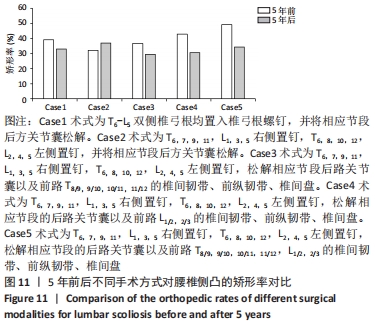
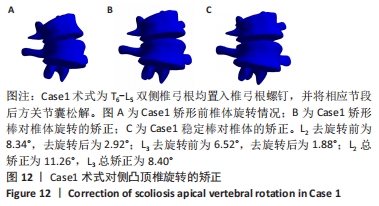
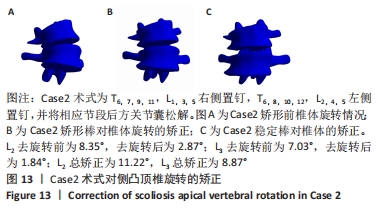
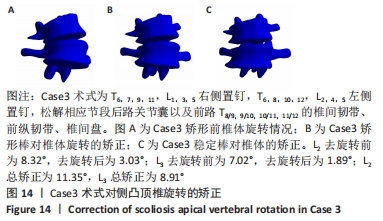
[1] WEI H, XU J, JIANG Z, et al. Effect of a Traditional Chinese Medicine combined therapy on adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a randomized controlled trial. J Tradit Chin Med. 2015;35(5):514-519.
[2] CANALE ST, BEATY JH.坎贝尔骨科手术学[M]. 北京:人民军医出版社,2012:1877.
[3] MONTICONE M, AMBROSINI E, CAZZANIGA D, et al. Adults with idiopathic scoliosis improve disability after motor and cognitive rehabilitation: results of a randomised controlled trial. Eur Spine J. 2016;25(10):3120-3129.
[4] THEIS JC, GRAUERS A, DIARBAKERLI E, et al. An observational study on surgically treated adult idiopathic scoliosis patients’ quality of life outcomes at 1- and 2-year follow-ups and comparison to controls. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2017;12:11.
[5] SÁNCHEZ-MARISCAL F, GOMEZ-RICE A, RODRÍGUEZ-LÓPEZ T, et al. Preoperative and postoperative sagittal plane analysis in adult idiopathic scoliosis in patients older than 40 years of age. Spine J. 2017; 17(1):56-61.
[6] ACAROĞLU RE, DEDE Ö, PELLISÉ F, et al. Adult spinal deformity: a very heterogeneous population of patients with different needs. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2016;50(1):57-62.
[7] NOLTE MT, LOUIE PK, HARADA GK, et al. Sagittal Balance in Adult Idiopathic Scoliosis. Clin Spine Surg. 2020;33(2):53-61.
[8] TAKEDA K, KOU I, HOSOGANE N, et al. Association of Susceptibility Genes for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis and Intervertebral Disc Degeneration With Adult Spinal Deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019; 44(23):1623-1629.
[9] OHASHI M, WATANABE K, HIRANO T, et al. Predicting Factors at Skeletal Maturity for Curve Progression and Low Back Pain in Adult Patients Treated Nonoperatively for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis With Thoracolumbar/Lumbar Curves: A Mean 25-year Follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018;43(23):E1403-E1411.
[10] TOPALIS C, GRAUERS A, DIARBAKERLI E, et al. Neck and back problems in adults with idiopathic scoliosis diagnosed in youth: an observational study of prevalence, change over a mean four year time period and comparison with a control group. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2017;12:20.
[11] ERWIN J, CARLSON BB, BUNCH J, et al. Impact of unoperated adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in adulthood: a 10-year analysis. Spine Deform. 2020;8(5):1009-1016.
[12] PIALASSE JP, MERCIER P, DESCARREAUX M, et al. Assessment of sensorimotor control in adults with surgical correction for idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2016;25(10):3347-3352.
[13] VERLA T, ADOGWA O, TOCHE U, et al. Impact of Increasing Age on Outcomes of Spinal Fusion in Adult Idiopathic Scoliosis. World Neurosurg. 2016;87:591-597.
[14] VIGNESWARAN HT, GRABEL ZJ, EBERSON CP, et al. Surgical treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in the United States from 1997 to 2012: an analysis of 20,346 patients. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2015;16(3):322-328.
[15] 方秀统,李明,赵颖川,等.成人特发性脊柱侧凸手术疗效的分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010, 18(3): 208-211.
[16] HA KY, JANG WH, KIM YH, et al. Clinical Relevance of the SRS-Schwab Classification for Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41(5):E282-288.
[17] KIM YJ, LENKE LG, KIM J, et al. Comparative analysis of pedicle screw versus hybrid instrumentation in posterior spinal fusion of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(3):291-298.
[18] LAVELLE W, KURRA S, HU X, et al. Clinical Outcomes of Idiopathic Scoliosis Surgery: Is There a Difference Between Young Adult Patients and Adolescent Patients? Cureus. 2020;12(5):e8118.
[19] ZHU F, BAO H, YAN P, et al. Comparison of Surgical Outcome of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis and Young Adult Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Match-Pair Analysis of 160 Patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017; 42(19):E1133-E1139.
[20] KIM W, PORRINO JA, HOOD KA, et al. Clinical Evaluation, Imaging, and Management of Adolescent Idiopathic and Adult Degenerative Scoliosis. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2019;48(4):402-414.
[21] CARR AJ. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in identical twins. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990;72(6):1077.
[22] GADEPALLI SK, HIRSCHL RB, TSAI WC, et al. Vertical expandable prosthetic titanium rib device insertion: does it improve pulmonary function? J Pediatr Surg. 2011;46(1):77-80.
[23] QIU XS, TANG NL, YEUNG HY, et al. Genetic association study of growth hormone receptor and idiopathic scoliosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;462:53-58.
[24] OGILVIE JW, CHETTEIR R. A replication study for association of 53 single nucleotide polymorphisms in ScoliScore test with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in French-Canadian population by Tang et al. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(17):E1002.
[25] STOKES IA, LAIBLE JP. Three-dimensional osseo-ligamentous model of the thorax representing initiation of scoliosis by asymmetric growth. J Biomech. 1990;23(6):589-595.
[26] AZEGAMI H, MURACHI S, KITOH J, et al. Etiology of idiopathic scoliosis. Computational study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;(357):229-236.
[27] HUYNH AM, AUBIN CE, RAJWANI T, et al. Pedicle growth asymmetry as a cause of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a biomechanical study. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(4):523-529.
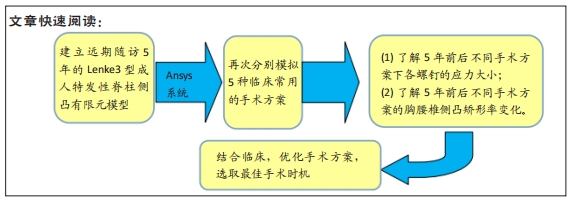
[28] 辛大奇,胡侦明,霍洪军,等. Lenke3型成人特发性脊柱侧凸有限元模型及胸椎钉道导靶3D模型的建立[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(53):8597-8602.
[29] 辛大奇,胡侦明,汉迪,等. Lenke3型成人特发性脊柱侧凸有限元模型的参数修正及有效性验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2017, 21(31):4975-4982.
[30] 辛大奇,胡侦明,霍洪军,等. Lenke3型成人特发性脊柱侧凸三维矫形手术模拟[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(16):2529-2537.
[31] LEE YH, CHUNG CJ, WANG CW, et al. Computational comparison of three posterior lumbar interbody fusion techniques by using porous titanium interbody cages with 50% porosity. Comput Biol Med. 2016; 71:35-45.
[32] 朱立新,王健,曹延林,等.基于 CT数据构建人体腰骶椎的有限元模型[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(30):5511-5515.
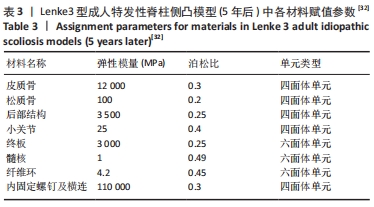
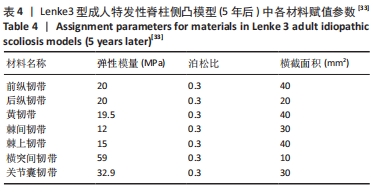
[33] 黄平.退变性腰椎侧凸演变过程及相关生物力学机制的有限元分析[D].上海:第二军医大学,2013.
[34] LENKE LG, BETZ RR, HARMS J, et al. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a new classification to determine extent of spinal arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83(8):1169-1181.
[35] QIU G, ZHANG J, WANG Y, et al. A new operative classification of idiopathic scoliosis: a peking union medical college method. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(12):1419-1426.
[36] 中国医师协会骨科医师分会, 中国医师协会骨科医师分会《早发性脊柱侧凸循证临床诊疗指南》编辑委员会. 中国医师协会骨科医师分会骨科循证临床诊疗指南:早发性脊柱侧凸循证临床诊疗指南[J].中华外科杂志,2019,57(3):166-169.
[37] 海涌,潘爱星.脊柱侧凸诊断与治疗的焦点问题[J].骨科临床与研究杂志,2021,6(4):193-196.
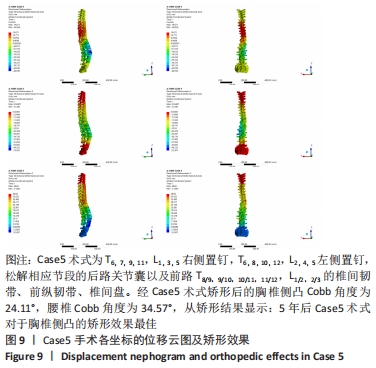
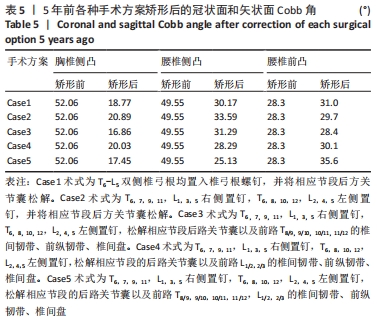
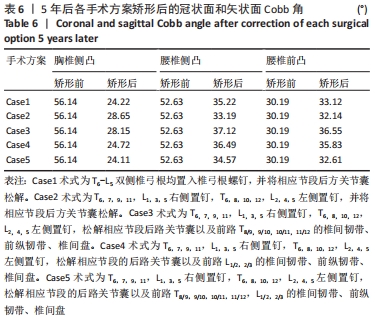
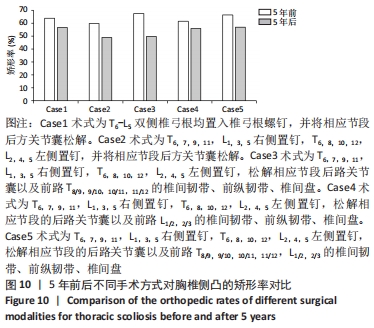
|