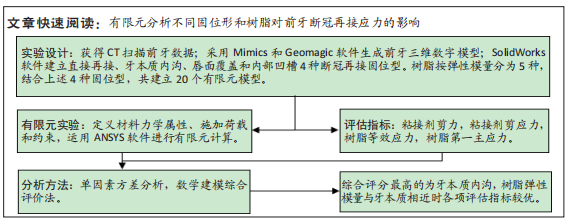
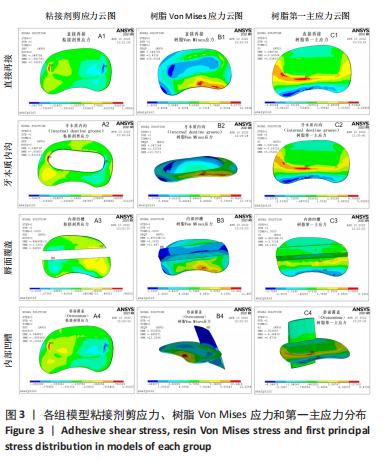
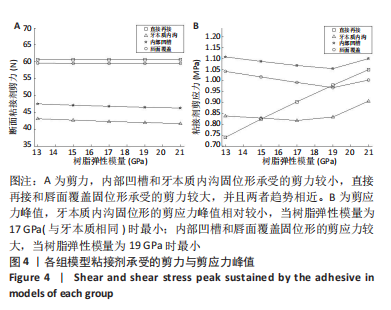
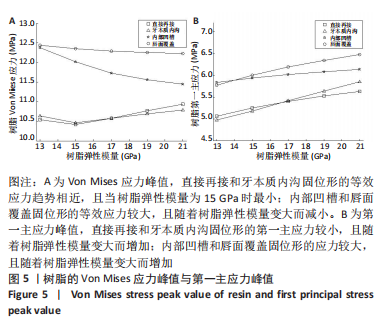
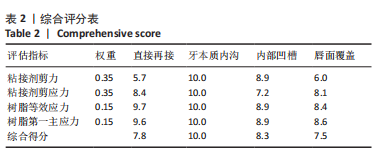
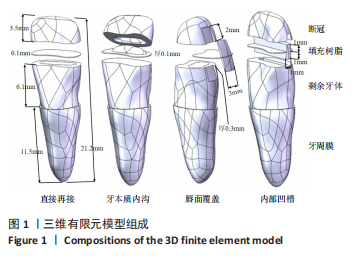
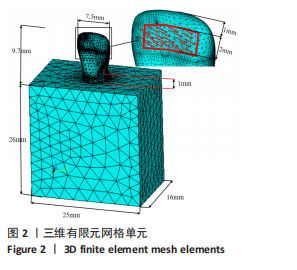
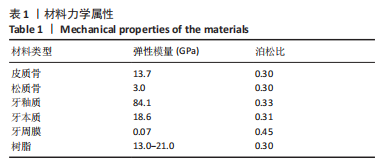
[1] LO GIUDICE G, ALIBRANDI A, LIPARI F, et al. The coronal tooth fractures: preliminary evaluation of a three year follow up of the anterior teeth direct fragment reattachment technique without additional preparation. Open Dent J. 2017;11(1):266-275.
[2] 彭彬.牙髓病学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2015:307-308.
[3] PEIXOTO RF, ALMEIDA KTD, CAMPOS JP, et al. Tooth fragment re-attachment in fracture with biological width violation: Case report. Revista Clínica de Periodoncia, Implantología y Rehabilitación Oral. 2016;91:223-228.
[4] DIANGELIS AJ. International Association of dental traumatology guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries. Dent Traumatol. 2014; 28(1):2-12.
[5] TAGUCHI CM, BERNARDON JK, ZIMMERMANN G, et al. Tooth fragment reattachment: a case report. Oper Dent. 2014;40(3):227-234.
[6] 黄娟,吴友农,梁红.三种固位形用于前牙断冠再接的效果评价[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2017,33(7):418-420.
[7] ABDULKHAYUM A, MUNJAL S, BABAJI P, et al. Invitro evaluation of fracture strength recovery of reattached anterior fractured tooth fragment using different reattachment techniques. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014;8(3):208-211.
[8] TONINI R. An Innovative Method for Fragment reattachment after complicated crown fracture. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2017;29(3):172-177.
[9] DEEPA VL, REDDY SN, GARAPATI VC, et al. Fracture fragment reattachment using projectors and anatomic everstick post: An Ultraconservative Approach. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2017;7( Suppl 1):S52-S54.
[10] 于文倩,李晓茜,陈思艺.上部结构材料对无牙下颌种植固定修复影响的三维有限元分析[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2021,56(2):190-195.
[11] 须敏依,蔡云飞,华滢婕.牙齿隐形矫治的三维有限元分析[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2022,15(1):109-112.
[12] 高羽轩,张岚,周学东.直线通路微创开髓洞型对上颌第一前磨牙力学性能影响的有限元分析[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2022,57(1):52-59.
[13] CHITRANCE KS, RAJAT K, DEBASHIS K. Fatigue behaviour of dental implant using finite element method. Mater Today Proc. 2022;21:185-196.
[14] 高健,赵守亮,周成杰.种植体直径-长度比的三维有限元应力分析[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2014,10(24):364-369.
[15] KURSAT C, SIMAY K, ALPER K, et al. A literature review on the linear elastic material properties assigned in finite element analyses in dental research. Mater Today Commun. 2022;30:146-151.
[16] LEE H, JO M, NOH G. Biomechanical effects of dental implant diameter, connection type and bone density on microgap formation and fatigue failure: A finite element analysis. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021;200:423-431.
[17] 洪煜锐,李阳,骆伟燕.树脂陶瓷复合材料单冠美学区种植修复的三维有限元分析[J].上海口腔医学,2020,29(3):262-266.
[18] PIRMORADIAN M, NAEENI HA, FIROUZBAKHT M, et al. Finite element analysis and experimental evaluation on stress distribution and sensitivity of dental implants to assess optimum length and thread pitch. Dent Mater. 2020;187:312-319.
[19] 刘逆舟,李磊丹,韦晓玲.不同修复方法对深型楔状缺损牙应力分布影响研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2020,13(4):232-236.
[20] SCHULZE KA, MARSHALL SJ, GANSKY SA, et al. Color stability and hardness in dental composites after accelerated aging. Dent Mater. 2003;19(7):612-619.
[21] 刘鸿文.材料力学[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2016:281-310.
[22] 张世斌.数学建模的思想和方法[M].上海:上海交通大学出版社,2015: 26-73.
[23] 王爽,孙江,于雁云.基于CBCT图像的颌骨及牙列有限元建模方法研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2019,35(1):55-59.
[24] 季梦真,漆美瑶,杜珂芯.开髓洞型对全冠修复后隐裂牙抗力影响的三维有限元研究[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2021,48(1):41-49.
[25] 庞国宝,赵凝,安美文.种植义齿相对位置对食物嵌塞影响的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(10):1521-1527.
[26] 梅秀芹.玻璃纤维桩联合自体断冠再接术治疗儿童恒前牙冠折的临床效果观察[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2019,35(12):745-747.
[27] 孙雅娜,胥阳.恒前牙冠折自体断冠粘接的临床治疗[J].粘接,2021,10(4): 54-57.
[28] 王超,孟戎.年轻恒前牙外伤冠折后断冠再接与复合树脂直接修复的疗效比较[J].中国医疗器械信息,2021,22(6):69-76.
[29] 张国梅,祝军,胡杨.E-Max 瓷嵌体三维有限元模型粘接界面应力分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,25(4):537-541.
[30] 佘雅鹄,张一祎,刘雨萱.牙尖覆盖厚度对全瓷高嵌体修复前磨牙应力分布影响的三维有限元分析[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志,2019,37(6):636-641.
[31] 于敬伟,谢伟丽,施梦汝.不同材料嵌体修复对楔状缺损患牙应力分布影响的三维有限元分析[J].口腔医学,2020,40(1):31-34.
[32] CHAKRABORTY A, DATTA P, MAJUMDER S, etal. Finite element and experimental analysis to select patient’s bone condition specific porous dental implant, fabricated using additive manufacturing. Comput Biol Med. 2020;124:384-392.
[33] 唐忠旺,石伟华,夏斌.儿童乳磨牙非金属冠设计及关键参数的三维有限元分析[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2022,57(3):242-250. |