1.1 设计 随机对照动物实验。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2020年5月至2021年7月在河南省中心实验室完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 实验动物 健康雄性SPF级SD大鼠38只,6-8周龄,体质量200-220 g,由郑州市惠济区华兴实验动物养殖场提供,许可证号SCXY豫2019-0002,饲养条件:室温22-26 ℃、相对湿度50%-60%、通风良好,在清洁安静的环境中适应性饲养1周,期间大鼠自由进食、饮水,昼夜节律光照。
实验方案经河南省中医院(河南中医药大学第二附属医院)伦理委员会审查通过(批准文号:PZ-HNSZYY-2020-041)。实验过程遵循了国际兽医学编辑协会《关于动物伦理与福利的作者指南共识》和本地及国家法规。实验动物在麻醉下进行所有的手术,并尽一切努力最大限度地减少其疼痛、痛苦和死亡。
1.3.2 主要试剂与仪器 2%TTC染液(索莱宝,G3005);总RNA提取试剂盒(索莱宝,R1200);RNA反转试剂盒(Takara,RR047A);蛋白电泳凝胶试剂盒(中晖赫彩,PE008);BCL-2兔多克隆抗体(Abclonal,A0208);BAX重组兔单克隆抗体(Abclonal,A20227);高效RIPA组织裂解液(索莱宝,R0010);BCA蛋白浓度测定试剂盒(碧云天,P0010);Marker (10-180 kD)(中晖赫彩,M221-01);β-Actin鼠抗(Proteintech,66009-1-1);鼠二抗(Proteintech,SA00001-1);兔二抗(Proteintech,SA00001-2);Serotonin抗体(Gene Tex,GTX31099);Sp(小鼠/兔IgG)-PODkit(索莱宝,SP0041);线栓(北京西农科技有限公司,Z634-A4);0.5 mm毛细软管(道冠,29319);SMUP-U4型生物信号采集器(上海嘉龙教仪厂);微量泵(20-50 mL)(思路高);张力换能器(30 g)(上海继德教学实验器械厂);大小鼠断头器(JNT-DTQ)(郑州点睛有限公司);恒温箱(上海智城分析仪器有限公司);电暖器(美菱)。
1.4 实验方法
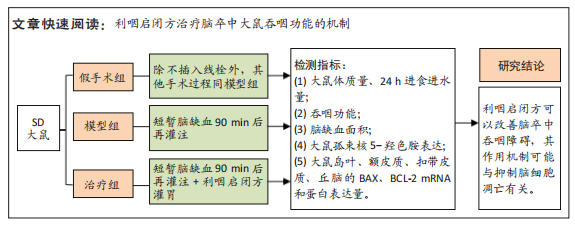
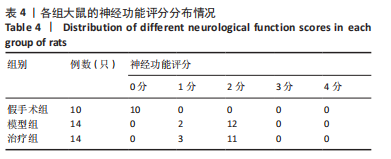
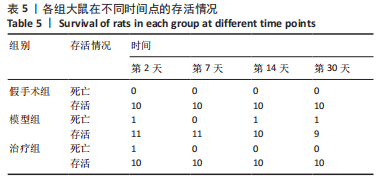
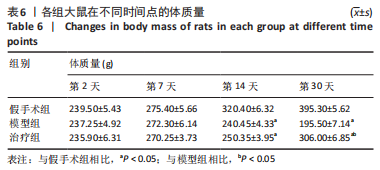
1.4.1 实验分组及流程 将38只SD大鼠称体质量后随机分为3组,即假手术组10只、模型组14只、治疗组14只。模型组、治疗组采用线栓法短暂阻塞大鼠的右侧大脑中动脉,90 min后进行缺血再灌注,形成右侧脑缺血再灌注模型;假手术组除不插入线栓外,其手术过程同模型组与治疗组。造模后6 h采用Longa神经功能症状评分标准对各组大鼠进行评分[11],模型组与治疗组纳入评分为2分的大鼠进入后续实验。造模后第2天治疗组给予中药复方利咽启闭方进行灌胃治疗,其余各组给予等量生理盐水灌胃,1次/d,治疗1个月。造模后第2,7,14,30天记录各组大鼠的体质量变化及24 h进食、进水量变化;造模后第14,30天,利用生物信号采集器及张力传感系统检测各组大鼠的吞咽启动反应时间和吞咽次数;在最后一次吞咽功能评估后麻醉状态下断头取脑,每组随机取5只延髓样本,免疫组化检测孤束核5-羟色胺的表达;各组剩余大鼠进行TTC染色,计算脑缺血面积,同时取岛叶、前运动皮质、扣带皮质、丘脑等组织采用RT-PCR和Western blot检测BCL-2、BAX mRNA及蛋白表达量。
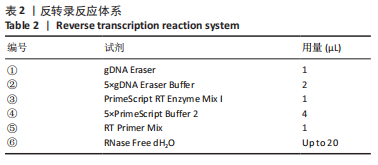
1.4.2 模型制备及评估 造模前,动物禁食不禁水12 h,采用2%戊巴比妥钠(3 mL/kg)麻醉大鼠;仰卧位固定于鼠板上,脱毛膏涂抹在颈中线处及周围约1 cm,脱毛后用碘伏消毒;沿颈正中线做约1 cm纵向切口,钝性分离右侧胸锁乳突肌和胸骨舌骨肌的肌间隙,暴露右侧颈总动脉;依次分离右侧颈外动脉和右侧颈内动脉,结扎右侧颈总动脉、右侧颈外动脉近心端,并在右侧颈内动脉靠近右侧颈总动脉、右侧颈外动脉处预留活结,动脉夹夹闭右侧颈内动脉,用弯镊挑起右侧颈总动脉,并用血管剪在右侧颈总动脉处剪一小口,将线栓插入右侧颈总动脉,松开右侧颈内动脉上动脉夹,使线栓上黑色标记处进入至分叉处(即线栓插入深度18-20 mm),于右侧颈内动脉上预留活结处结扎右侧颈内动脉,用于固定线栓,最后缝合切口;将其放置于干净的垫料上,并用电暖器取暖;计时90 min后将线栓拔出,完成手术。采取Zea-Longa神经功能缺损症状评分标准进行神经功能评估[11],见表1。在大鼠苏醒后,对各组大鼠进行评分,模型组及治疗组纳入评分为2分的大鼠进入后续实验。
1.4.3 给药方法
利咽启闭方组成:炒桃仁15 g,红花12 g,当归9 g,桔梗10 g,柴胡6 g,枳壳6 g,赤芍9 g,半夏12 g,天麻9 g,郁金9 g,石菖蒲10 g,僵蚕9 g。药物采用四川新绿色药业科技发展有限公司生产的中药免煎配方颗粒,用加热后的去离子水稀释。药物剂量换算参照剂量-体表面积换算法,利咽启闭方等效剂量浓度为1.16 g/mL,配制好的药液在4 ℃冰箱保存。每次灌胃前将药物预热(在37 ℃水浴锅中放置约20 min),灌胃量为1 mL/100 g,灌胃时间为4周。
1.4.4 取材方法
(1)延髓样本制备:每组取5只大鼠,用2%戊巴比妥钠(3 mL/kg)麻醉后,动脉夹夹闭腹主动脉,迅速剪开膈肌,打开胸腔,沿腋前线剪开胸壁,充分暴露心脏,持镊子捏住心脏,同时持灌注针从心尖部位插入,向上进针到升主动脉,用剪刀在右心耳处剪一小口,开放静脉血,只灌注头部及上肢;快速灌注生理盐水约100 mL,待大鼠双上肢及肺部发白后灌注液更换为40 g/L多聚甲醛,刚开始灌注时大鼠前肢剧烈抽动(下肢不抽动表明腹主动脉夹闭完全),前肢及颈部僵硬即多聚甲醛灌注成功;灌注结束后使用大鼠断头仪切下大鼠头部,止血钳打开头骨(分离颅骨时注意硬脑膜,避免硬脑膜划伤脑组织),参考《大脑立体定位图谱》(第3版)用刀片取大鼠对耳线-3 mm至-5 mm孤束核所在部分延髓标本分组放入提前装有40 g/L多聚甲醛的离心管里[12],固定48 h,进行后续免疫组化检测。
(2)TTC染色及基因蛋白检测样本制备:每组剩余大鼠用2%戊巴比妥钠(3 mL/kg)麻醉后,迅速开胸充分暴露心脏,经心尖插入灌注针头,灌注生理盐水100 mL,同时剪开右心耳,开放静脉血,夹闭腹主动脉,只灌注上肢及头部;前肢和颈部颜色发白标志灌注成功。断头取出大脑后,将大脑放置脑槽内,脑槽放置于冰盐水中,参照《大脑立体定位图谱》(第3版)在视交叉处切第一刀[12],然后往前每隔1 mm切一片,共3片,即前囟-2 mm至1 mm处脑组织用于TTC染色;在前囟-5 mm至-2 mm位置分离右侧丘脑,前囟1 mm至3.7 mm位置分离右侧岛叶及扣带皮质,前囟1 mm至4.2 mm位置分离右侧前运动皮质,各组织分装放入提前标记好的冻存管后迅速放入液氮中,并置于-80 ℃冰箱保存,用于RT-qPCR和Western blot检测。
1.5 主要观察指标
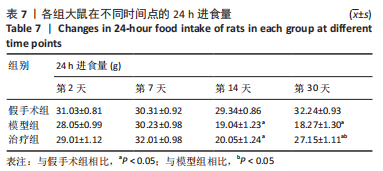
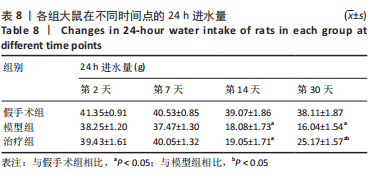
1.5.1 大鼠体质量、24 h进食进水量检测 造模后第2,7,14,30天记录各组大鼠的体质量及24 h进食、进水量。每次测量各组大鼠体质量均固定在早上同一时间;给予大鼠充足的饲料和饮用水并称质量,24 h后再次称质量,2次质量相减即大鼠的24 h进食、进水量。
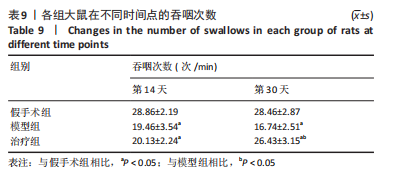
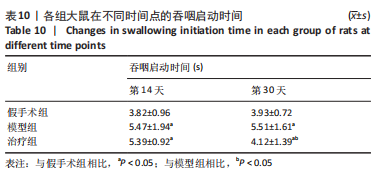
1.5.2 吞咽功能检测 将大鼠用2%戊巴比妥钠(3 mL/kg)麻醉后,仰卧位固定,颈部下颌舌骨肌处用脱毛膏去毛,碘伏消毒后,切开一小口暴露下颌舌骨肌,使大鼠头部抬高45°,用张力换能器连接生物信号器及下颌舌骨肌。经大鼠口腔插入直径0.5 mm的毛细软管直达舌根下,使用微量泵以10 mL/h的速度注入蒸馏水1 min,停止1 min后,再次重复以上步骤3次,记录大鼠1 min内的吞咽次数和从打开微量泵进行刺激至第1次吞咽发生的时间即吞咽启动反应时间。用BSP System 3.04软件记录测量结果,并计算3次测量的平均数,即得到平均吞咽启动反应时间和平均吞咽次数。
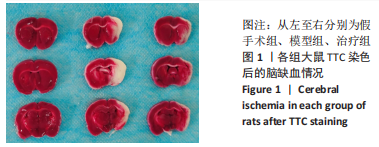
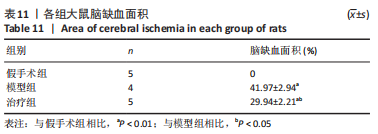
1.5.3 TTC染色 将2%TTC染色液倒入小培养皿中,用锡箔纸盖住后,放入37 ℃恒温箱,不时翻动脑片,使其均匀接触到染色液;30 min后取出照相,白色区域为梗死区,红色区城为未梗死区,并用Image Pro Plus6.0 软件计算每个脑组织梗死的总面积。
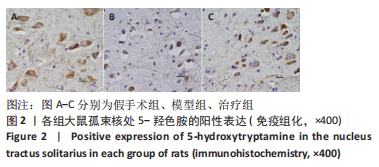
1.5.4 免疫组化法检测大鼠孤束核5-羟色胺表达 将固定后的各组脑组织修片后脱水机梯度脱水,石蜡包埋,用切片机将样品切成5 μm切片,烤片,二甲苯及梯度乙醇脱蜡复水,滴加体积分数为3%H2O2灭活内源性酶,用1×柠檬酸钠修复液修复,封闭液室温封闭20 min,用稀释液将5-羟色胺一抗按1∶100比例稀释后4 ℃冰箱孵育过夜,加入二抗37 ℃孵育30 min,DAB显色,苏木精复染,乙醇脱水,中性树胶封固,显微镜下观察。
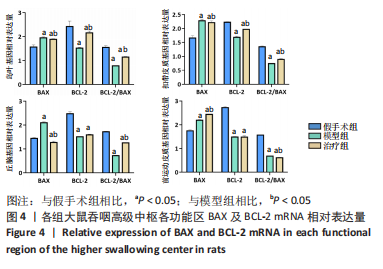
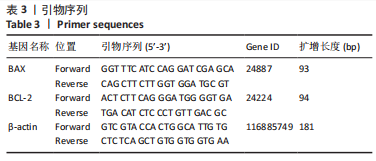
1.5.5 RT-PCR法检测大鼠岛叶、额皮质、扣带皮质、丘脑的BAX、BCL-2 mRNA表达量 每组取米粒大小(约100 mg)样本,加入1 mL裂解液,按说明书提取RNA,取小透明反应管,标记,加入相应量的RNA样本和RNasefree ddH2O,反应体系见表2;将RNA反应管放置于反转录机中反转,参数:37 ℃ 15 min;85 ℃ 5 s;4 ℃。然后配制引物,引物序列合成见表3,根据样品数及引物布板,加入引物、cDNA,充分混匀后放入QPCR仪,反应参数:预变性 95 ℃ 30 s;PCR反应95 ℃ 5 s,60 ℃ 34 s,40个循环。以β-actin为内参基因,采用2-ΔΔCt作为统计数据进行分析。
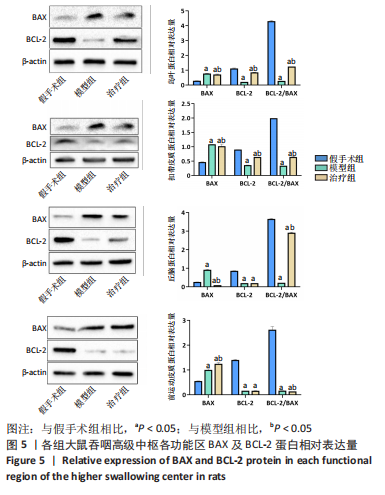
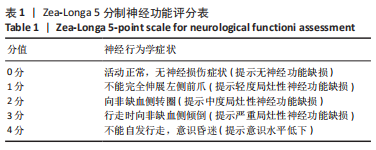
1.5.6 Western blot法检测大鼠岛叶、额皮质、扣带皮质、丘脑的BCL-2、BAX蛋白表达量 各组取米粒大小标本,每20 g组织加200 μL裂解液,在匀浆机中以30 r/s速度匀浆5 min;振荡离心后,放置冰上裂解1 h,蛋白定量后,水浴锅提前升温至100 ℃,将样品煮5 min使蛋白变性;制胶,上样后放置电泳仪进行电泳,参数:80 V,20 min;200 V,40 min;转膜仪中进行转膜,恒流240 A,1.5 h;用5%脱脂奶粉溶液室温封闭1.5 h;将BCL-2、BAX一抗按照1∶1 000稀释,内参β-actin按照1∶5 000稀释,加入一抗4 ℃孵育过夜;洗膜;将羊抗兔及羊抗鼠二抗按照1∶2 000进行稀释后室温孵育1 h;用1×TBST溶液进行洗膜;加入ECL发光液进行显影;用Image J软件计算条带灰度值。
1.6 统计学分析 采用SPSS 22.0软件进行分析,计量资料采用x±s表示,对满足正态分布且方差齐的数据采用方差分析,组间两两比较采用LSD-t检验,若不符合正态分布或方差不齐,则采用非参数检验;上述检验方法均以0.05为检验水准,P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。文章统计学方法已经河南省中医院统计学专家审核。