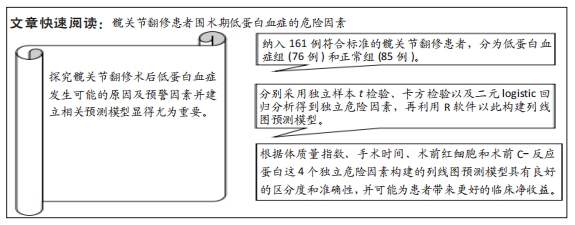
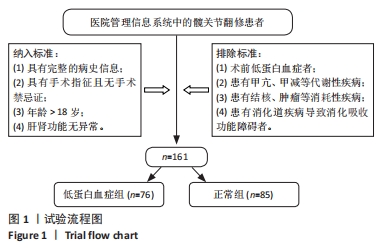
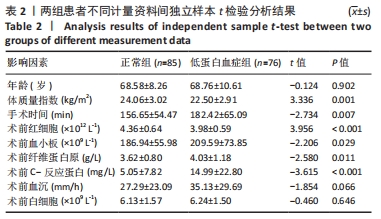
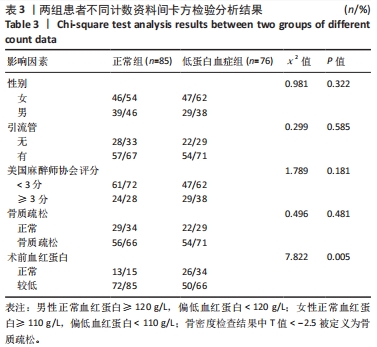
[1] HONG WS, ZHANG YX, LIN Q, et al. Risk Factors Analysis and the Establishment of Nomogram Prediction Model of Hidden Blood Loss After Total Hip Arthroplasty for Femoral Neck Fracture in Elderly Women. Clin Interv Aging. 2022;17:707-715.
[2] SCOTT CEH, CLEMENT ND, DAVIS ET, et al. Modern total hip arthroplasty: peak of perfection or room for improvement? Bone Joint J. 2022;104-b(2):189-192.
[3] LEWIS DP, WÆVER D, THORNINGER R, et al. Hemiarthroplasty vs Total Hip Arthroplasty for the Management of Displaced Neck of Femur Fractures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(8):1837-1843.e1832.
[4] SANTANA DC, ANIS HK, MONT MA, et al. What is the Likelihood of Subsequent Arthroplasties after Primary TKA or THA? Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020;478(1):34-41.
[5] MOREY VM, SONG YD, WHANG JS, et al. Can Serum Albumin Level and Total Lymphocyte Count be Surrogates for Malnutrition to Predict Wound Complications After Total Knee Arthroplasty? J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(6):1317-1321.
[6] KAMATH AF, MCAULIFFE CL, KOSSEIM LM, et al. Malnutrition in Joint Arthroplasty: Prospective Study Indicates Risk of Unplanned ICU Admission. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2016;4(2):128-131.
[7] NICHOLSON JA, DOWRICK AS, LIEW SM. Nutritional status and short-term outcome of hip arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2012;20(3):331-335.
[8] YI PH, FRANK RM, VANN E, et al. Is potential malnutrition associated with septic failure and acute infection after revision total joint arthroplasty? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(1):175-182.
[9] KISHAWI D, SCHWARZMAN G, MEJIA A, et al. Low Preoperative Albumin Levels Predict Adverse Outcomes After Total Joint Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020;102(10):889-895.
[10] ALAMANDA VK, SPRINGER BD. Perioperative and Modifiable Risk Factors for Periprosthetic Joint Infections (PJI) and Recommended Guidelines. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2018;11(3):325-331.
[11] SCHWARTZ AM, WILSON JM, FARLEY KX, et al. Concomitant Malnutrition and Frailty Are Uncommon, but Significant Risk Factors for Mortality and Complication Following Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(10):2878-2885.
[12] JABERI FM, PARVIZI J, HAYTMANEK CT, et al. Procrastination of wound drainage and malnutrition affect the outcome of joint arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(6):1368-1371.
[13] IHLE C, WEIß C, BLUMENSTOCK G, et al. Interview based malnutrition assessment can predict adverse events within 6 months after primary and revision arthroplasty - a prospective observational study of 351 patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):83.
[14] BOHL DD, SHEN MR, KAYUPOV E, et al. Hypoalbuminemia Independently Predicts Surgical Site Infection, Pneumonia, Length of Stay, and Readmission After Total Joint Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(1):15-21.
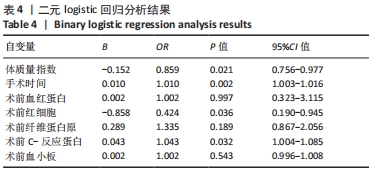
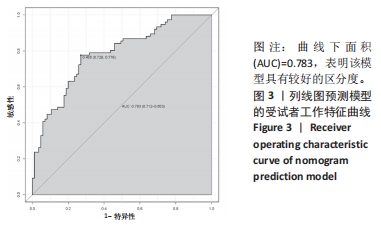
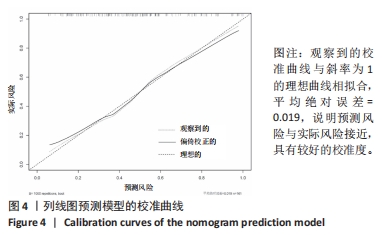
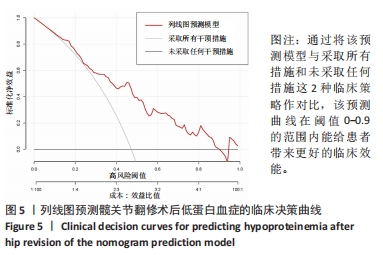
[15] 洪尉师,张亚鑫,林群,等.髋关节翻修术后输血的危险因素分析及列线图预测模型建立[J].实用医学杂志,2022,38(13):1652-1656.
[16] 林群,张亚鑫,贾大洲,等.股骨头坏死行全髋关节置换术后输血的危险因素分析及列线图预测模型建立[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2022,15(2):87-92.
[17] SOETERS PB, WOLFE RR, SHENKIN A. Hypoalbuminemia: Pathogenesis and Clinical Significance. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2019;43(2):181-193.
[18] CARVALHO JR, VERDELHO MACHADO M. New Insights About Albumin and Liver Disease. Ann Hepatol. 2018;17(4):547-560.
[19] KIM S, MCCLAVE SA, MARTINDALE RG, et al. Hypoalbuminemia and Clinical Outcomes: What is the Mechanism behind the Relationship? Am Surg. 2017; 83(11):1220-1227.
[20] WIEDERMANN CJ. Phases of fluid management and the roles of human albumin solution in perioperative and critically ill patients. Curr Med Res Opin. 2020; 36(12):1961-1973.
[21] WIEDERMANN CJ. Hypoalbuminemia as Surrogate and Culprit of Infections. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(9):4496.
[22] ZHANG Z, PEREIRA SL, LUO M, et al. Evaluation of Blood Biomarkers Associated with Risk of Malnutrition in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2017;9(8):829.
[23] ELSAID RM, NAMROUTI AS, SAMARA AM, et al. Assessment of pain and postoperative nausea and vomiting and their association in the early postoperative period: an observational study from Palestine. BMC Surg. 2021; 21(1):177.
[24] CORONA LP, DE OLIVEIRA DUARTE YA, LEBRÃO ML. Markers of nutritional status and mortality in older adults: The role of anemia and hypoalbuminemia. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2018;18(1):177-182.
[25] ZHAO DW, ZHAO FC, ZHANG XY, et al. Association between postoperative hypoalbuminemia and postoperative pulmonary imaging abnormalities patients undergoing craniotomy for brain tumors: a retrospective cohort study. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):64.
[26] FRANCH-ARCAS G. The meaning of hypoalbuminaemia in clinical practice. Clin Nutr. 2001;20(3):265-269.
[27] AUGUSTUS E, HAYNES E, GUELL C, et al. The Impact of Nutrition-Based Interventions on Nutritional Status and Metabolic Health in Small Island Developing States: A Systematic Review and Narrative Synthesis. Nutrients. 2022; 14(17):3529.
[28] LAPIĆ I, PADOAN A, BOZZATO D, et al. Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate and C-Reactive Protein in Acute Inflammation. Am J Clin Pathol. 2020;153(1):14-29.
[29] ECKART A, STRUJA T, KUTZ A, et al. Relationship of Nutritional Status, Inflammation, and Serum Albumin Levels During Acute Illness: A Prospective Study. Am J Med. 2020;133(6):713-722.e717.
[30] JACOB M, BRUEGGER D, REHM M, et al. Contrasting effects of colloid and crystalloid resuscitation fluids on cardiac vascular permeability. Anesthesiology. 2006;104(6):1223-1231.
[31] NORBERG Å, ROOYACKERS O, SEGERSVÄRD R, et al. Albumin Kinetics in Patients Undergoing Major Abdominal Surgery. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0136371.
|