤,等.退行性颈椎病矢状位曲度参数与颈肩部肌肉痛阈的相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024,28(24):3879-3884. [48] AKBAR M, ALMANSOUR H, DIEBO B, et al. Normal sagittal profile of the cervical spine - must the cervical spine always be lordotic? Orthopade. 2018;47(6):460-466. [49] 裴帅,姜宏,刘锦涛,等.颈椎曲度与颈椎病严重程度相关性的研究进展[J].中医正骨,2020,32(3):35-38. [50] LI X, CHEN H, QI X, et al. H-DenseUNet: Hybrid Densely Connected UNet for Liver and Tumor Segmentation From CT Volumes. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2018;37(12):2663-2674. [51] FUJIMORI T, SUZUKI Y, TAKENAKA S, et al. Development of artificial intelligence for automated measurement of cervical lordosis on lateral radiographs. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):15732. [52] WANG C, NI M, TIAN S, et al. Deep learning model for measuring the sagittal Cobb angle on cervical spine computed tomography. BMC Med Imaging. 2023;23(1):196. [53] 冉宇.两种颈前路手术疗效分析及深度学习下的Cobb角模型构建与软件开发[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2023. [54] 肖强强.颈椎X线角度测量及不稳定诊断深度学习模型的构建与应用[D].上海:中国人民解放军海军军医大学,2023. [55] VOGT S, SCHOLL C, GROVER P, et al. Novel AI-Based Algorithm for the Automated Measurement of Cervical Sagittal Balance Parameters. A Validation Study on Pre- and Postoperative Radiographs of 129 Patients. Global Spine J. 2024:21925682241227428. [56] NAKARAI H, CINA A, JUTZELER C, et al. Automatic Calculation of Cervical Spine Parameters Using Deep Learning: Development and Validation on an External Dataset. Global Spine J. 2023:21925682231205352. [57] FU S, ZHANG C, YAN X, et al. A New Automated AI-Assisted System to Assess Cervical Disc Herniation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2022;47(16): E536-E544. [58] 延亚洁,袁细国.基于深度学习的颈椎间盘突出识别方法[J].聊城大学学报(自然科学版),2021,34(1):11-19. [59] 马少龙.基于深度学习技术-Faster R-CNN对颈脊髓损伤及颈间盘疾病核磁图像的识别检测[D].长春:吉林大学,2020. [60] SEO G, LEE SJ, PARK DH, et al. Image quality and lesion detectability of deep learning-accelerated T2-weighted Dixon imaging of the cervical spine. Skeletal Radiol. 2023;52(12):2451-2459. [61] 饶显锋,杨舒文,陈静,等.基于深度学习重建超快速扫描方案用于颈椎MR检查[J].中国医学影像技术,2024,40(6):843-847. [62] RIAZI ESFAHANI P, GUIRGUS M, MAALOUF M, et al. Development of a Machine Learning-Based Model for Accurate Detection and Classification of Cervical Spine Fractures Using CT Imaging. Cureus. 2023;15(10):e47328. [63] SMALL JE, OSLER P, PAUL AB, et al. CT Cervical Spine Fracture Detection Using a Convolutional Neural Network. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2021; 42(7):1341-1347. [64] VOTER AF, LARSON ME, GARRETT JW, et al. Diagnostic Accuracy and Failure Mode Analysis of a Deep Learning Algorithm for the Detection of Cervical Spine Fractures. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2021;42(8):1550-1556. [65] 朱晓龙,黄婧潇,邹殿俊,等.上颈椎损伤诊断及治疗中应用多层螺旋CT结合人工智能模式的效果分析[J].中国临床医生杂志, 2022,50(3):348-350. [66] GOLLA AK, LORENZ C, BUERGER C, et al. Cervical spine fracture detection in computed tomography using convolutional neural networks. Phys Med Biol. 2023;68(11). doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/acd48b. [67] VAN DEN WITTENBOER GJ, VAN DER KOLK BYM, NIJHOLT IM, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of an artificial intelligence algorithm versus radiologists for fracture detection on cervical spine CT. Eur Radiol. 2024;34(8):5041-5048. [68] RUITENBEEK HC, OEI EHG, SCHMAHL BL, et al. Towards clinical implementation of an AI-algorithm for detection of cervical spine fractures on computed tomography. Eur J Radiol. 2024;173:111375. [69] MURATA K, ENDO K, AIHARA T, et al. Use of residual neural network for the detection of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament on plain cervical radiography. Eur Spine J. 2021;30(8): 2185-2190. [70] MIURA M, MAKI S, MIURA K, et al. Automated detection of cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament in plain lateral radiographs of the cervical spine using a convolutional neural network. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):12702. [71] TAMAI K, TERAI H, HOSHINO M, et al. A deep learning algorithm to identify cervical ossification of posterior longitudinal ligaments on radiography. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):2113. [72] OGAWA T, YOSHII T, OYAMA J, et al. Detecting ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament on plain radiographs using a deep convolutional neural network: a pilot study. Spine J. 2022;22(6):934-940. [73] QU Z, DENG B, SUN W, et al. Feng H. A Convolutional Neural Network for Automated Detection of Cervical Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament using Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Clin Spine Surg. 2024;37(3):E106-E112. [74] MAKI S, FURUYA T, YOSHII T, et al. Machine Learning Approach in Predicting Clinically Significant Improvements After Surgery in Patients with Cervical Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2021;46(24):1683-1689. [75] MATHEW R, PALATINUS S, PADALA S, et al. Neural networks for classification of cervical vertebrae maturation: a systematic review. Angle Orthod. 2022;92(6):796-804. [76] CAO L, HE H, HUA F. Current neural networks demonstrate potential in automated cervical vertebral maturation stage classification based on lateral cephalograms. J Evid Based Dent Pract. 2024;24(1):101928. [77] LI H, CHEN Y, WANG Q, et al. Convolutional neural network-based automatic cervical vertebral maturation classification method. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2022;51(6):20220070. [78] KIM DW, KIM J, KIM T, et al. Prediction of hand-wrist maturation stages based on cervical vertebrae images using artificial intelligence. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2021;24 Suppl 2:68-75. [79] RADWAN MT, SIN Ç, AKKAYA N, et al. Artificial intelligence-based algorithm for cervical vertebrae maturation stage assessment. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2023;26(3):349-355. [80] AKAY G, AKCAYOL MA, ÖZDEM K, et al. Deep convolutional neural network-the evaluation of cervical vertebrae maturation. Oral Radiol. 2023;39(4):629-638. [81] KHAZAEI M, MOLLABASHI V, KHOTANLOU H, et al. Automatic determination of pubertal growth spurts based on the cervical vertebral maturation staging using deep convolutional neural networks. J World Fed Orthod. 2023;12(2):56-63. [82] ATICI SF, ANSARI R, ALLAREDDY V, et al. Fully automated determination of the cervical vertebrae maturation stages using deep learning with directional filters. PLoS One. 2022;17(7):e0269198. [83] TARAJI S, ATICI SF, VIANA G, et al. Novel Machine Learning Algorithms for Prediction of Treatment Decisions in Adult Patients With Class III Malocclusion. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2023;81(11):1391-1402. [84] AMASYA H, CESUR E, YILDIRIM D, et al. Validation of cervical vertebral maturation stages: Artificial intelligence vs human observer visual analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2020;158(6):e173-e179. [85] WANG KY, SURESH KV, PUVANESARAJAH V, et al. Using Predictive Modeling and Machine Learning to Identify Patients Appropriate for Outpatient Anterior Cervical Fusion and Discectomy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2021;46(10):665-670. [86] RUDISILL SS, HORNUNG AL, BARAJAS JN, et al. Artificial intelligence in predicting early-onset adjacent segment degeneration following anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. Eur Spine J. 2022;31(8):2104-2114. [87] GOEDMAKERS CMW, LAK AM, DUEY AH, et al. Deep Learning for Adjacent Segment Disease at Preoperative MRI for Cervical Radiculopathy. Radiology. 2021;301(3):E446. [88] KHAZANCHI R, BAJAJ A, SHAH RM, et al. Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning Algorithms to Predict Postoperative Outcomes Following Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion. Clin Spine Surg. 2023;36(3):143-149. [89] KARABACAK M, BHIMANI AD, SCHUPPER AJ, et al. Machine learning models on a web application to predict short-term postoperative outcomes following anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024;25(1):401. [90] KARABACAK M, MARGETIS K. Development of personalized machine learning-based prediction models for short-term postoperative outcomes in patients undergoing cervical laminoplasty. Eur Spine J. 2023;32(11):3857-3867. [91] KHAN O, BADHIWALA JH, AKBAR MA, et al. Prediction of Worse Functional Status After Surgery for Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy: A Machine Learning Approach. Neurosurgery. 2021;88(3):584-591. [92] MERALI ZG, WITIW CD, BADHIWALA JH, et al. Using a machine learning approach to predict outcome after surgery for degenerative cervical myelopathy. PLoS One. 2019;14(4):e0215133. [93] SONG J, LI J, ZHAO R, et al. Developing predictive models for surgical outcomes in patients with degenerative cervical myelopathy: a comparison of statistical and machine learning approaches. Spine J. 2024;24(1):57-67. [94] MOUSTAFA IM, OZSAHIN DU, MUSTAPHA MT, et al. Utilizing machine learning to predict post-treatment outcomes in chronic non-specific neck pain patients undergoing cervical extension traction. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):11781. [95] LU K, TU Y, SU S, et al. Machine learning application for prediction of surgical site infection after posterior cervical surgery. Int Wound J. 2024;21(4):e14607. [96] OKIMATSU S, MAKI S, FURUYA T, et al. Determining the short-term neurological prognosis for acute cervical spinal cord injury using machine learning. J Clin Neurosci. 2022;96:74-79. [97] ZHANG Z, MAO S, COYLE J, et al. Automatic annotation of cervical vertebrae in videofluoroscopy images via deep learning. Med Image Anal. 2021;74:102218. [98] OKITA Y, HIRANO T, WANG B, et al. Automatic evaluation of atlantoaxial subluxation in rheumatoid arthritis by a deep learning model. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023;25(1):181. [99] JARDON M, TAN ET, CHAZEN JL, et al. Deep-learning-reconstructed high-resolution 3D cervical spine MRI for foraminal stenosis evaluation. Skeletal Radiol. 2023;52(4):725-732. [100] MARAŞ Y, TOKDEMIR G, ÜRETEN K, et al. Diagnosis of osteoarthritic changes, loss of cervical lordosis, and disc space narrowing on cervical radiographs with deep learning methods. Jt Dis Relat Surg. 2022;33(1):93-101. [101] HWANG UJ, KWON OY, KIM JH, et al. Machine learning models for classifying non-specific neck pain using craniocervical posture and movement. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2024;71:102945. |
| [1] | 张艺博, 卢健棋, 毛美玲, 庞 延, 董 礼, 杨尚冰, 肖 湘. 类风湿关节炎与冠状动脉粥样硬化的因果关系:GWAS数据库血清代谢物和炎症因子数据[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | 李良奎, 黄永灿, 王鹏, 于滨生. 颈椎前路椎体骨化物可控前移融合对后纵韧带骨化物和内植物影响的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1761-1767. |
| [3] | 苗嘉航, 马 胜, 李渠蓬, 余会林, 胡天宇, 高 啸, 冯 虎. 颈椎前凸比率可作为多节段脊髓型颈椎病后路术式选择的决策指标[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1796-1802. |
| [4] | 周盼盼, 崔应麟, 张文涛, 王姝瑞, 陈佳慧, 杨 潼. 细胞自噬在脑缺血损伤中的作用及中药调控机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1650-1658. |
| [5] | 杨 彬, 陶广义, 杨 顺, 许俊杰, 黄俊卿. 人工智能在脊髓神经损伤与修复领域研究热点的可视化分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(4): 761-770. |
| [6] | 冉亚琴, 陈 曦, 谢晏讷, 袁 军. 细胞焦亡在乳腺癌治疗中的机制及潜在应用策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(36): 7880-7888. |
| [7] | 刘 璐, 钟 畅, 余 欣, 任晨媛, 巩杨杨, 周 平, 王迎斌. 体外合成微环境促进人多能干细胞来源心肌细胞成熟的学术进展及临床应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(36): 7856-7862. |
| [8] | 赵 聪, 付慧渊, 苏尼特, 及 捷, 张 蕾, 王雅仙. 生物可降解镁及镁基材料在口腔疾病领域的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(34): 7423-7430. |
| [9] | 曹 勇, 李 信, 陈志刚, 顾红林, 吕书军. 腰椎退行性侧弯矫正后颈椎和胸椎的代偿性对齐变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(33): 7196-7202. |
| [10] | 李 靖, 路广琦, 庄明辉, 崔 莹, 俞张镜泽, 孙馨悦, 马明明, 朱立国, 于 杰. 基于机器学习构建中青年人群颈椎失稳临床预测模型[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(33): 7203-7210. |
| [11] | 于庆贺, 蔡子鸣, 吴锦涛, 马鹏飞, 张 鑫, 周龙千, 王亚坤, 林晓钦, 林文平. 香草酸抑制终板软骨细胞炎症反应和细胞外基质降解[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(30): 6391-9397. |
| [12] | 樊佳欣, 贾 祥, 徐田杰, 刘凯楠, 郭小玲, 张 辉, 王 茜. 二甲双胍抑制铁死亡改善骨关节炎模型大鼠的软骨损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(30): 6398-6408. |
| [13] | 周 颖, 田 勇, 钟芝梅, 古雍翔, 方 昊. 抑制TRAF6调节mTORC1/ULK1信号通路促进自噬改善脓毒症小鼠的心肌损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(30): 6434-6440. |
| [14] | 王万春, 易 军, 严张仁, 杨 悦, 董德刚, 李玉梅. 717解毒合剂重塑细胞外基质稳态促进蝮蛇伤大鼠局部损伤组织的修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(30): 6457-6465. |
| [15] | 张 鑫, 郭宝娟, 徐慧鑫, 沈玉珍, 杨晓帆, 杨旭芳, 陈 培 . 丁苯酞对帕金森病细胞模型的保护作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(30): 6466-6473. |
人工智能由MCCARTHY于1956年首次提出,近年来随着计算机技术的快速进步,人工智能技术也有了突破性进展[5]。最早由HINTON等[6]于2006年提出的深度学习通过利用预设的训练方法构建模型,提取多种低层信息进行重组从而生成更高层次的抽象信息用于数据和属性的分类。卷积神经网络是深度学习应用中提取图像特征的典型模型,应用也最广泛,卷积神经网络能够学习图像的复杂特征,并进行高级的图像识别、目标检测等任务,其优势在于能够代替传统手工对特征的缓慢获取,这样可以极大提高学习效能,同时对图像的平移、缩放等变化具有一定的不变性,因此在医学影像研究等领域具有重要的应用价值,特别是在脊柱疾病的科学研究与临床诊断领域,其应用价值尤为显著[7-21]。人工智能的引入也为颈椎相关病变的检测和诊疗提供了新的可能性,此文在介绍模型采用的基本方法的基础上,综述了人工智能技术在颈椎影像分析中的应用,包括颈椎曲度参数测量、椎间盘识别、颈椎骨折检测、颈椎成熟度评估以及其他病变检测等多个方面的进展和应用实例,同时讨论了现有模型面临的挑战,并对未来的发展趋势进行了展望。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在2024年6月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 检索时间范围为 2014年6月至2024年6月,同时纳入少数远期经典及特别相关文献。
1.1.3 检索数据库 万方数据库、中国知网和PubMed数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 以“人工智能、深度学习、颈椎” 为 中文检索词,以“Artificial Intelligence、AI、Cervical Vertebrae、Cervical”为英文检索词分别进行检索。中文检索策略为题名同时包含上述检索词的文献,以“(篇名:颈椎 )AND(篇名:人工智能)”和“(篇名:颈椎)AND(篇名:深度学习)”为检索式。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 包括研究原著、综述、述评、经验交流、病例报告、荟萃分析等。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 对于文献中的高价值参考文献,先阅读文题,再以标题进行检索,阅读摘要或全文。
1.1.7 检索策略 以PubMed 数据库检索策略为例,见图1。
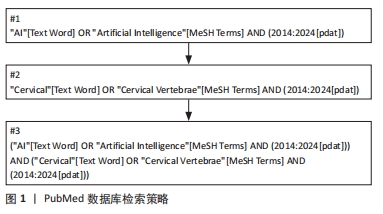
纳入标准:研究内容与人工智能、深度学习和颈椎的相关研究。
排除标准:文献内容与主题无关或关联性很小的文章、重复性文章。
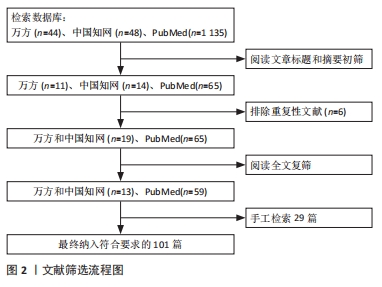
1.3 质量评估和数据的提取 检索获得1 227篇文章,其中英文文献1 135篇、中文文献92篇,排除重复文献及与文章相关性低的文献,结合手工检索及远期经典文献,最终纳入101篇文献进行综述分析,检索过程见图2。
(1)鉴于医学图像和疾病表现的异质性,构建一个既准确又具备泛化能力的模型,并使其能够在大范围内得到推广和应用,面临着多重挑战。当前,大多数用于模型训练的数据源自单中心医疗机构,且样本量往往偏小,同时影像设备的种类及成像参数较为单一,这些因素共同制约了模型的泛化性。未来的研究亟需采取多中心协作策略,汇集来自不同地区、不同设备条件下的大数据资源,以此来增强模型对多样性和复杂性的适应能力。开发出更为鲁棒、适用性广泛的医学图像分析模型,从而推动其在临床实践中的广泛应用和普及。
(2)模型的训练需要高质量的图像标注,然而颈椎复杂的解剖结构以及标注者间的主观性也会影响到模型训练结果的准确性和可靠性。为减少主观偏差,提升标注人员的技能水平进而提升模型的性能,制定统一的标注标准以及实施系统性的培训尤为关键。同时,借助集成深度学习与半监督学习的方法,模型可以从少量标注数据中自动提取特征,逐步改进标注质量。此外,增强现实技术能够为标注者提供实时的视觉辅助,从而进一步提高标注的精度。
(3)随着人工智能技术在医学领域的广泛应用,诊断效率和准确性得到了显著提升。然而,医疗数据的敏感性不可避免地触及到了患者的隐私保护问题。联邦学习作为一种分布式机器学习技术,允许多个医疗机构共同训练机器学习模型,各自保留数据的处理权,而无需直接共享各自的数据。这种方式可以在保证数据隐私的同时,充分利用分布在不同机构的数据资源,提升模型的性能和泛化能力。同时,探索数据脱敏技术和数据合成技术,可以进一步减少隐私泄露的风险,同时确保数据的有效性和代表性。因此,建立和完善数据保护机制,避免直接数据共享并严格遵守相关法律法规是平衡技术创新与隐私保护的关键,这将推动医学影像分析朝着更加智能、安全的方向发展。
尽管人工智能技术在颈椎研究领域已展现出巨大潜力,但仍处于初期探索与快速发展阶段,有无限的发展与创新空间。当前,人工智能技术正以前所未有的速度迭代升级,向着更高效、更精准的方向迈进。相信随着研究的深入和技术的进步,未来将涌现出更多创新算法,不仅能够显著简化颈椎分析流程,提高诊断与治疗决策的准确性,还能进一步提升患者的诊疗体验,最终推动整个医疗行业的现代化与智能化转型,为患者带来更高水平的医疗服务和满意度。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
人工智能:是一门新兴的技术科学,致力于研究开发用于模拟、延伸和扩展人类智能理论、方法、技术及应用系统。作为智能学科的重要组成部分,人工智能旨在理解智能的本质,并开发类似于人类并能够做出反应的智能机器。深度学习:是机器学习领域中一个新的研究方向,它的最终目标是让机器能够像人一样具有分析学习能力,能够识别文字、图像和声音等数据。
颈椎病在临床上作为一种多发的退行性疾病,严重威胁了患者的健康与生活质量,目前对颈椎病的初步诊断主要依赖放射科医师对医学影像的解读,但这对操作人员技术要求高且存在主观性强、劳动强度大、效率低等问题。近年来,随着人工智能技术在医学图像分析领域的应用越来越广泛,通过深度学习实现对颈椎各解剖结构精准关键点的识别和分割的模型不断涌现。尽管国内外已有部分学者对这些模型的应用进行了综述,但这些综述往往不够详尽,且未详细介绍模型所采用的基本方法。本文在详细描述现有模型基本方法的基础上,全面综述了近年来人工智能技术在颈椎影像分析中的应用,涵盖了深度学习模型在图像分割、关键点识别、颈椎曲度参数测量、椎间盘识别、颈椎骨折检测、颈椎成熟度评估以及其他病变检测等多个方面的进展和应用实例。文章最后还深入探讨了当前模型所面临的挑战,并展望了未来的研究方向,为相关领域的研究人员提供了有价值的参考和思路。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||