中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (17): 2625-2630.doi: 10.12307/2022.525
• 口腔组织构建 oral tissue construction • 下一篇
三维成像技术评估骨性Ⅱ类错颌不同垂直骨面型的牙轴倾斜特征
周星宇,贾 莹,李仲伟,丁 琪
- 贵州医科大学,贵州省贵阳市 550004
Characteristics of dental inclination in different vertical skeletal types of skeletal class II malocclusion: a three-dimensional imaging evaluation
Zhou Xingyu, Jia Ying, Li Zhongwei, Ding Qi
- Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
骨性Ⅱ类:通过头影测量得出的上下颌骨在矢状方向相对位置的关系,可分为3种类型:Ⅰ类、Ⅱ类及Ⅲ类,其中骨性Ⅱ类代表下颌相对上颌位置靠后。
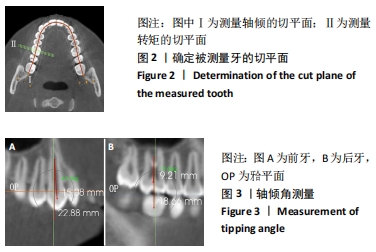
转矩角、轴倾角:通常指牙齿长轴与牙合平面垂线的夹角,唇舌方向的倾斜角度即为转矩角,近远中方向的倾斜角度即为轴倾角。
背景:课题组前期通过锥形束CT测量研究发现,Ⅲ类错颌的牙轴倾斜特征受垂直方向不调的影响存在一定的代偿表现。而中国人作为Ⅱ类错颌的高发人群,在不同骨面型的诊治策略上有所不同,推测与各牙位的牙轴倾斜代偿差异有关。
目的:探究骨性Ⅱ类错颌不同垂直骨面型的全牙长轴在矢状向及冠状向的倾斜特征,以期为临床诊治提供指导。
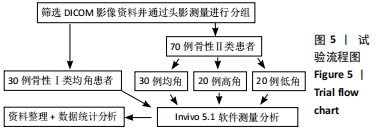
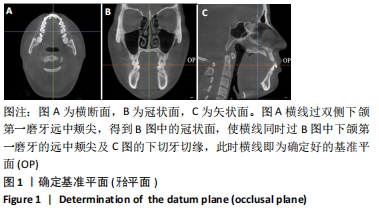
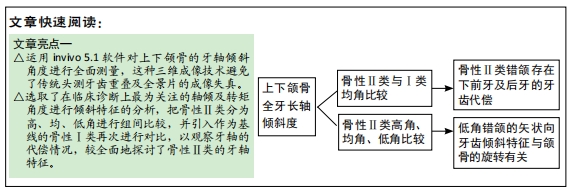
方法:收集不同垂直面型的骨性Ⅱ类错颌70例(均角30例、高角20例、低角20例)、骨性Ⅰ类均角30例患者头颅锥形束CT影像的Dicom数据,应用invivo 5.1软件进行骨性Ⅱ类高、均、低角错颌及骨性Ⅰ类均角错颌全牙轴倾角、转矩角的测量,并进行对比分析。
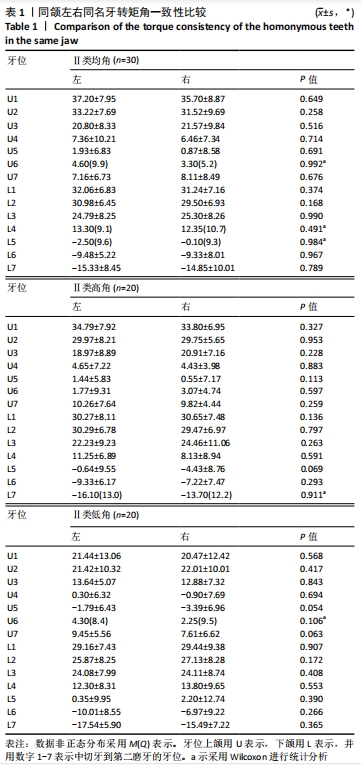
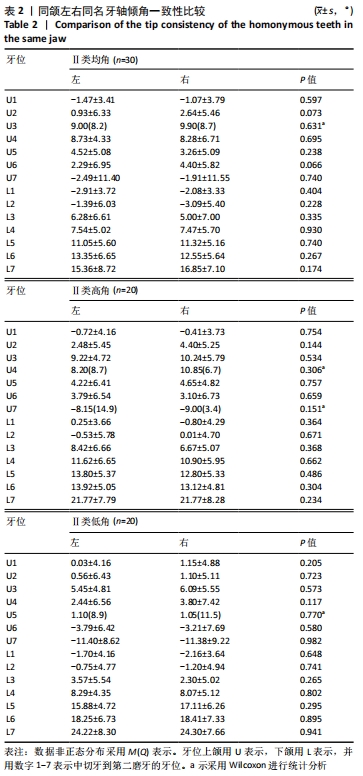
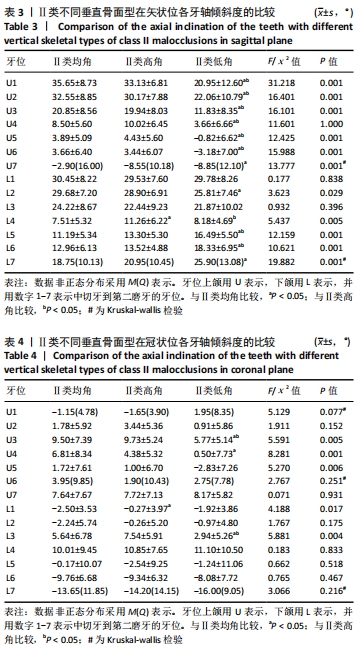
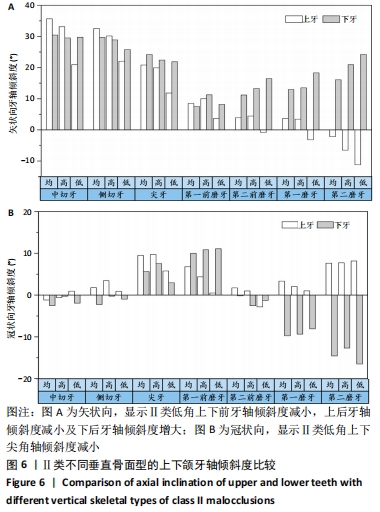
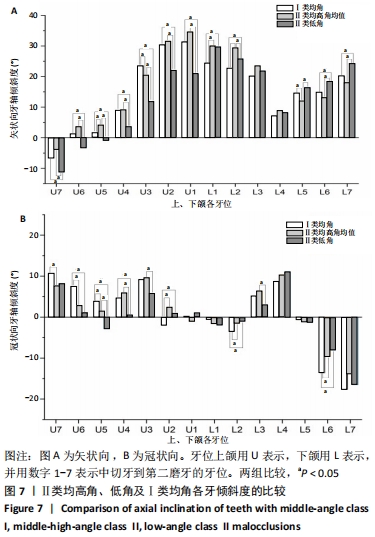
结果与结论:①骨性Ⅱ类错颌中,低角骨面型的牙轴倾角与高角、均角骨面型相比,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);高角和均角骨面型的牙轴倾斜特征基本相似;②骨性Ⅱ类低角与Ⅱ类均、高角比较:矢状向,上前牙正转矩角减小及下前牙相对倾斜直立,上后牙冠近中轴倾角减小及下后牙近中轴倾角增大;冠状向上,Ⅱ类低角上下尖牙的近中轴倾度减小,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);③骨性Ⅱ类与Ⅰ类均角比较:矢状向,除下前牙外,Ⅱ类高、均角与Ⅰ类均角的牙轴特征基本相似,但两组与Ⅱ类低角相比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);下前牙中,Ⅱ类错颌组间差异较小但与Ⅰ类均角相比下前牙表现为牙轴唇倾增加;冠状向,后牙中,Ⅱ类各组间牙轴倾斜特征相似,但与Ⅰ类相比上后牙有舌向倾斜趋势,下后牙有颊向倾斜趋势,且在上颌第二前磨牙、第一磨牙、第二磨牙及下颌第一磨牙中差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);前牙中,Ⅱ类错颌与Ⅰ类错颌牙轴倾斜特无明显差异;④提示骨性Ⅱ类错颌整体存在下前牙及后牙的牙齿代偿,其中低角较高角、均角的牙齿代偿明显;骨性Ⅱ类低角错颌的矢状向牙齿倾斜特征与颌骨的旋转有关。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3283-1290 (周星宇)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: