[1] SAINI MK, REDDY NR, REDDY PJ. Disassembly of components of a monoblock bipolar hip prosthesis following Dislocation: a case report and review on “bottle opener effect”. J Orthop Case Rep. 2020;10(9): 90-93.
[2] KAGAN R, ANDERSON MB, PETERS C, et al. Pinnacle polyethylene liner dissociation: a report of 3 cases. Arthroplast Today. 2018;4(4):441-446.
[3] GWYNNE-JONES DP, MEMON A. Acetabular liner dissociation: a comparative study of two contemporary uncemented acetabular components. Arthroplast Today. 2020;6(3):354-359.
[4] CIOLLI G, SILVA R, GIOVANNETTI DSE, et al. Liner dissociation in total hip arthroplasty: a systematic review. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022;26(1 Suppl):138-150.
[5] WASEEM S, FONG D, ONSA M, et al. Dual mobility total hip replacements in young patients- a systematic review. Indian J Orthop. 2023;57(2):203-210.
[6] NAPIER RJ, DIAMOND O, O’NEILL C, et al. The incidence of dissociated liners in 4,751 consecutive total hip arthroplasties using Pinnacle polyethylene acetabular liners. Hip Int. 2017;27(6):537-545.
[7] KAWANO S, SONOHATA M, KITAJIMA M, et al. Highly cross-linked polyethylene liner dissociation from a cement-less modular acetabular shell: two Case Reports. Open Orthop J. 2016;10:732-740.
[8] YUN A, KOLI EN, MORELAND J, et al. Polyethylene liner dissociation is a complication of the depuy pinnacle Cup: a report of 23 Cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(2):441-446.
[9] PERKINS TJ, KOP AM, WHITEWOOD C, et al. Dissociation of polyethylene liners with the depuy pinnacle cup: a report of 26 cases. Hip Int. 2023;33(1):28-33.
[10] CIRIELLO V, LA CHINA R, CHIRILLO DF, et al. Is modular dual mobility superior to standard bearings for reducing dislocation risk after primary total hip arthroplasty? A retrospective comparative multicenter study. J Clin Med. 2023;12(13):4200.
[11] BARRACK RL, BURKE DW, COOK SD, et al. Complications related to modularity of total hip components. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993;75(5): 688-692.
[12] LI L, REN J, LIU J, et al. What are the risk factors for dislocation of Hip bipolar hemiarthroplasty through the anterolateral approach? A nested case-control study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(12):2622-2629.
[13] ELLANTI P, BAHARI S, MCCARTHY T. Significantly displaced femoral head component in a dissociated bipolar hip hemiarthroplasty. Orthop Surg. 2012;4(3):194-196.
[14] SEVINÇ HF. Dissociation of bipolar components following bipolar hemiarthroplasty: a report of two different cases and review of the literature. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2021;27(5):600-603.
[15] FEHRING KA, BERRY DJ. Dissociation and intrapelvic entrapment of a dual-mobility polyethylene component. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(4):1072-1076.
[16] JAMESON SS, BAKER PN, MASON J, et al. Independent predictors of failure up to 7.5 years after 35 386 single-brand cementless total hip replacements: a retrospective cohort study using national joint registry data. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(6):747-757.
[17] YANG Y, FU G, LI Q, et al. Multivariable analysis of risk factors affecting dislocation after bipolar hemiarthroplasty in patients with femoral neck fracture. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2022;18:101-111.
[18] 郑昱新, 汤荣光. 全髋置换术后聚乙烯内衬与金属壳分离[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2001(1):77-78.
[19] HASEGAWA M, SUDO A, UCHIDA A. Disassembly of bipolar cup with self-centering system: a report of seven cases Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(425):163-167.
[20] KOSTRETZIS L, MARTINOV S, LAVIGNE M, et al. Liner dissociation in a large-diameter ceramic-bearing acetabular component: a report of five cases. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):136.
[21] PHILIPPOT R, BOYER B, FARIZON F. Intraprosthetic dislocation: a specific complication of the dual-mobility system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013; 471(3):965-970.
[22] BAEK SH, KIM JY, HAN JW, et al. Potential risk of AMC ceramic liner for dissociation after square seating. J Orthop Sci. 2018;23(3):600-603.
[23] NEAL S. Polyethylene liner dissociation with the depuy pinnacle cup: a report of 6 cases. Orthop Res Online. 2018;3:293.
[24] SHNAEKEL AW, MAYES WH, STAMBOUGH JB, et al. dissociation of acetabular polyethylene liners with a morse taper design. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(12):3754-3757.
[25] SAITO S, RYU J, SEKI M, et al. Analysis and results of dissociation of the polyethylene liner in the harris-galante I acetabular component. J Arthroplasty. 2008;23(4):522-526.
[26] 刘新, 李卫国. 人工髋关节置换术后脱位及内衬分离的原因和防治[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2008,23(2):107-109.
[27] MEMON AR, GWYNNE-JONES D. Polyethylene liner dissociation with the Pinnacle acetabular component: should we be concerned? Arthroplast Today. 2020;6(1):5-8.
[28] GRAY CF, MOORE RE, LEE GC. Spontaneous dissociation of offset, face-changing polyethylene liners from the acetabular shell: a report of four cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(9):841-845.
[29] MAYER SW, WELLMAN SS, BOLOGNESI MP, et al. Late liner disassociation of a Pinnacle system acetabular component. Orthopedics. 2012;35(4):e561-e565.
[30] GEORGIOU G, SIAPKARA A, DIMITRAKOPOULOU A, et al. Dissociation of bipolar hemiarthroplasty of the hip after dislocation. A report of five different cases and review of literature. Injury. 2006;37(2):162-168.
[31] SU EP, CALLANDER PW, SALVATI EA. The bubble sign: a new radiographic sign in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2003;18(1):110-112.
[32] ENDO Y, GEANNETTE C, CHANG WT. Imaging evaluation of polyethylene liner dissociation in total hip arthroplasty. Skeletal Radiol. 2019;48(12):1933-1939.
[33] BEDARD NA, TETREAULT MW, HANSSEN AD, et al. Intermediate to long-term follow-up of cementing liners into well-fixed acetabular components. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020;102(16):1397-1404.
[34] CHAUHAN A, FITZPATRICK S, SCIULLI RL, et al. Using double-contrast CT arthrography to confirm suspected dissociation of a cemented polyethylene liner in the setting of revision total hip arthroplasty: a case report. JBJS Case Connect. 2017;7(2):e34.
[35] USREY MM, NOBLE PC, RUDNER LJ, et al. Does neck/liner impingement increase wear of ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene liners? J Arthroplasty. 2006;21(6 Suppl 2):65-71.
[36] SHON WY, BALDINI T, PETERSON MG, et al. Impingement in total hip arthroplasty a study of retrieved acetabular components. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(4):427-435.
[37] ISAAC GH, WROBLEWSKI BM, ATKINSON JR, et al. A tribological study of retrieved hip prostheses. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992;(276):115-125.
[38] 张海林, 翁文杰, 袁涛, 等. Harris-Galante Ⅱ型髋臼假体与聚乙烯内衬分离1例报告[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(3):236-237.
[39] 黄野, 张洪, 周乙雄. Harris-GalanteⅡ组配型髋臼的内衬脱落二例报告[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2003(4):62-63.
[40] ITO H, MATSUNO T, KANEDA K. Bipolar hemiarthroplasty for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. A 7- to 18-year followup. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;(374):201-211.
[41] YAMAGUCHI M, AKISUE T, BAUER TW, et al. The spatial location of impingement in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2000;15(3):305-313.
[42] HABE Y, HAMADA H, UEMURA K, et al. Cup safe zone and optimal stem anteversion in total hip arthroplasty for patients with highly required range of motion. J Orthop Res. 2024;42(6):1283-1291.
[43] 郭卓涛, 张凯, 查国春, 等. 腰椎融合对全髋关节置换后中期疗效影响的匹配对照试验[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(36):5801-5805.
[44] MALIK A, DORR LD, LONG WT. Impingement as a mechanism of dissociation of a metasul metal-on-metal liner. J Arthroplasty. 2009; 24(2):313-323.
[45] HEMMILÄ M, KARVONEN M, LAAKSONEN I, et al. Survival of 11,390 continuum cups in primary total hip arthroplasty based on data from the Finnish Arthroplasty Register. Acta Orthopaedica. 2019;90(4): 312-317.
[46] AYORA A, GONZALEZ G, FERNANDEZ C. A polyethylene liner dissociation case report in depuy pinnacle cup. An impingement problem? Arch Clin Exp Surg (ACES). 2019:1.
[47] TSIKANDYLAKIS G, OVERGAARD S, ZAGRA L, et al. Global diversity in bearings in primary THA. EFORT Open Rev. 2020;5(10):763-775.
[48] TSIKANDYLAKIS G, MOHADDES M, CNUDDE P, et al. Head size in primary total hip arthroplasty. EFORT Open Rev. 2018;3(5):225-231.
[49] JALALI O, SCUDDAY T, FICKENSCHER MC, et al. Third-Generation medium cross-linked polyethylene demonstrates very low wear in total hip arthroplasty. Arthroplast Today. 2020;6(3):316-321.
[50] PAGANO S, PLATE JF, KAPPENSCHNEIDER T, et al. Polyethylene liner dissociation in total hip arthroplasty: a retrospective case-control study on a single implant design. J Orthop Traumatol. 2024;25(1):38.
[51] GOYAL P, HOWARD JL, YUAN X, et al. Effect of Acetabular Position on polyethylene liner wear measured using simultaneous biplanar acquisition. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(5):1670-1674.
[52] FRANSEN BL, BENGOA FJ, NEUFELD ME, et al. Thin highly cross-linked polyethylene liners combined with large femoral heads in primary total hip arthroplasty show excellent survival and low wear rates at a mean follow-up of 12.8 years. Bone Joint J. 2023;105-B(1):29-34.
[53] YEE MA, O’KEEFE TJ, WINTER S. Incarcerated fracture fragments of longevity polyethylene liners after total hip arthroplasty. Arthroplasty Today. 2016;2(1):6-10.
[54] SARACCO M, PASSIATORE M, CAZZATO G, et al. Use of ceramic bearings in hip arthroplasty: correct implantation and review of clinical and radiographic results. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020;34(4 Suppl. 3): 237-242.
[55] LEWINNEK GE, LEWIS JL, TARR R, et al. Dislocations after total hip-replacement arthroplasties. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978;60(2):217-220.
[56] URUÇ V, ÖZDEN R, DUMAN IG, et al. Five cases of early dissociation between the bipolar hip endoprosthesis cup components; either spontaneously or during reduction maneuvers. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2017;51(2):172-176.
[57] MÖLLERS M, STEDTFELD HW, PAECHTNER S, et al. Hemi-arthroplasty of the hip joint: concentric or positive eccentric (self-centering) dual head prosthesis? A retrospective comparison. Unfallchirurg. 1992;95(5): 224-229.
[58] BARMADA R, MESS D. Bateman hemiarthroplasty component disassembly. A report of three cases of high-density polyethylene failure. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987;(224):147-149.
[59] WANG XD, LAN H, HU ZX, et al. SuperPATH minimally invasive approach to total hip arthroplasty of femoral neck fractures in the elderly: preliminary clinical results. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(1):74-85.
[60] LANGDOWN AJ, PICKARD RJ, HOBBS CM, et al. Incomplete seating of the liner with the trident acetabular system: a cause for concern? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89(3):291-295.
[61] GONZÁLEZ DELLA VALLE A, RUZO PS, LI S, et al. Dislodgment of polyethylene liners in first and second-generation harris-galante acetabular components. A report of eighteen cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83(4):553-559.
[62] HAN CD, CHOE WS, YOO JH. Late dissociation of the polyethylene liner from a modular acetabular metal shell after primary total hip arthroplasty--a report of five cases. Yonsei Med J. 1998;39(3):277-282.
[63] VASILEIOS A, SPYRIDON P. Dissociation of bipolar hemiarthroplasty of the Hip and review of literature. Arthroplast Today. 2022;16:119-123.
[64] BIAN YY, WANG LC, XIAO K, et al. Hip dislocation and femoral component disassembly after bipolar hemiarthroplasty: a report of four cases and introduction of new reduction maneuvers. Chin Med J (Engl). 2019;132(3):370-372.
[65] SIM SB, SON SW, SHIM BJ. Be aware of the “O” sign in the bipolar cup dissociation during closed reduction of bipolar dislocation: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023;102(37):e35234.
[66] 王上增, 王禛, 游明灿, 等.人工股骨头置换后的髋臼磨损:原因和处理[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(13):2028-2032.
[67] LAPORTE DM, MONT MA, PIERRE-JACQUES H, et al. Technique for acetabular liner revision in a nonmodular metal-backed component. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13(3):348-350.
[68] WERLE J, GOODMAN S, SCHURMAN D, et al. Polyethylene liner dissociation in harris-galante acetabular components: a report of 7 cases. J Arthroplasty. 2002;17(1):78-81. |

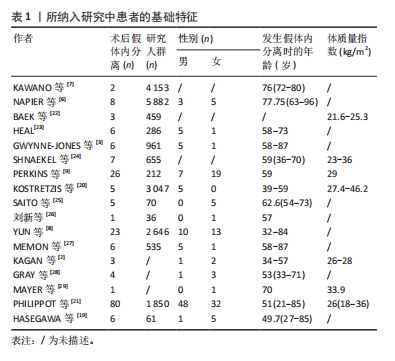
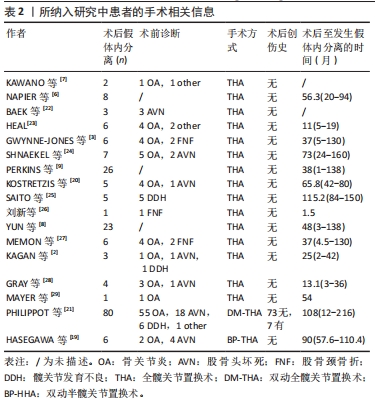
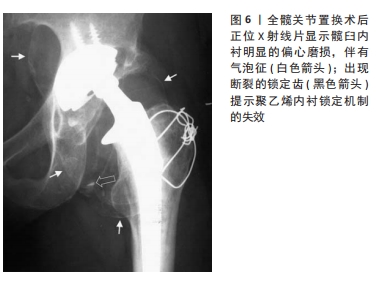
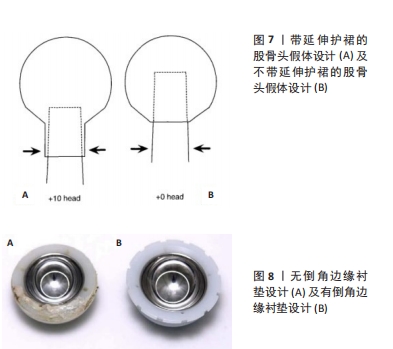

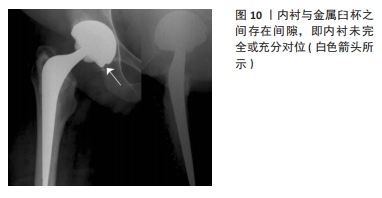
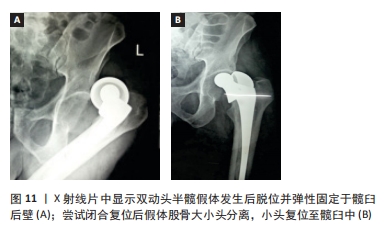
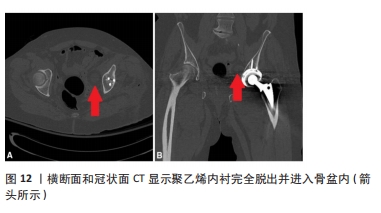
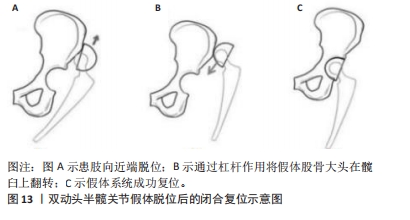
 尽管假体内分离并发症的发生相对少见,但一旦发生临床处理相当棘手。对于骨关节科医生而言,全面认识假体内分离发生的流行病学及影像学特点、发生机制及原因等内容,有助于建立科学合理的诊疗及防治策略。因此,作者对髋关节置换术后假体内分离并发症的相关研究作一综述。
尽管假体内分离并发症的发生相对少见,但一旦发生临床处理相当棘手。对于骨关节科医生而言,全面认识假体内分离发生的流行病学及影像学特点、发生机制及原因等内容,有助于建立科学合理的诊疗及防治策略。因此,作者对髋关节置换术后假体内分离并发症的相关研究作一综述。

