中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (12): 1963-1968.doi: 10.12307/2022.524
• 骨与关节循证医学 evidence-based medicine of the bone and joint • 上一篇
儿童足型分类方法的系统综述
汤运启1,邹灵秋1,李 毅2,王志康1,惠 雪1,李灵君1,郭新宇1
- 1陕西科技大学设计与艺术学院,陕西省西安市 710021;2西安交通大学附属红会医院足踝外科诊疗中心,陕西省西安市 710054
A systematic review of children’s foot type classification methods
Tang Yunqi1, Zou Lingqiu1, Li Yi2, Wang Zhikang1, Hui Xue1, Li Lingjun1, Guo Xinyu1
- 1College of Art and Design, Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, Xi’an 710021, Shaanxi Province, China; 2Department of Foot and Ankle Surgery, Honghui Hospital Affiliated to Medical College of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710054, Shaanxi Province, China
摘要:
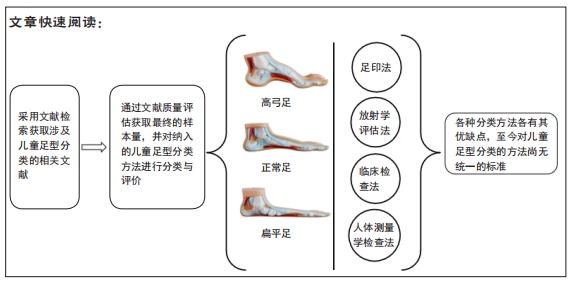
文题释义:
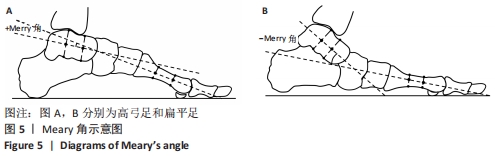
扁平足:是足部畸形的一种,在解剖学层面上是足内侧纵弓的塌陷或消失,且伴随着跟骨外翻和距骨下沉,是3种主要的足型之一。扁平足通常分为柔性和僵硬性扁平足,柔性扁平足在负重状态下足内侧纵弓塌陷或消失,在非负重状态下恢复为正常足弓;僵硬性扁平足在负重和非负重状态下足内侧纵弓都处于塌陷或消失状态。
高弓足:是3种主要足型之一,指足内侧纵弓异常增高为主要改变的足部畸形。高弓足通常分为先天性和后天性高弓足,先天性高弓足指受到遗传因素所造成的高足弓症状;后天性高弓足是由于一些病理原因或意外损伤等因素所造成的高足弓症状。
目的:非正常足型的发展会对儿童的生长和生活带来不利的影响,儿童非正常足型的早期诊断有利于对儿童足型的及时矫正。文章对文献中儿童足型分类的方法进行总结与回顾,以期为临床医生在儿童非正常足型的预防与矫正策略的研究上提供有价值的参考信息。
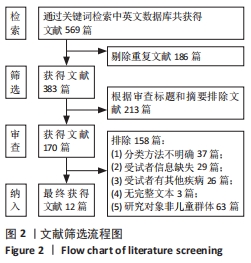
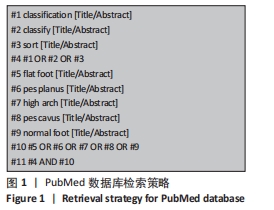
方法:在万方、维普、中国知网、Web of Science和PubMed数据库中对儿童足型分类的相关文献进行检索,并对儿童足型分类的方法进行分类、归纳与系统评价。
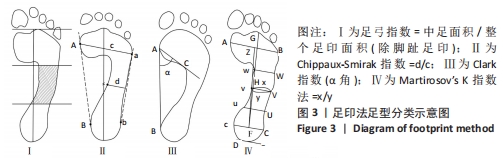
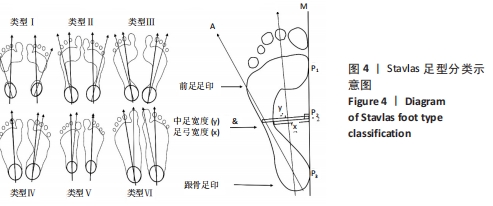
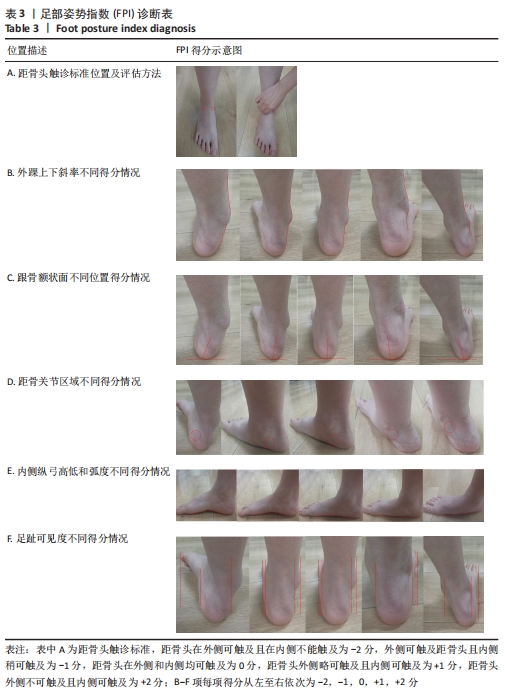
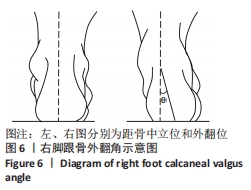
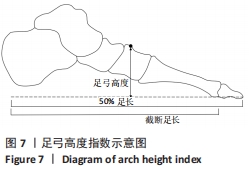
结果:①最终纳入12篇文献,其中儿童足型分类方法主要包括足印指数法、放射学评估法、临床检查法和人体测量学检查法共4种;②各种分类方法的优缺点:足印法简单快捷,但测量结果具有片面性;放射学评估法具有潜在的辐射风险,且成本高、流程复杂;临床检查法虽快捷、成本低,但具有较强的主观性;人体测量学检查法虽然较为准确,但耗时较长;③在以往研究中,研究人员大多数选择经济快捷的足印法作为儿童足型的分类方法,且部分研究采用多种指标相结合的方式以提高儿童足型分类的准确性;④目前较为准确的儿童足型的分类方法就是采用多种指标相结合的方式。
结论:目前儿童足型的分类缺乏金标准,多数足型分类方法仅显示足部静态的结构特征,未来的研究需建立静态足部结构和动态足部功能之间的关系,以增加儿童足型分类结果的准确性和科学性,从而在儿童骨骺闭合年龄结束前对儿童足部的健康成长和发育提供良好的策略。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6696-0934 (汤运启);https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2839-4078 (李毅)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: