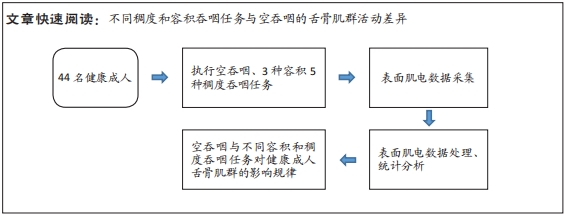
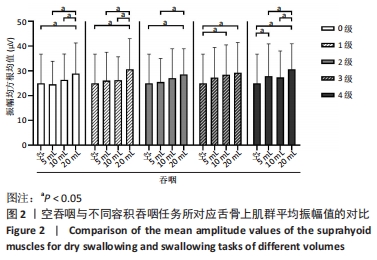
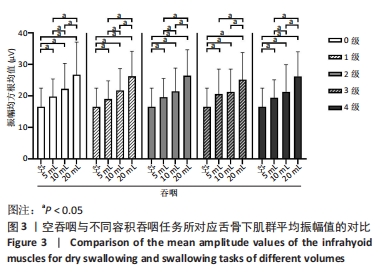
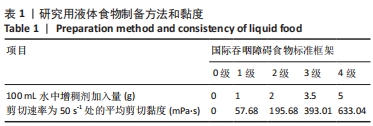
[1] 陈卓铭.语言治疗学[M].3版.北京: 人民卫生出版社,2018:240-300.
[2] ZAVALA-SOLARES MR, REYES-TORRES CA, FUNEZ-MADRID V. Oropharyngeal dysphagia treatment. NeuroGastroLatam Rev. 2020; 4(1):7-19.
[3] ZHANG M, LI C, ZHANG F, et al. Prevalence of Dysphagia in China: An Epidemiological Survey of 5943 Participants. Dysphagia. 2021;36(3): 339-350.
[4] BOOT E, EKKER MS, PUTAALA J, et al. Ischaemic stroke in young adults: a global perspective. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2020;91(4):411-417.
[5] HELLIWELL K, HUGHES VJ, BENNION CM, et al. The use of videofluoroscopy (VFS) and fibreoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing (FEES) in the investigation of oropharyngeal dysphagia in stroke patients: A narrative review. Radiography. 2023;29(2):284-290.
[6] WARNECKE T, DZIEWAS R, LANGMORE S. FEES and Other Instrumental Methods for Swallowing Evaluation//WARNECKE T, DZIEWAS R, LANGMORE S. Neurogenic Dysphagia. Cham: Springer International Publishing,2021:55-107.
[7] BAYONA HHG, PIZZORNI N, TACK J, et al. Accuracy of high-resolution pharyngeal manometry metrics for predicting aspiration and residue in oropharyngeal dysphagia patients with poor pharyngeal contractility. Dysphagia. 2022;37(6):1560-1575.
[8] HSIAO M, WU C, WANG T. Emerging Role of Ultrasound in Dysphagia Assessment and Intervention: A Narrative Review. Front Rehabilit Sci. 2021;2:708102.
[9] LIU L, ZHONG Y, CHEN X, et al. Surface Electromyography of Pharyngeal Swallowing in Healthy Chinese Individuals: Establishment of a Timing and Amplitude Database. Dysphagia. 2023. doi: 10.1007/s00455-023-10569-y.
[10] OROZCO-DUQUE A, SUAREZ-ESCUDERO JC, OROZCO-ARROYAVE JR, et al. Surface electromyography for evaluation of swallowing phases in dysphagia: a pilot study. Dysphagia. 2022;34(5):797-799.
[11] ANDRADE RAD, DO SALES CORIOLANO MDGW, de SOUZA ELH, et al. Reliability of ultrasound examination of hyoid bone displacement amplitude: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dysphagia. 2022; 37(6):1375-1385.
[12] SPEYER R, CORDIER R, SUTT A, et al. Behavioural interventions in people with oropharyngeal dysphagia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. J Clin Med. 2022;11(3):685-717.
[13] PARK HS, OH DH, YOON T, et al. Effect of effortful swallowing training on tongue strength and oropharyngeal swallowing function in stroke patients with dysphagia: a double‐blind, randomized controlled trial. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2019;54(3):479-484.
[14] SU M, ZHENG G, CHEN Y, et al. Clinical applications of IDDSI framework for texture recommendation for dysphagia patients. J Texture Stud. 2018;49(1):2-10.
[15] AN S, LEE W, YOO B. Comparison of National Dysphagia Diet and International Dysphasia Diet Standardization Initiative Levels for Thickened Drinks Prepared with a Commercial Xanthan Gum-Based Thickener Used for Patients with Dysphagia. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2023; 28(1):83-88.
[16] UESHIMA J, SHIMIZU A, MAEDA K, et al. Nutritional Management in Adult Patients With Dysphagia: Position Paper From Japanese Working Group on Integrated Nutrition for Dysphagic People. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2022;23(10):1676-1682.
[17] CICHERO J, LAM P, CHEN J, et al. Release of updated International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative Framework (IDDSI 2.0). J Texture Stud. 2020;51(1):195-196.
[18] HASEGAWA M, KUROSE M, OKAMOTO K, et al. Differential Response Pattern of Oropharyngeal Pressure by Bolus and Dry Swallows. Dysphagia. 2018;33(1):83-90.
[19] PEDERSEN A, SORENSEN CE, PROCTOR GB, et al. Salivary functions in mastication, taste and textural perception, swallowing and initial digestion. Oral Dis. 2018;24(8):1399-1416.
[20] 彭昕珂,贾飞阳,刘静,等.健康成年人反复唾液吞咽测试期间的近红外脑功能成像[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(32):5103-5107.
[21] 王维,贾玉洁,蔡洪梅,等.表面肌电生物反馈与功能贴布治疗脑卒中后吞咽障碍[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(29):4697-4701.
[22] MOMOSAKI R, ABO M, KAKUDA W, et al. Applicability of the two-step thickened water test in patients with poststroke dysphagia: a novel assessment tool for paste food aspiration. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013;22(6):817-821.
[23] CHANG W, CHEN M, LIU J, et al. Surface Electromyography for Evaluating the Effect of Aging on the Coordination of Swallowing Muscles. Dysphagia. 2023. doi:10.1007/s00455-023-10572-3.
[24] PARK MW, LEE D, SEO HG, et al. Reliability of Suprahyoid and Infrahyoid Electromyographic Measurements during Swallowing in Healthy Subjects. J Korean Dysphagia Soc. 2021;11(2):128-136.
[25] VAN DEN ENGEL-HOEK L, de GROOT IJM, ESSER E, et al. Biomechanical events of swallowing are determined more by bolus consistency than by age or gender. Physiol Behav. 2012;106(2):285-290.
[26] ZHU M, YU B, YANG W, et al. Evaluation of normal swallowing functions by using dynamic high-density surface electromyography maps. Biomed Eng Online. 2017;16(133):133.
[27] RUARK JL, MCCULLOUGH GH, PETERS RL, et al. Bolus consistency and swallowing in children and adults. Dysphagia. 2002;17(1):24-33.
[28] IGARASHI A, KAWASAKI M, NOMURA S, et al. Sensory and motor responses of normal young adults during swallowing of foods with different properties and volumes. Dysphagia. 2010;25(3):198-206.
[29] MIYAOKA Y, ASHIDA I, KAWAKAMI S, et al. Activity patterns of the suprahyoid muscles during swallowing of different fluid volumes. J Oral Rehabil. 2010;37(8):575-582.
[30] UESUGI Y, IHARA Y, YUASA K, et al. Sole‐ground contact and sitting leg position influence suprahyoid and sternocleidomastoid muscle activity during swallowing of liquids. Clin Exp Dent Res. 2019,5(5):505-512.
[31] ZARETSKY E, PLUSCHINSKI P, SADER R, et al. Identification of the most significant electrode positions in electromyographic evaluation of swallowing-related movements in humans. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017;274(2):989-995.
[32] 李珍珍.健康成人吞咽不同粘度和一口量液体食物对舌骨肌群激活特征的影响[D].济南:山东体育学院,2020.
[33] SHIBAMOTO I. Factors affect swallowing sEMG: systematic review. J Rehabil Sci. 2021;16(2020):55-69.
[34] KONRAD P. The ABC of EMG: A practical introduction to kinesiological electromyography. USA: Noraxon INC, 2005: 3-100.
[35] ARCHER SK, GARROD R, HART N, et al. Dysphagia in Duchenne muscular dystrophy assessed objectively by surface electromyography. Dysphagia. 2013;28(2):188-198.
[36] STEELE CM, MILLER AJ. Sensory input pathways and mechanisms in swallowing: a review. Dysphagia. 2010;25(4):323-333.
[37] ITO Y, INAMOTO Y, SAITOH E, et al. The effect of bolus consistency on pharyngeal volume during swallowing: Kinematic analysis in three dimensions using dynamic Area Detector CT. J Oral Rehabil. 2020;47(10):1287-1296.
[38] SMAOUI S, PELADEAU-PIGEON M, STEELE CM. Variations in Hyoid Kinematics Across Liquid Consistencies in Healthy Swallowing. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2021;64(1):51-58.
[39] CHANG MC, PARK S, CHO JY, et al. Comparison of three different types of exercises for selective contractions of supra- and infrahyoid muscles. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):7131.
[40] UEDA N, NOHARA K, KOTANI Y, et al. Effects of the bolus volume on hyoid movements in normal individuals. J Oral Rehabil. 2013;40(7): 491-499.
[41] NAGY A, MOLFENTER SM, PÉLADEAU-PIGEON M, et al. The effect of bolus volume on hyoid kinematics in healthy swallowing. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:738971.
[42] PONGPIPATPAIBOON K, INAMOTO Y, AIHARA K, et al. Thin Liquid Bolus Volume Alters Pharyngeal Swallowing: Kinematic Analysis Using 3D Dynamic CT. Dysphagia. 2022;37(6):1423-1430.
[43] RUARK JL, MCCULLOUGH GH, PETERS RL, et al. Bolus consistency and swallowing in children and adults. Dysphagia. 2002;17(1):24-33. |