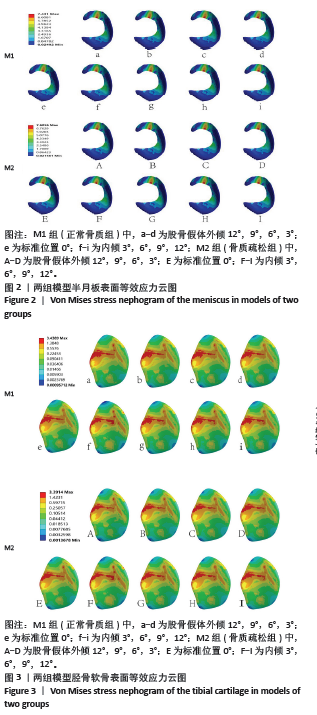
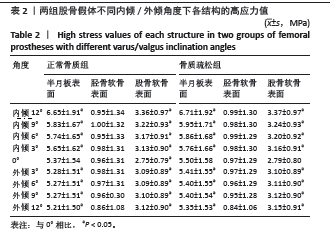
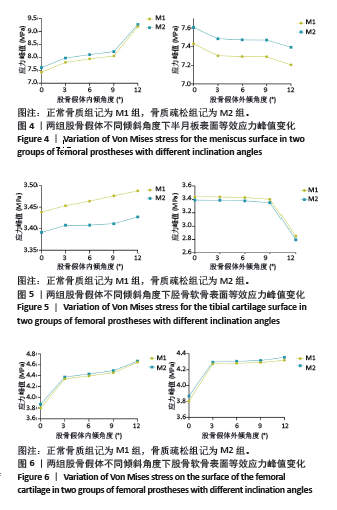
[1] SENG CS, HO DC, CHONG HC, et al. Outcomes and survivorship of unicondylar knee arthroplasty in patients with severe deformity. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(3):639-644.
[2] KANG KT, SON J, BAEK C, et al. Femoral component alignment in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty leads to biomechanical change in contact stress and collateral ligament force in knee joint. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2018;138(4):563-572.
[3] BONANZINGA T, TANZI P, ALTOMARE D, et al. High survivorship rate and good clinical outcomes at mid-term follow-up for lateral UKA: a systematic literature review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29(10): 3262-3271.
[4] VAN DER LIST JP, ZUIDERBAAN HA, PEARLE AD. Why Do Medial Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasties Fail Today? J Arthroplasty. 2016; 31(5):1016-1021.
[5] KWON HM, LEE JA, KOH YG, et al. Effects of contact stress on patellarfemoral joint and quadriceps force in fixed and mobile-bearing medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):517.
[6] KONO K, INUI H, TOMITA T, et al. Weight-bearing status affects in vivo kinematics following mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29(3):718-724.
[7] HU J, XIONG R, CHEN X, et al. Effect of components mal-alignment on biomechanics in fixed unicompartmental knee arthroplasty using multi-body dynamics model during a walking cycle. Med Eng Phys. 2022;100: 103747.
[8] KWON HM, LEE JA, KOH YG, et al.Computational analysis of tibial slope adjustment with fixed-bearing medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in ACL- and PCL-deficient models. Bone Joint Res. 2022;11(7):494-502.
[9] LIDDLE AD, JUDGE A, PANDIT H, et al. Adverse outcomes after total and unicompartmental knee replacement in 101,330 matched patients: a study of data from the National Joint Registry for England and Wales. Lancet. 2014;384(9952):1437-1445.
[10] LIOW MH, TSAI TY, DIMITRIOU D, et al. Does 3-Dimensional In Vivo Component Rotation Affect Clinical Outcomes in Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty? J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(10):2167-2172.
[11] KUIPERS BM, KOLLEN BJ, BOTS PC, et al. Factors associated with reduced early survival in the Oxford phase III medial unicompartment knee replacement. Knee. 2010;17(1):48-52.
[12] MA P, MUHEREMU A, ZHANG S, et al. Biomechanical effects of fixed-bearing femoral prostheses with different coronal positions in medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):150.
[13] ZHU GD, GUO WS, ZHANG QD, et al. Finite Element Analysis of Mobile-bearing Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty: The Influence of Tibial Component Coronal Alignment. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015;128(21): 2873-2878.
[14] DANESE I, PANKAJ P, SCOTT CEH. The effect of malalignment on proximal tibial strain in fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: A comparison between metal-backed and all-polyethylene components using a validated finite element model. Bone Joint Res. 2019;8(2):55-64.
[15] DU G, LI Z, LAO S, et al. [Biomechanical analysis of sitting-up movement of knee joint after robot-assisted unicompartmental knee arthroplasty]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021;35(10):1259-1264.
[16] NIE Y, YU Q, SHEN B. Impact of Tibial Component Coronal Alignment on Knee Joint Biomechanics Following Fixed-bearing Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty: A Finite Element Analysis. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(4): 1423-1429.
[17] KANG KT, PARK JH, KOH YG, et al.Biomechanical effects of posterior tibial slope on unicompartmental knee arthroplasty using finite element analysis. Biomed Mater Eng. 2019;30(2):133-144.
[18] DAI X, FANG J, JIANG L, et al. How does the inclination of the tibial component matter? A three-dimensional finite element analysis of medial mobile-bearing unicompartmental arthroplasty. Knee. 2018;25(3):434-444.
[19] THOREAU L, MORCILLO MARFIL D, THIENPONT E. Periprosthetic fractures after medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: a narrative review. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022;142(8):2039-2048.
[20] 许瀚,吕波,赵永正,等.单髁置换术治疗70岁以上老年膝内侧间室骨关节炎合并骨质疏松症的近期疗效观察[J].实用骨科杂志,2020,26(12): 1075-1078.
[21] HOLLENSTEINER M, SANDRIESSER S, BLIVEN E, et al. Biomechanics of Osteoporotic Fracture Fixation. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2019;17(6):363-374.
[22] 涂意辉,马童,蔡珉巍,等.微创膝关节单髁置换术治疗合并骨质疏松的内侧间室骨关节炎[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2012,18(6):535-538.
[23] KIM YS, KANG KT, SON J, et al. Graft Extrusion Related to the Position of Allograft in Lateral Meniscal Allograft Transplantation: Biomechanical Comparison Between Parapatellar and Transpatellar Approaches Using Finite Element Analysis. Arthroscopy. 2015;31(12):2380-2391.e2.
[24] 范熹微,聂涌,吴元刚,等.膝关节内侧固定平台单髁假体放置位置优化的有限元分析[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2020,40(3):169-177.
[25] MA P, MUHEREMU A, ZHANG S, et al. Biomechanical effects of fixed-bearing femoral prostheses with different coronal positions in medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):150.
[26] 蔡明,马朋朋,张春林,等.骨质疏松性腰1椎体有限元模型的建立和应力分析[J].中国数字医学,2020,15(4):80-83.
[27] POLIKEIT A, NOLTE LP, FERGUSON SJ. Simulated influence of osteoporosis and disc degeneration on the load transfer in a lumbar functional spinal unit. J Biomech. 2004;37(7):1061-1069.
[28] SANO M, OSHIMA Y, MURASE K, et al. Finite-Element Analysis of Stress on the Proximal Tibia After Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty. J Nippon Med Sch. 2020;87(5):260-267.
[29] SCOTT CE, EATON MJ, NUTTON RW, et al.Metal-backed versus all-polyethylene unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: Proximal tibial strain in an experimentally validated finite element model. Bone Joint Res. 2017; 6(1):22-30.
[30] LI L, YANG L, ZHANG K, et al. Three-dimensional finite-element analysis of aggravating medial meniscus tears on knee osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. 2019;20:47-55.
[31] CHU L, LIU X, HE Z, et al. Articular Cartilage Degradation and Aberrant Subchondral Bone Remodeling in Patients with Osteoarthritis and Osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(3):505-515.
[32] 韦荣斌,王小清,邹宪武,等.聚乙烯的杨氏模量及力常数的计算[J].武汉大学学报(理学版),2004,50(5):551-554. |