中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (32): 5162-5167.doi: 10.12307/2023.826
• 神经组织构建 nerve tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
糖痹康减轻糖尿病周围神经病变大鼠坐骨神经的氧化应激损伤
蒋昇源1,张亚奇1,毕境新2,张程斐3,张秋娥4,穆晓红1,白惠中1,左心玮3,刘铜华2,秦灵灵5,6
- 1北京中医药大学东直门医院,北京市 100700;北京中医药大学,2教育部中医养生学重点实验室,3生命科学学院,4中医学院,5科技处,北京市 100029;6教育部高等学校学科创新引智基地,北京市 100029
Tangbikang reduces sciatic nerve oxidative stress injury in a rat model of diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Jiang Shengyuan1, Zhang Yaqi1, Bi Jingxin2, Zhang Chengfei3, Zhang Qiue4, Mu Xiaohong1, Bai Huizhong1, Zuo Xinwei3, Liu Tonghua2, Qin Lingling5, 6
- 1Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China; 2Key Laboratory of Health Preservation of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Ministry of Education, 3College of Life Sciences, 4College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 5Technology Department, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China; 6Academic Innovation Introduction Base of the Ministry of Education, Beijing 100029, China
摘要:
文题释义:
糖痹康:中药复方糖痹康是由传统经方黄芪桂枝五物汤加减优化而得,主要用于糖尿病周围神经病变,现已被证实具有改善血糖及坐骨神经传导速度、调控施万细胞自噬等作用。
氧化应激:线粒体内过量的活性氧累积会诱导细胞器氧化应激,大量氧化中间产物积存于细胞,直接损伤如蛋白质、脂质等各类生物分子,诱导细胞死亡。
背景:中药复方糖痹康具有改善血糖、减轻糖尿病周围神经病变的作用,但其调控作用机制尚未清楚。
目的:观察中药复方糖痹康对糖尿病大鼠坐骨神经氧化应激的影响,探索糖痹康减轻糖尿病周围神经病变的靶向调控机制。
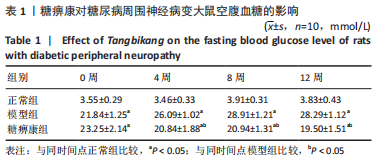
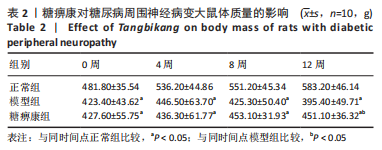
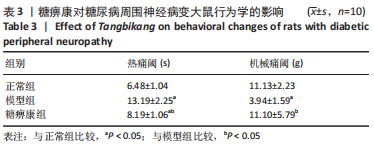
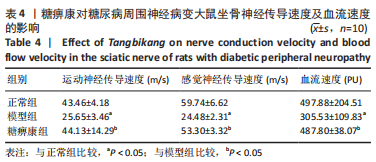
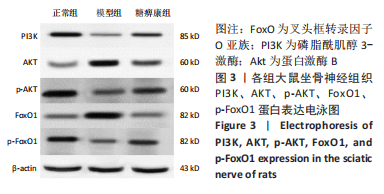
方法:30只SD大鼠随机分为正常组、模型组和糖痹康组,每组10只。后两组构建糖尿病周围神经病变模型,成模后分别灌胃生理盐水或糖痹康2.5 g/(kg·d),持续12周。给药后0,4,8,12周检测大鼠的体质量、空腹血糖水平;通过热板实验及Von Frey实验检测给药12周各组大鼠热痛阈及机械痛阈;给药12周后取材,取材前检测各组大鼠坐骨神经传导速度及坐骨神经血流速度,苏木精-伊红染色和透射电镜检测观察大鼠坐骨神经形态学变化,采用比色法和ELISA试剂盒分别检测坐骨神经中超氧化物歧化酶、丙二醛、白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α表达,Western blot检测坐骨神经组织PI3K/AKT/FoxO1通路相关蛋白表达水平。
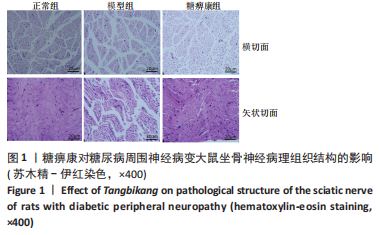
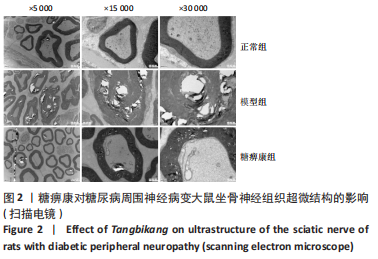
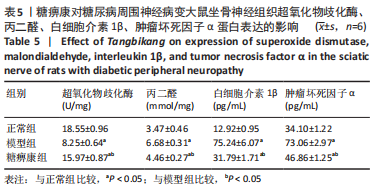
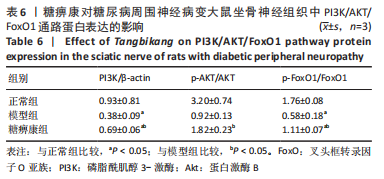
结果与结论:①糖痹康组大鼠造模后4,8,12周血糖水平均显著低于模型组(P < 0.05),模型组大鼠第12周体质量明显低于糖痹康组(P < 0.05);②造模后12周,糖痹康组机械痛阈及热痛阈相较于模型组有明显改善(P < 0.05),糖痹康组坐骨神经传导速度及血流速度均明显高于模型组(P < 0.05);③糖痹康组神经纤维排列秩序、致密程度、髓鞘化程度均优于模型组;④ELISA及比色法结果显示,与模型组相比,糖痹康组坐骨神经组织中丙二醛、白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α蛋白表达显著降低,超氧化物歧化酶蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05);⑤Western blot结果显示,糖痹康组坐骨神经组织中PI3K、p-AKT/AKT、p-FoxO1/FoxO1蛋白表达量较模型组升高(P < 0.05);⑥糖痹康可改善糖尿病大鼠坐骨神经功能、减轻坐骨神经氧化应激损伤,其机制可能与糖痹康调控PI3K/AKT/FoxO1通路相关。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4391-2360(蒋昇源)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: